18 releases
| 0.3.8 | Apr 11, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.3.3 | Jul 7, 2024 |
| 0.2.7 | Feb 25, 2024 |
| 0.1.6 | Jul 18, 2023 |
| 0.1.1 | Mar 12, 2023 |
#14 in Data formats
856 downloads per month
Used in 2 crates
620KB
14K
SLoC
Geometry processing library in pure Rust
Features
- Implicit/voxel/volume modeling
- Voxel remeshing
- Boolean operations
- Offsetting
- Explicit modeling
- Mesh simplification (decimation)
- Isotropic remeshing
IO
Reading/writing mesh from/to STL file
You can read/write STL files using StlReader and StlWriter structs. Ony binary STLs are supported.
Example
use std::path::Path;
use baby_shark::{
io::stl::{StlReader, StlWriter},
mesh::corner_table::prelude::CornerTableF
};
fn main() {
let mut reader = StlReader::new();
let mesh: CornerTableF = reader.read_stl_from_file(Path::new("./read.stl"))
.expect("Read mesh from STL file");
let writer = StlWriter::new();
writer.write_stl_to_file(&mesh, Path::new("./write.stl"))
.expect("Save mesh to STL file");
}
Implicit modeling
Boolean operations
Boolean operations are a set of operations that can be performed on volumes to combine or modify their shapes. The supported boolean operations in this library are:
- Union - combines two volumes into a single volume, resulting in a shape that includes the combined volume of both models.
- Subtract - removes the volume from another, resulting in a shape that is the difference between the two models.
- Intersect - returns the volume that is common to both models, resulting in a shape that includes only the overlapping region.
These boolean operations can be useful in various applications, such as creating complex shapes by combining simpler shapes, removing unwanted parts from a volume, or finding the intersection between two volumes.
Example
| Subtract | Union |
|---|---|
 |
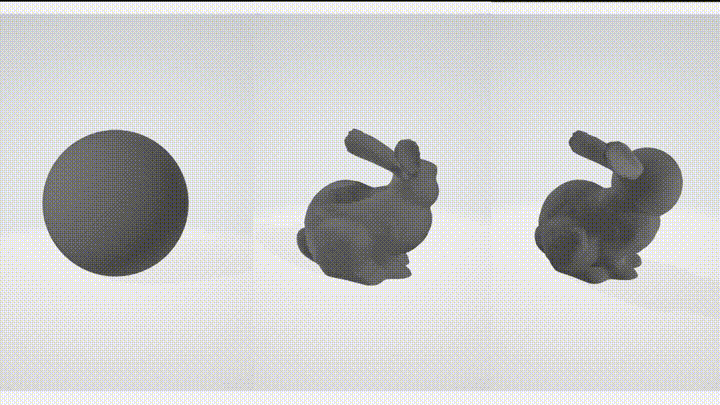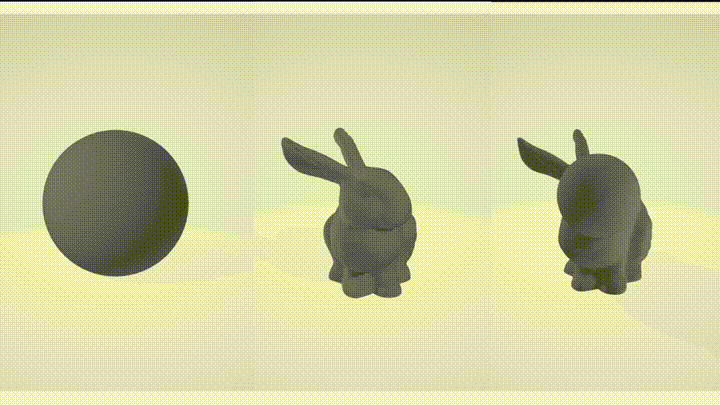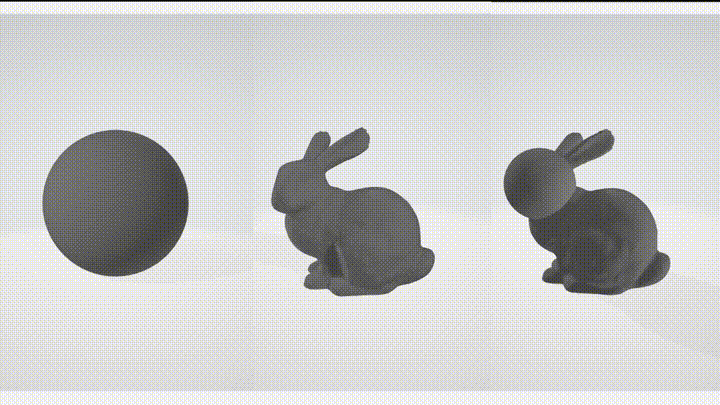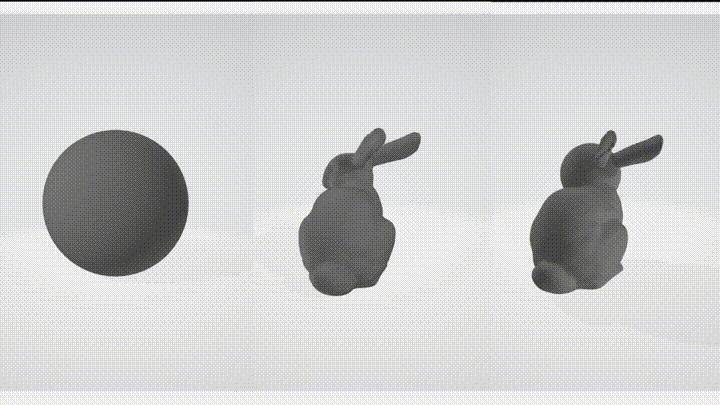 |
Volume offset
The volume offsetting allows for the expansion or contraction of a model shape, serving various applications like CNC machining, collision detection, and rapid prototyping. It's a vital tool in model generation and toolpath creation. Inwards and outwards offsets are supported.
Example

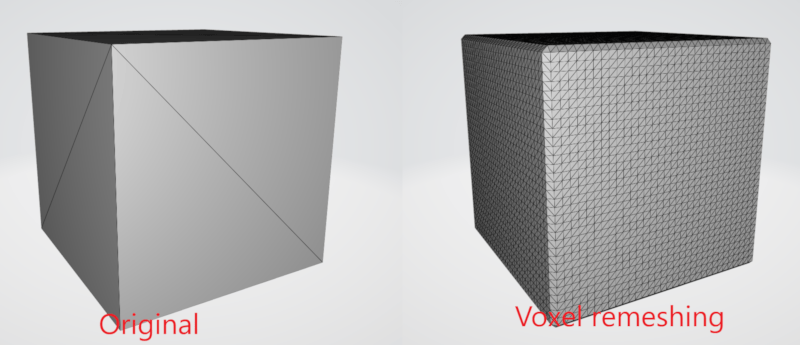
Voxel remeshing
Voxel remeshing is a computational process used in computer graphics to reconstruct or optimize the topology of a three-dimensional (3D) model. Voxels are volumetric pixels that make up the 3D space, and remeshing involves reorganizing these voxels to create a more uniform and well-defined mesh structure. Also, it comes with the benefit of removing overlapping geometry, a valuable asset in sculpting applications.
Example
Explicit modeling
Isotropic remeshing
This algorithm incrementally performs simple operations such as edge splits, edge collapses, edge flips, and Laplacian smoothing.
All the vertices of the remeshed patch are reprojected to
the original surface to keep a good approximation of the input.
Any of those operations can be turned off using appropriate method (with_<operation>(false)).

Example
let remesher = IncrementalRemesher::new()
.with_iterations_count(10)
.with_split_edges(true)
.with_collapse_edges(true)
.with_flip_edges(true)
.with_shift_vertices(true)
.with_project_vertices(true);
remesher.remesh(&mut mesh, 0.002f32);
Mesh simplification (decimation)
This library implements incremental edge decimation algorithm. On each iteration edge with lowest collapse cost is collapsed. Several stop condition are supported:
- Max error - algorithm stops when collapse lowest cost is bigger than given value
- Min faces count - algorithm stops when faces count drops below given value
- Bounding sphere - adaptive error algorithm based upon distance from a point. Useful for LOD mesh decimation.
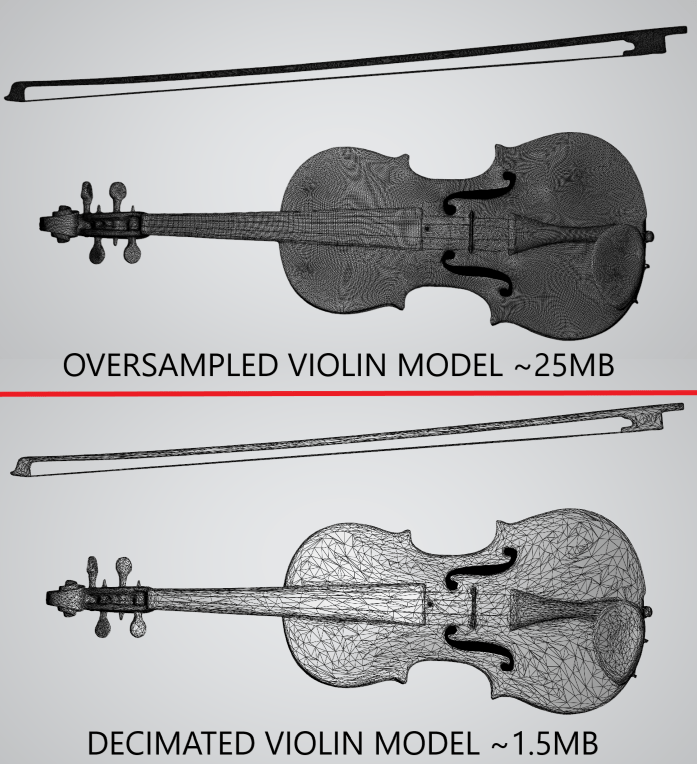
Example
let mut decimator = EdgeDecimator::new()
.decimation_criteria(ConstantErrorDecimationCriteria::new(0.0005))
.min_faces_count(Some(10000));
decimator.decimate(&mut mesh);
Bounded Sphere Example
let origin = Point3::<f32>::origin();
let radii_error_map = vec![
(10.0f32, 0.0001f32),
(15.0f32, 0.05f32),
(40.0f32, 0.8f32),
];
let criteria = BoundingSphereDecimationCriteria::new(origin, radii_error_map);
let mut decimator = EdgeDecimator::new().decimation_criteria(criteria);
decimator.decimate(&mut mesh);
Dependencies
~4.5MB
~94K SLoC