15 releases (3 stable)
| 1.1.0 | May 1, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.9.0 | Jan 18, 2024 |
| 0.8.0 | Oct 26, 2023 |
| 0.5.0 | Jul 3, 2023 |
| 0.1.0 | Oct 23, 2021 |
#149 in Math
Used in pmsim
2MB
33K
SLoC
Geometry, meshes, and numerical integration for finite element analyses
Contents
- Introduction
- Installation
- Examples
- Roadmap
- Appendix A - Shapes and local numbering of nodes
- Appendix B - Geometry versus space dimensions
Introduction
This crate contains structures and functions for geometry computations, generate meshes, and perform numerical integration for finite element analyses (FEM/FEA).
Documentation
Installation
At this moment, Gemlab works on Linux (Debian/Ubuntu; and maybe Arch).
TL;DR (Debian/Ubuntu/Linux)
First:
sudo apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
g++ \
gdb \
gfortran \
liblapacke-dev \
libmumps-seq-dev \
libopenblas-dev \
libsuitesparse-dev
Then:
cargo add gemlab
Details
This crates depends on russell_lab and, hence, needs some external libraries. See the installation of required dependencies on russell_lab.
Setting Cargo.toml
👆 Check the crate version and update your Cargo.toml accordingly:
[dependencies]
gemlab = "*"
Examples
use gemlab::integ;
use gemlab::mesh::{At, Features, Mesh};
use gemlab::shapes::Scratchpad;
use gemlab::StrError;
use std::collections::HashSet;
fn main() -> Result<(), StrError> {
// Input the raw mesh data using a text file
//
// 1.0 5------,6.------7
// | [3],' `.[4] |
// | ,' `. |
// |,' `.|
// 0.5 3 [2] 4
// |`. .'|
// | `. .' |
// | [0]`. .'[1] |
// 0.0 0------`1'------2
// 0.0 0.5 1.0
let path = "./data/meshes/four_tri3_one_qua4.msh";
let mesh = Mesh::from_text_file(path)?;
// Extract features such boundary edges and faces.
// Search entities along the boundary of the mesh given coordinates.
// The `At` enum provides an easy way to define the type of the
// constraint such as line, plane, circle, etc.
let feat = Features::new(&mesh, false);
assert_eq!(feat.search_point_ids(At::Y(0.5), |_| true)?, &[3, 4]);
assert_eq!(feat.search_edge_keys(At::X(1.0), |_| true)?, &[(2, 4), (4, 7)]);
// Perform numerical integration to compute
// the area of cell # 2
let ndim = 2;
let cell_2 = &mesh.cells[2];
let mut pad = Scratchpad::new(ndim, cell_2.kind)?;
mesh.set_pad(&mut pad, &cell_2.points);
let ips = integ::default_points(cell_2.kind);
let mut area = 0.0;
for p in 0..ips.len() {
let iota = &ips[p];
let weight = ips[p][3];
let det_jac = pad.calc_jacobian(iota)?;
area += weight * det_jac;
}
assert_eq!(area, 0.5);
Ok(())
}
Roadmap
- Implement read/write mesh functions
- Add tests for the numerical integrations
- Implement triangle and tetrahedron generators
- Implement drawing functions
Appendix A - Shapes and local numbering of nodes
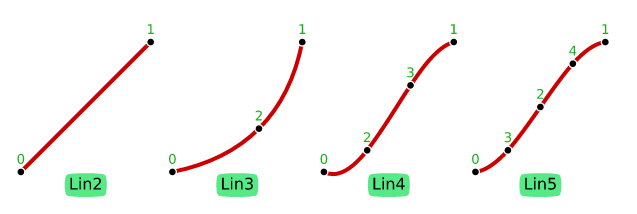
Lines (Lin)
Triangles (Tri)
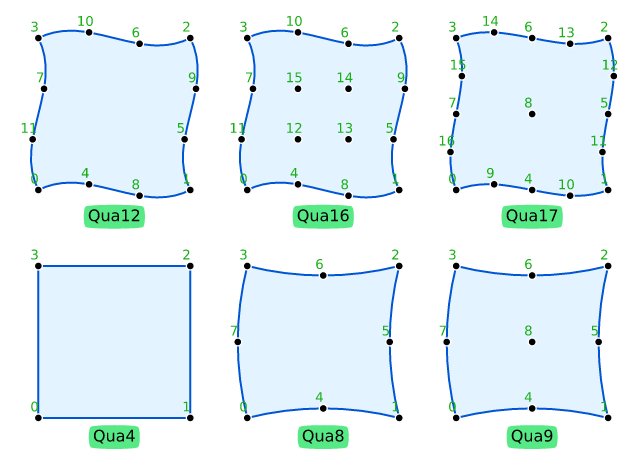
Quadrilaterals (Qua)
Tetrahedra (Tet)
Hexahedra (Hex)
Appendix B - Geometry versus space dimensions
The following table shows what combinations of geometry-number-of-dimensions (geo_ndim) and
space-number-of-dimensions (space_ndim) are possible. There are three cases:
- Case
CABLE--geo_ndim = 1andspace_ndim = 2 or 3; e.g., line in 2D or 3D (cables and rods) - Case
SHELL--geo_ndim = 2andspace_ndim = 3; e.g. Tri or Qua in 3D (shells and surfaces) - Case
SOLID--geo_ndim = space_ndim; e.g., Tri and Qua in 2D or Tet and Hex in 3D
geo_ndim |
space_ndim = 2 |
space_ndim = 3 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CABLE |
CABLE |
| 2 | SOLID |
SHELL |
| 3 | impossible | SOLID |
Dependencies
~11MB
~191K SLoC