3 releases (breaking)
| 0.3.0 | Oct 15, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.1 | Jul 30, 2023 |
| 0.1.0 | Feb 1, 2022 |
#356 in Simulation
1.5MB
7.5K
SLoC
Porous Media Simulator using the Finite Element Method
🚧 Work in progress...
Contents
Introduction
This code implements simulator using the finite element method for the behavior of solids, structures, and porous media.
See the documentation for further information:
- pmsim documentation - Contains the API reference and examples
Installation
This crates depends on russell_lab and, hence, needs some external libraries. See the installation of required dependencies on russell_lab.
Setting Cargo.toml
👆 Check the crate version and update your Cargo.toml accordingly:
[dependencies]
gemlab = "*"
Examples
For all simulations:
Legend:
✅ : converged
👍 : converging
🥵 : diverging
😱 : found NaN or Inf
❋ : non-scaled max(R)
? : no info abut convergence
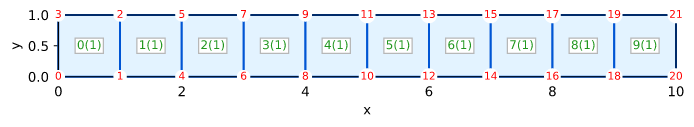
Heat: Arpaci Nonlinear 1d
Arpaci's Example 3-8 on page 130 (variable conductivity)
- Arpaci V. S. (1966) Conduction Heat Transfer, Addison-Wesley, 551p
Test goal
This tests verifies the nonlinear solver for the diffusion equation with a variable conductivity coefficient.
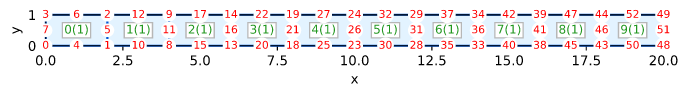
Mesh
Initial conditions
Temperature T = 0 at all points
Boundary conditions
Temperature T = 0 on right side @ x = L
Configuration and parameters
- Steady simulation
- Source = 5
- Variable conductivity (k = (1 + β T) kᵣ I) with kᵣ = 2
Note
The temperature at the right T = 0 (T_inf) must be zero in order to result in k(T_inf) = kᵣ as required by the analytical solution.
Simulation and results
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 2.50e0❋
. . . 2 1.28e0?
. . . 3 9.36e-2👍
. . . 4 1.25e-3👍
. . . 5 1.42e-7👍
. . . 6 1.35e-14✅
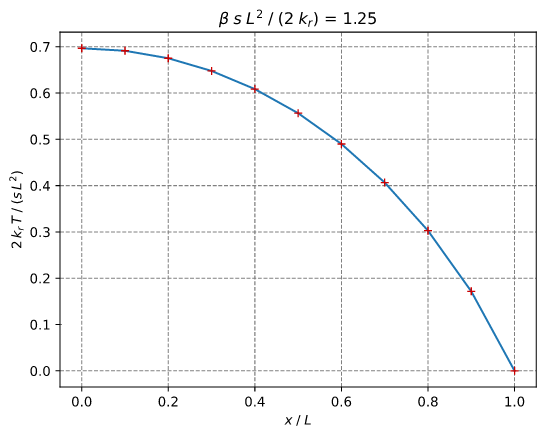
T(0) = 87.08286933869708 (87.08286933869707)
The figure below compares the numerical with the analytical results.
Heat: Bhatti Example 1.5 Convection
Bhatti's Example 1.5 on page 28
- Bhatti, M.A. (2005) Fundamental Finite Element Analysis and Applications, Wiley, 700p.
Test goal
This test verifies the steady heat equation with prescribed temperature and convection
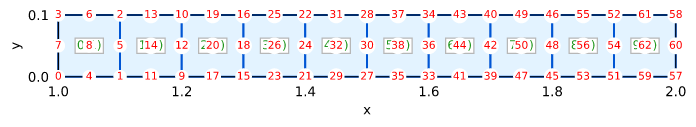
Mesh
Boundary conditions
- Convection Cc = (27, 20) on the right edge
- Prescribed temperature T = 300 on the left edge
Configuration and parameters
- Steady simulation
- No source
- Constant conductivity kx = ky = 1.4
Simulation and results
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 1.05e3❋
. . . 2 1.71e-15✅
Heat: Bhatti Example 6.22 Convection
Bhatti's Example 6.22 on page 449
- Bhatti, M.A. (2005) Fundamental Finite Element Analysis and Applications, Wiley, 700p.
Test goal
This test verifies the steady heat equation with prescribed temperature, convection, flux, and a volumetric source term. Also, it checks the use of Qua8 elements.
Mesh
Boundary conditions (see page 445)
- Flux Qt = 8,000 on left side, edge (0,10,11)
- Convection Cc = (55, 20) on top edges (0,2,1), (2,4,3), and (4,6,5)
- Prescribed temperature T = 110 on the bottom edge (8,10,9)
Configuration and parameters
- Steady simulation
- Source = 5e6 over the region
- Constant conductivity kx = ky = 45
Simulation and results
heat_bhatti_6d22_convection.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 3.09e4❋
. . . 2 6.09e-16✅
Heat: Lewis Example 6.4.2 Transient 1d
Lewis' Example 6.4.2 on page 159
- Lewis R, Nithiarasu P, and Seetharamu KN (2004) Fundamentals of the Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow, Wiley, 341p
Test goal
This test verifies the transient diffusion in 1D
Mesh
o-----------------------------------------------------------o
| | | | | | | | | | ..... | h = 1
o-----------------------------------------------------------o
<- L = 20 ->
Initial conditions
Temperature T = 0 at all points
Boundary conditions
Flux Qt = 1 on left side @ x = 0
Configuration and parameters
- Transient simulation
- No source
- Constant conductivity kx = ky = 1
- Coefficient ρ = 1
Simulation and results
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 6.67e-1❋
. . . 2 2.36e-16✅
2 2.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 1.24e0❋
. . . 2 6.07e-16✅
3 3.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 1.08e0❋
. . . 2 2.55e-16✅
4 4.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 9.73e-1❋
. . . 2 3.38e-16✅
5 5.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 8.94e-1❋
. . . 2 3.25e-16✅
6 6.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 8.33e-1❋
. . . 2 4.24e-16✅
7 7.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 7.84e-1❋
. . . 2 6.89e-16✅
8 8.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 7.44e-1❋
. . . 2 4.46e-16✅
9 9.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 7.09e-1❋
. . . 2 5.85e-16✅
10 1.000000e0 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 6.79e-1❋
. . . 2 1.03e-15✅
point = 0, x = 0.00, T = 1.105099, diff = 2.3280e-2
point = 3, x = 0.00, T = 1.105099, diff = 2.3280e-2
point = 7, x = 0.00, T = 1.105099, diff = 2.3280e-2
point = 4, x = 1.00, T = 0.376835, diff = 2.2447e-2
point = 6, x = 1.00, T = 0.376835, diff = 2.2447e-2
point = 1, x = 2.00, T = 0.085042, diff = 1.5467e-2
point = 2, x = 2.00, T = 0.085042, diff = 1.5467e-2
Heat: Mathematica Axisymmetric Nafems
From Mathematica Heat Transfer Model Verification Tests (HeatTransfer-FEM-Stationary-2DAxisym-Single-HeatTransfer-0002)
NAFEMS benchmark test
Test goal
This test verifies the steady heat equation with a localized flux boundary condition
MESH (not-to-scale, not-equal-axis)
0.14 ||++++++++++++++++++++++++
|| | | | | +
||-----------------------+
|| | | | | +
0.10 →→ |------------------------+ yb
→→ | | | | | +
→→ |------------------------+
→→ | | | | | +
→→ |------------------------+
→→ | | | | | +
0.04 →→ |--------(#)-------------+ ya
|| | | | | +
||-----------------------+
|| | | | | +
0.00 ||++++++++++++++++++++++++
0.02 0.04 0.10
rin rref rout
'+' indicates sides with T = 273.15
|| means insulated
→→ means flux with Qt = 5e5
(#) indicates a reference point to check the results
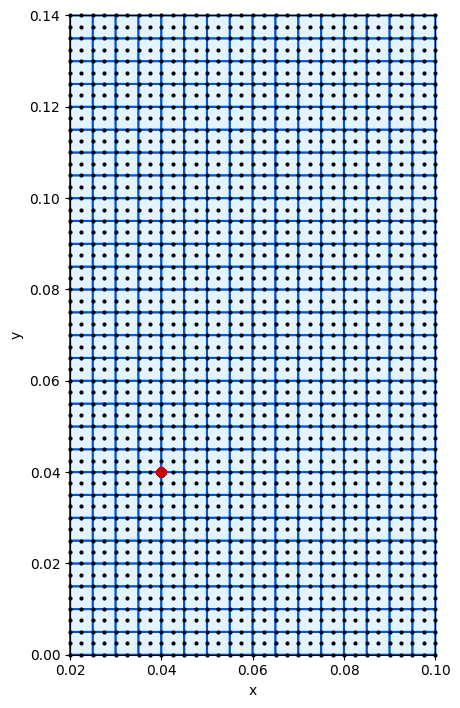
Initial conditions
Temperature T = 0 at all points
Boundary conditions
- Temperature T = 273.15 on the top, bottom, and right edges
- Flux Qt = 5e5 on the middle-left edges from y=0.04 to y=0.10
Configuration and parameters
- Steady simulation
- No source
- Constant conductivity kx = ky = 52
Simulation and results
heat_mathematica_axisym_nafems.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 4.45e3❋
. . . 2 3.23e-12✅
T = 332.9704335048643, reference = 332.97, rel_error = 0.00013019 %
Heat: Mathematica Axisymmetric Simple
From Mathematica Heat Transfer Model Verification Tests (HeatTransfer-FEM-Stationary-2DAxisym-Single-HeatTransfer-0001)
2D Axisymmetric Single Equation
Test goal
This test verifies the steady heat equation in 1D with prescribed flux
Mesh
→→ ---------------------
→→ | | | | | h
→→ ---------------------
1.0 2.0
rin rout
Initial conditions
Temperature T = 0 at all points
Boundary conditions
- Temperature T = 10.0 on the right edge
- Flux Qt = 100.0 on the left edge
Configuration and parameters
- Steady simulation
- No source
- Constant conductivity kx = ky = 10.0
Simulation and results
heat_mathematica_axisym_simple.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 3.51e2❋
. . . 2 3.55e-13✅
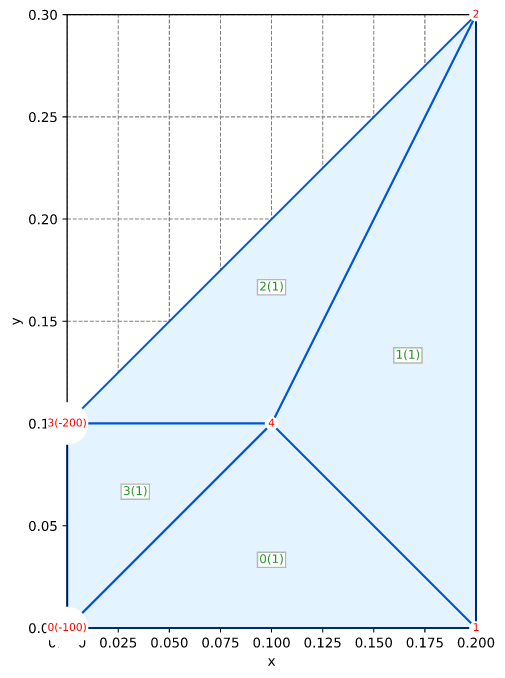
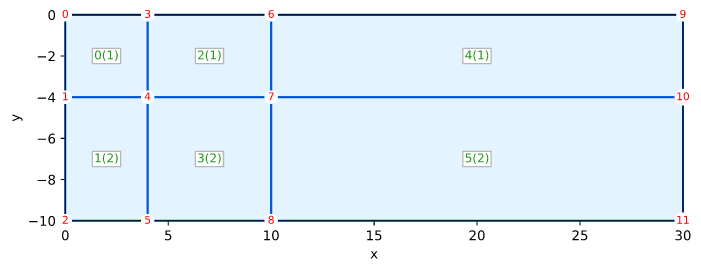
Rod: Bhatti Example 1.4 Truss
Bhatti's Example 1.4 on page 25
- Bhatti, M.A. (2005) Fundamental Finite Element Analysis and Applications, Wiley, 700p.
Test goal
This test verifies a 2D frame with rod elements and concentrated forces
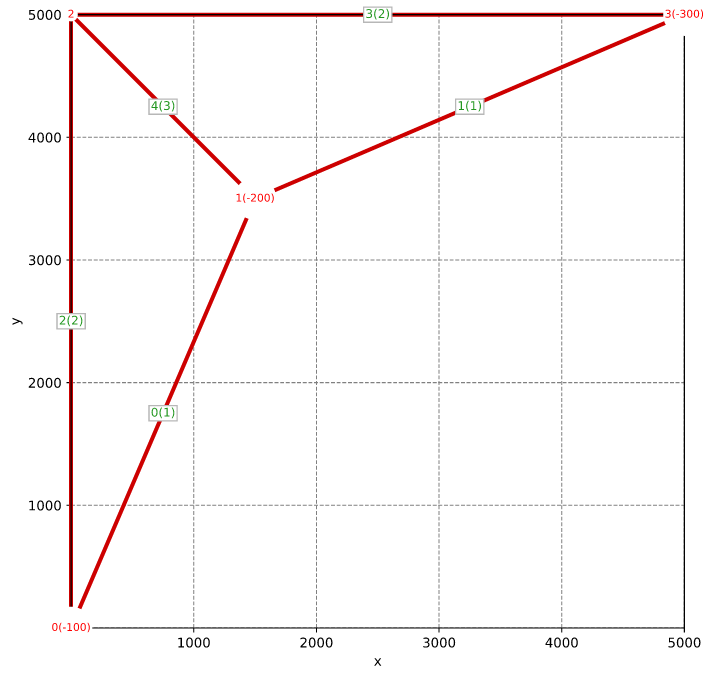
Mesh
Boundary conditions
- Fully fixed @ points 0 and 3
- Concentrated load @ point 1 with Fy = -150,000
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Attribute 1: Area = 4,000; Young = 200,000
- Attribute 2: Area = 3,000; Young = 200,000
- Attribute 3: Area = 2,000; Young = 70,000
Simulation and results
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 1.50e5❋
. . . 2 1.46e-11✅
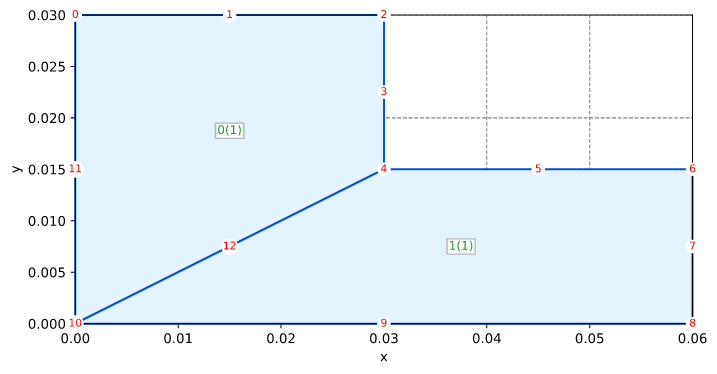
Solid Bhatti Example 1.6 Plane Stress
Bhatti's Example 1.6 on page 32
- Bhatti, M.A. (2005) Fundamental Finite Element Analysis and Applications, Wiley, 700p.
Test goal
This test verifies the equilibrium of a thin bracket modelled by assuming plane-stress
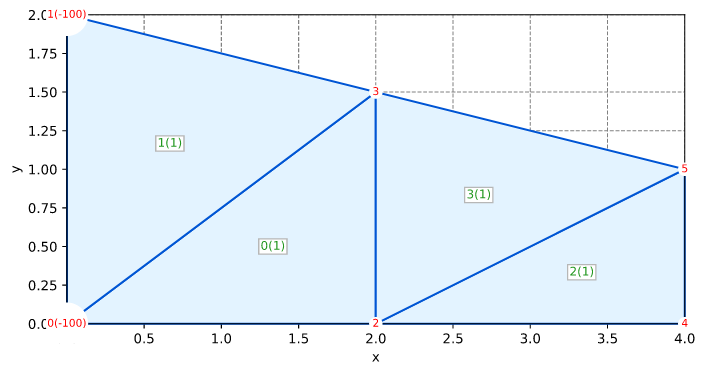
Mesh
Boundary conditions
- Fully fixed @ points 0 and 1
- Distributed load along edges (1,3) and (3,5) with Qn = -20
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Young = 10,000
- Poisson = 0.2
- Plane-stress with thickness = 0.25
Simulation and results
solid_bhatti_1d6_plane_stress.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 1.00e1❋
. . . 2 3.91e-14✅
Solid Felippa Thick Cylinder Axisymmetric
Felippa's Benchmark 14.1 (Figure 14.1) on page 14-3
- Felippa C, Advanced Finite Elements
Test goal
This test verifies the axisymmetric modelling of a chick cylindrical tube under internal pressure. There is an analytical solution, developed for the plane-strain case. However, this tests employs the AXISYMMETRIC representation.
Mesh
Uy FIXED
→o------o------o------o------o
→| | ....... | |
→o------o------o------o------o
Uy FIXED
Boundary conditions
- Fix bottom edge vertically
- Fix top edge vertically
- Distributed load Qn = -PRESSURE on left edge
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Young = 1000, Poisson = 0.0
- Axisymmetric
- NOTE: using 4 integration points because it gives better results with Qua8
Simulation and results
solid_felippa_thick_cylinder_axisym.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 5.33e1❋
. . . 2 3.16e-13✅
point = 0, r = 4.0, Ux = 0.055238095238095454, diff = 2.1510571102112408e-16
point = 1, r = 7.0, Ux = 0.040544217687075015, diff = 1.8735013540549517e-16
point = 4, r = 5.5, Ux = 0.04510822510822529, diff = 1.8041124150158794e-16
point = 8, r = 10.0, Ux = 0.03809523809523828, diff = 1.8041124150158794e-16
point = 10, r = 8.5, Ux = 0.03859943977591054, diff = 1.8041124150158794e-16
Solid Smith Figure 5.2 Tri3 Plane Strain
Smith's Example 5.2 (Figure 5.2) on page 173
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies a plane-strain simulation with Tri3 elements
Mesh
1.0 kN/m²
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
0.0 ▷0---------1---------2
| ,'| ,'| E = 1e6 kN/m²
| 0 ,' | 2 ,' | ν = 0.3
| ,' | ,' |
| ,' 1 | ,' 3 | connectivity:
-0.5 ▷3'--------4'--------5 0 : 1 0 3
| ,'| ,'| 1 : 3 4 1
| 4 ,' | 6 ,' | 2 : 2 1 4
| ,' | ,' | 3 : 4 5 2
| ,' 5 | ,' 7 | 4 : 4 3 6
-1.0 ▷6'--------7'--------8 5 : 6 7 4
△ △ △ 6 : 5 4 7
7 : 7 8 5
0.0 0.5 1.0
Boundary conditions
- Fix left edge horizontally
- Fix bottom edge vertically
- Distributed load Qn = -1.0 on top edge
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Young = 1e6
- Poisson = 0.3
- Plane-strain
Simulation and results
solid_smith_5d2_tri3_plane_strain.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 5.00e-1❋
. . . 2 5.55e-16✅
Solid Smith Figure 5.7 Tri15 Plane Strain
Smith's Example 5.7 (Figure 5.7) on page 178
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies a plane-strain simulation with Tri15 elements
MESH
1.0 kN/m²
↓↓↓↓↓↓
0.0 Ux o----o---------------o Ux
F | /| _.-'| F
I | / | _.-' | I 15-node
X | / | _.-' | X triangles
E |/ |.-' | E
-2.0 D o----o---------------o D
0.0 1.0 6.0
Ux and Uy FIXED
Boundary conditions
- Fix left edge horizontally
- Fix right edge horizontally
- Fix bottom edge horizontally and vertically
- Concentrated load (Fy) on points 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 equal to -0.0778, -0.3556, -0.1333, -0.3556, -0.0778, respectively
NOTE: the distributed load is directly modelled by concentrated forces just so we can compare the numeric results with the book results.
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Young = 1e5
- Poisson = 0.2
- Plane-strain
NOTE: the Poisson coefficient in the book's figure is different than the coefficient in the code. The results given in the book's Fig 5.8 correspond to the code's coefficient (Poisson = 0.2)
Simulation and results
solid_smith_5d7_tri15_plane_strain.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 3.56e-1❋
. . . 2 2.16e-15✅
Solid Smith Figure 5.11 Qua4 Plane Strain Uy
Smith's Example 5.11 (Figure 5.11) on page 180
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies a plane-strain simulation with prescribed displacements
Mesh
Uy DISPLACEMENT
0.0 0----------3----------6----------9
Ux | | | | Ux
F | | | | F
I 1----------4----------7---------10 I
X | | | | X
E | | | | E
-10.0 D 2----------5----------8---------11 D
0.0 10.0 20.0 30.0
Ux and Uy FIXED
Boundary conditions
- Fix left edge horizontally
- Fix right edge horizontally
- Fix bottom edge horizontally and vertically
- Displacement Uy = -1e-5 prescribed on top edge with x ≤ 10
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Young = 1e6
- Poisson = 0.3
- Plane-strain
Simulation and results
solid_smith_5d11_qua4_plane_strain_uy.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 2.21e1❋
. . . 2 4.50e-16✅
Solid Smith Figure 5.15 Qua8 Plane Strain
Smith's Example 5.15 (Figure 5.15) on page 183
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies a plane-strain simulation with Qua8 elements and reduced integration.
Mesh
1.0 kN/m²
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
0.0 0----1----2----3----4
| | |
5 6 7
| | |
-3.0 Ux 8----9---10---11---12 Ux
F | | | F
I 13 14 15 I
X | | | X
-6.0 E 16---17---18---19---20 E
D | | | D
21 22 23
| | |
-9.0 24---25---26---27---28
0.0 3.0 6.0
Ux and Uy FIXED
Boundary conditions
- Fix left edge horizontally
- Fix right edge horizontally
- Fix bottom edge horizontally and vertically
- Distributed load Qn = -1 on top edge with x ≤ 3
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Young = 1e6
- Poisson = 0.3
- Plane-strain
- NOTE: using reduced integration with 4 points
Solid Smith Figure 5.17 Qua4 Axisymmetric
Smith's Example 5.17 (Figure 5.17) on page 187
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies an axisymmetric equilibrium problem.
Mesh
1.0 kN/m²
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
0.0 0------3----------6-------------------9
Ux | (0) | (2) | (4) | Ux
F | [1] | [1] | [1] | F
-4.0 I 1------4----------7------------------10 I
X | (1) | (3) | (5) | X
E | [2] | [2] | [2] | E
-10.0 D 2------5----------8------------------11 D
0.0 4.0 10.0 30.0
Ux and Uy FIXED
Boundary conditions
- Fix left edge horizontally
- Fix right edge horizontally
- Fix bottom edge horizontally and vertically
- Concentrated load (Fy) on points 0, 3, 6, equal to
- -2.6667, -23.3333, -24.0, respectively
- Distributed load Qn = -1 on top edge with x ≤ 4
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Upper layer: Young = 100, Poisson = 0.3
- Lower layer: Young = 1000, Poisson = 0.45
- Plane-strain
- NOTE: using 9 integration points
Simulation and results
solid_smith_5d15_qua8_plane_strain.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 2.00e0❋
. . . 2 7.16e-15✅
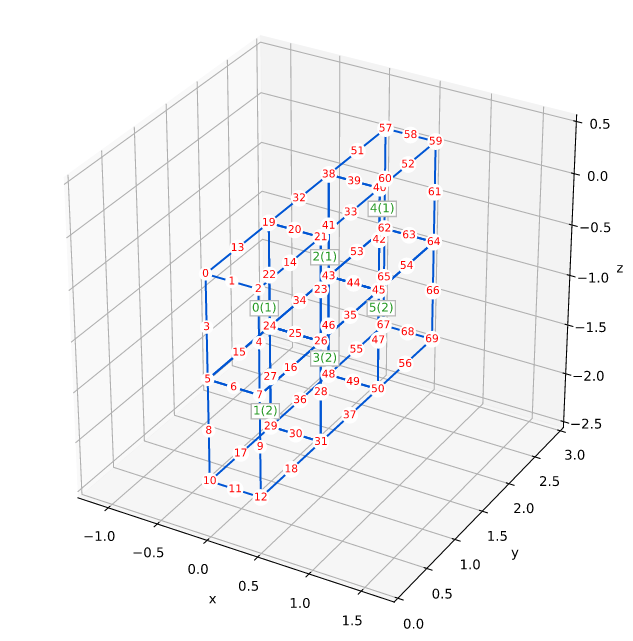
Solid Smith Figure 5.24 Hex20 3D
Smith's Example 5.24 (Figure 5.24) on page 195
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies a 3D simulation with Hex20.
Mesh
Boundary conditions
- Horizontally fix the vertical boundary faces perpendicular to x on the "back side" with x=0
- Horizontally fix the vertical boundary faces perpendicular to y on the "left side" with y=0
- Set all Ux,Uy,Uz to zero for the horizontal boundary faces perpendicular to z on the "bottom" with z=0
- Apply distributed load Qn = -1 on the portion of the top face with y ≤ 1
- NOTE: The "front" and "right" faces with x>0 or y>0 are NOT fixed.
Configuration and parameters
- Upper layer: Young = 100, Poisson = 0.3
- Lower layer: Young = 50, Poisson = 0.3
- Using reduced integration with 8 points
Simulation and results
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 1.67e-1❋
. . . 2 4.73e-16✅
Solid Smith Figure 5.27 Qua9 Plane Strain
Smith's Example 5.27 (Figure 5.27) on page 200
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies a plane-strain simulation with Qua9 elements and full integration. NOTE: This Example is similar to Example 5.15, with the difference being Qua9 elements.
Mesh
1.0 kN/m²
↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
0.0 0----1----2----3----4
| | |
5 6 7 8 9
| | |
-3.0 Ux 10---11---12---13---14 Ux
F | | | F
I 15 16 17 18 19 I
X | | | X
-6.0 E 20---21---22---23---24 E
D | | | D
25 26 27 28 29
| | |
-9.0 30---31---32---33---34
0.0 3.0 6.0
Ux and Uy FIXED
Boundary conditions
- Fix left edge horizontally
- Fix right edge horizontally
- Fix bottom edge horizontally and vertically
- Distributed load Qn = -1 on top edge with x ≤ 3
Configuration and parameters
- Static simulation
- Young = 1e6
- Poisson = 0.3
- Plane-strain
Simulation and results
solid_smith_5d27_qua9_plane_strain.rs
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 2.00e0❋
. . . 2 5.66e-15✅
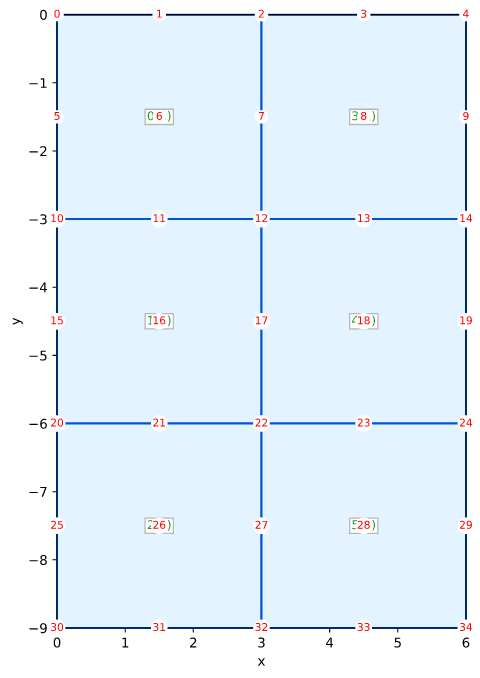
Solid Smith Figure 5.30 Tet4 3D
Smith's Example 5.30 (Figure 5.30) on page 202
- Smith IM, Griffiths DV, and Margetts L (2014) Programming the Finite Element Method, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 664p
Test goal
This test verifies a 3D simulation with Tet4.
Mesh
Boundary conditions
- Horizontally fix the vertical boundary faces perpendicular to x on the "back side" with x=0
- Horizontally fix the vertical boundary faces perpendicular to y on the "left side" with y=0
- Vertically fix the horizontal boundary faces perpendicular to z on the "bottom" with z=0
- Apply vertical (Fz) concentrated loads to the top nodes:
- Fz @ 0 and 5 = -0.1667, Fz @ 1 and 4 = -0.3333
- (Do not USE more digits, as in the code, so we can compare with the Book results)
Configuration and parameters
Young = 100, Poisson = 0.3
Simulation and results
_
timestep t Δt iter max(R)
1 1.000000e-1 1.000000e-1 . .
. . . 1 3.33e-1❋
. . . 2 9.30e-17✅
Dependencies
~18–29MB
~437K SLoC