67 releases (breaking)
| new 0.50.0 | Apr 30, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.48.0 | Mar 26, 2025 |
| 0.36.1 | Dec 16, 2024 |
| 0.35.0 | Nov 29, 2024 |
| 0.8.1 | Mar 18, 2024 |
#74 in Text processing
1,535 downloads per month
1MB
32K
SLoC
xan, the CSV magician
xan is a command line tool that can be used to process CSV files directly from the shell.
It has been written in Rust to be as fast as possible, use as little memory as possible, and can easily handle very large CSV files (Gigabytes). It is also able to leverage parallelism (through multithreading) to make some tasks complete as fast as your computer can allow.
It can easily preview, filter, slice, aggregate, sort, join CSV files, and exposes a large collection of composable commands that can be chained together to perform a wide variety of typical tasks.
xan also leverages its own expression language so you can perform complex tasks that cannot be done by relying on the simplest commands. This minimalistic language has been tailored for CSV data and is way faster than evaluating typical dynamically-typed languages such as Python, Lua, JavaScript etc.
Note that this tool is originally a fork of BurntSushi's xsv, but has been nearly entirely rewritten at that point, to fit SciencesPo's médialab use-cases, rooted in web data collection and analysis geared towards social sciences (you might think CSV is outdated by now, but read our love letter to the format before judging too quickly).
xan therefore goes beyond typical data manipulation and expose utilities related to lexicometry, graph theory and even scraping.
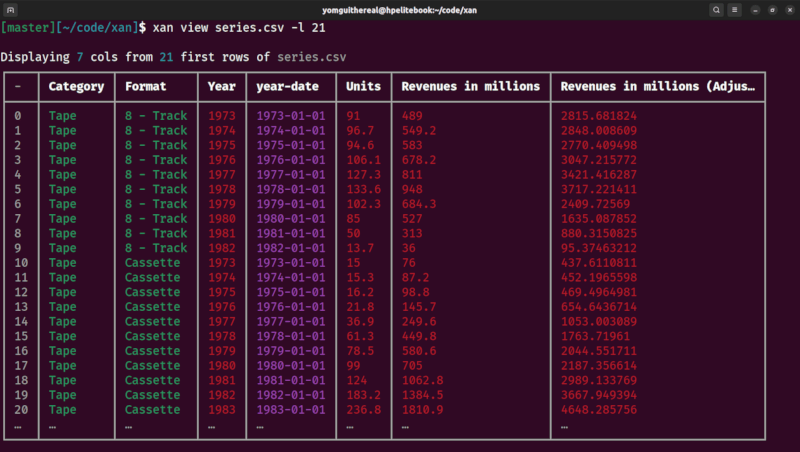
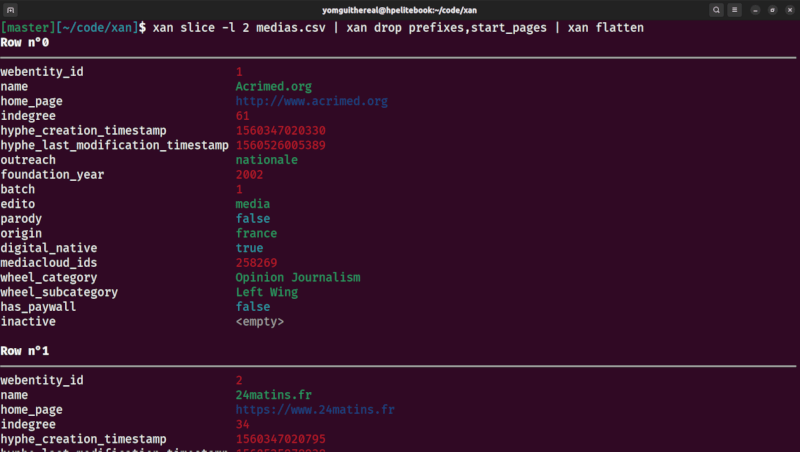
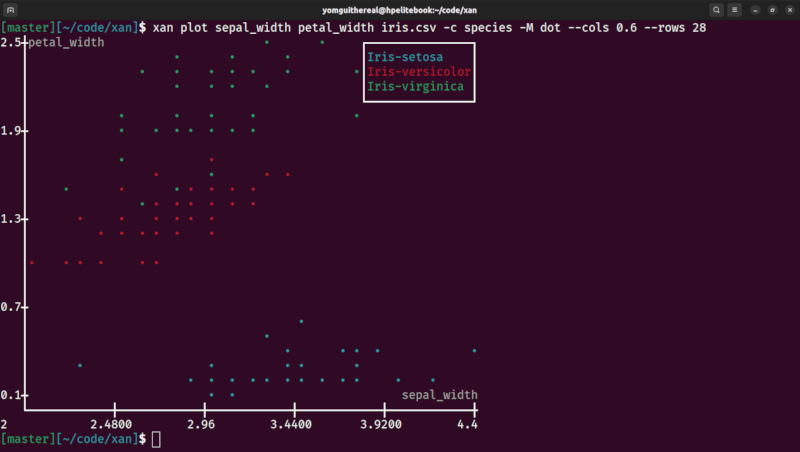
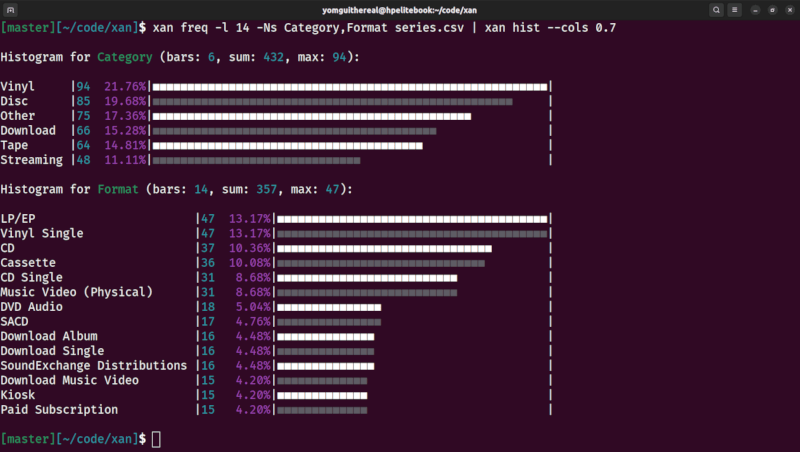
Finally, xan can be used to display CSV files in the terminal, for easy exploration, and can even be used to draw basic data visualisations:
| view command | flatten command |
|---|---|
 |
 |
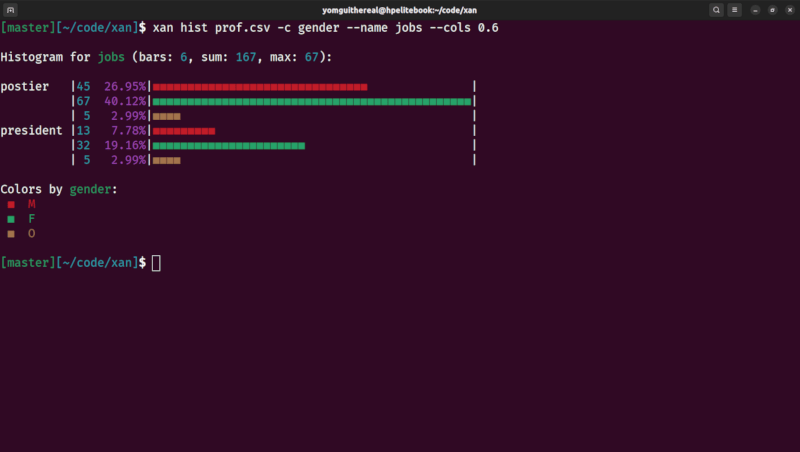
| categorical histogram | scatterplot |
 |
 |
| categorical scatterplot | histograms |
 |
 |
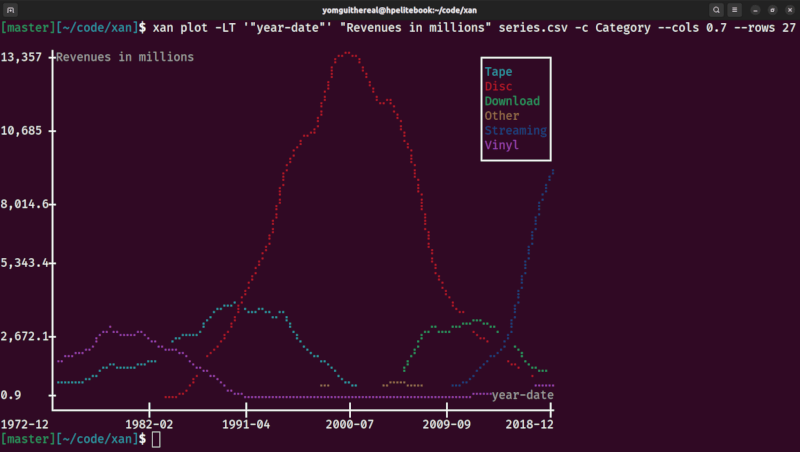
| parallel processing | time series |
 |
 |
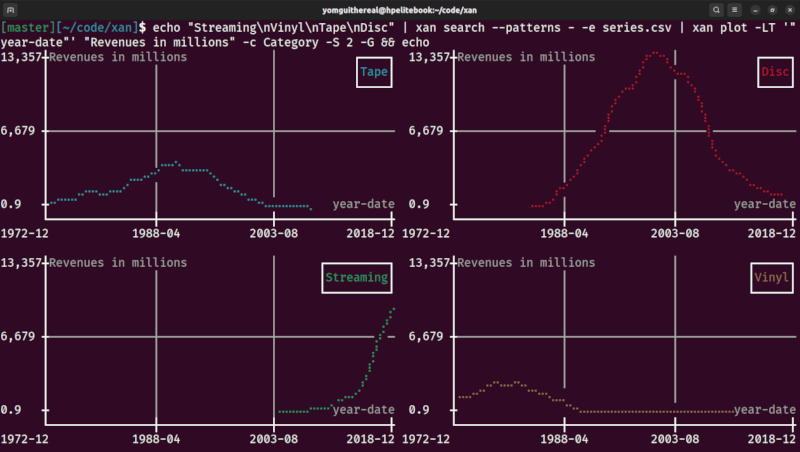
| small multiples (facet grid) | grouped view |
 |
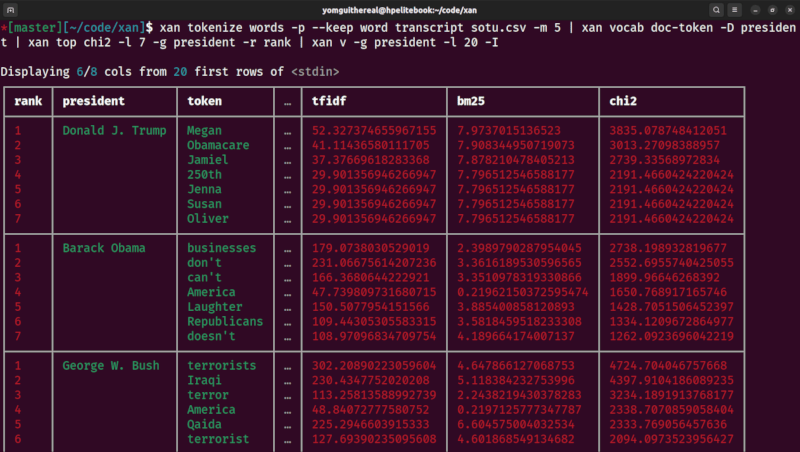 |
| correlation matrix heatmap | heatmap |
 |
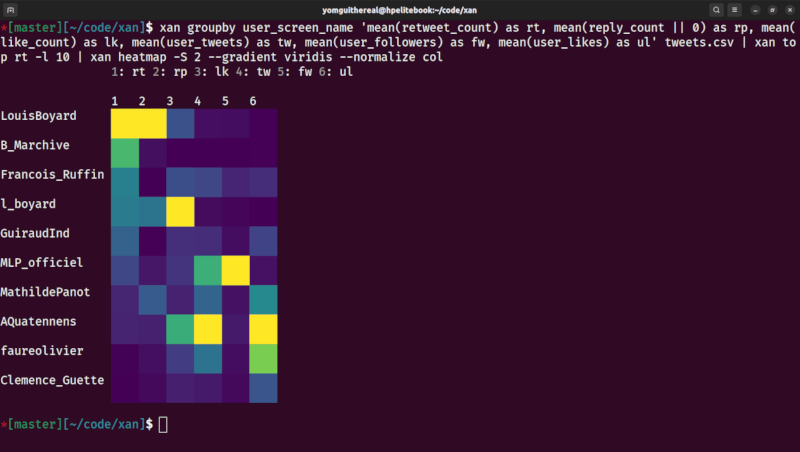 |
Summary
- How to install
- Quick tour
- Available commands
- General flags and IO model
- Expression language reference
- Cookbook
- News
- Frequently Asked Questions
How to install
Cargo
xan can be installed using cargo (it usually comes with Rust):
cargo install xan
You can also tweak the build flags to make sure the Rust compiler is able to leverage all your CPU's features:
CARGO_BUILD_RUSTFLAGS='-C target-cpu=native' cargo install xan
You can also install the latest dev version thusly:
cargo install --git https://github.com/medialab/xan
Scoop (Windows)
xan can be installed using Scoop on Windows:
scoop bucket add extras
scoop install xan
Homebrew (macOS)
xan can be installed with Homebrew on macOS thusly:
brew install xan
Arch Linux
You can install xan from the extra repository using pacman:
sudo pacman -S xan
Nix
xan is packaged for Nix, and is available in Nixpkgs as of 25.05 release. To
install it, you may add it to your environment.systemPackages as pkgs.xan or
use nix-shell to enter an ephemeral shell.
nix-shell -p xan
Pre-built binaries
Pre-built binaries can be found attached to every GitHub releases.
Currently supported targets include:
x86_64-apple-darwinx86_64-unknown-linux-gnux86_64-pc-windows-msvc
Feel free to open a PR to improve the CI by adding relevant targets.
Installing completions
Note that xan also exposes handy automatic completions for command and header/column names that you can install through the xan completions command.
Run the following command to understand how to install those completions:
xan completions -h
Quick tour
Let's learn about the most commonly used xan commands by exploring a corpus of French medias:
Downloading the corpus
curl -LO https://github.com/medialab/corpora/raw/master/polarisation/medias.csv
Displaying the file's headers
xan headers medias.csv
0 webentity_id
1 name
2 prefixes
3 home_page
4 start_pages
5 indegree
6 hyphe_creation_timestamp
7 hyphe_last_modification_timestamp
8 outreach
9 foundation_year
10 batch
11 edito
12 parody
13 origin
14 digital_native
15 mediacloud_ids
16 wheel_category
17 wheel_subcategory
18 has_paywall
19 inactive
Counting the number of rows
xan count medias.csv
478
Previewing the file in the terminal
xan view medias.csv
Displaying 5/20 cols from 10 first rows of medias.csv
┌───┬───────────────┬───────────────┬────────────┬───┬─────────────┬──────────┐
│ - │ name │ prefixes │ home_page │ … │ has_paywall │ inactive │
├───┼───────────────┼───────────────┼────────────┼───┼─────────────┼──────────┤
│ 0 │ Acrimed.org │ http://acrim… │ http://ww… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 1 │ 24matins.fr │ http://24mat… │ https://w… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 2 │ Actumag.info │ http://actum… │ https://a… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 3 │ 2012un-Nouve… │ http://2012u… │ http://ww… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 4 │ 24heuresactu… │ http://24heu… │ http://24… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 5 │ AgoraVox │ http://agora… │ http://ww… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 6 │ Al-Kanz.org │ http://al-ka… │ https://w… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 7 │ Alalumieredu… │ http://alalu… │ http://al… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 8 │ Allodocteurs… │ http://allod… │ https://w… │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 9 │ Alterinfo.net │ http://alter… │ http://ww… │ … │ <empty> │ true │
│ … │ … │ … │ … │ … │ … │ … │
└───┴───────────────┴───────────────┴────────────┴───┴─────────────┴──────────┘
On unix, don't hesitate to use the -p flag to automagically forward the full output to an appropriate pager and skim through all the columns.
Reading a flattened representation of the first row
# NOTE: drop -c to avoid truncating the values
xan flatten -c medias.csv
Row n°0
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
webentity_id 1
name Acrimed.org
prefixes http://acrimed.org|http://acrimed69.blogspot…
home_page http://www.acrimed.org
start_pages http://acrimed.org|http://acrimed69.blogspot…
indegree 61
hyphe_creation_timestamp 1560347020330
hyphe_last_modification_timestamp 1560526005389
outreach nationale
foundation_year 2002
batch 1
edito media
parody false
origin france
digital_native true
mediacloud_ids 258269
wheel_category Opinion Journalism
wheel_subcategory Left Wing
has_paywall false
inactive <empty>
Row n°1
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
webentity_id 2
...
Searching for rows
xan search -s outreach internationale medias.csv | xan view
Displaying 4/20 cols from 10 first rows of <stdin>
┌───┬──────────────┬────────────────────┬───┬─────────────┬──────────┐
│ - │ webentity_id │ name │ … │ has_paywall │ inactive │
├───┼──────────────┼────────────────────┼───┼─────────────┼──────────┤
│ 0 │ 25 │ Businessinsider.fr │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 1 │ 59 │ Europe-Israel.org │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 2 │ 66 │ France 24 │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 3 │ 220 │ RFI │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 4 │ 231 │ fr.Sott.net │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 5 │ 246 │ Voltairenet.org │ … │ true │ <empty> │
│ 6 │ 254 │ Afp.com /fr │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 7 │ 265 │ Euronews FR │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 8 │ 333 │ Arte.tv │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ 9 │ 341 │ I24News.tv │ … │ false │ <empty> │
│ … │ … │ … │ … │ … │ … │
└───┴──────────────┴────────────────────┴───┴─────────────┴──────────┘
Selecting some columns
xan select foundation_year,name medias.csv | xan view
Displaying 2 cols from 10 first rows of <stdin>
┌───┬─────────────────┬───────────────────────────────────────┐
│ - │ foundation_year │ name │
├───┼─────────────────┼───────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 0 │ 2002 │ Acrimed.org │
│ 1 │ 2006 │ 24matins.fr │
│ 2 │ 2013 │ Actumag.info │
│ 3 │ 2012 │ 2012un-Nouveau-Paradigme.com │
│ 4 │ 2010 │ 24heuresactu.com │
│ 5 │ 2005 │ AgoraVox │
│ 6 │ 2008 │ Al-Kanz.org │
│ 7 │ 2012 │ Alalumieredunouveaumonde.blogspot.com │
│ 8 │ 2005 │ Allodocteurs.fr │
│ 9 │ 2005 │ Alterinfo.net │
│ … │ … │ … │
└───┴─────────────────┴───────────────────────────────────────┘
Sorting the file
xan sort -s foundation_year medias.csv | xan view -s name,foundation_year
Displaying 2 cols from 10 first rows of <stdin>
┌───┬────────────────────────────────────┬─────────────────┐
│ - │ name │ foundation_year │
├───┼────────────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┤
│ 0 │ Le Monde Numérique (Ouest France) │ <empty> │
│ 1 │ Le Figaro │ 1826 │
│ 2 │ Le journal de Saône-et-Loire │ 1826 │
│ 3 │ L'Indépendant │ 1846 │
│ 4 │ Le Progrès │ 1859 │
│ 5 │ La Dépêche du Midi │ 1870 │
│ 6 │ Le Pélerin │ 1873 │
│ 7 │ Dernières Nouvelles d'Alsace (DNA) │ 1877 │
│ 8 │ La Croix │ 1883 │
│ 9 │ Le Chasseur Francais │ 1885 │
│ … │ … │ … │
└───┴────────────────────────────────────┴─────────────────┘
Deduplicating the file on some column
# Some medias of our corpus have the same ids on mediacloud.org
xan dedup -s mediacloud_ids medias.csv | xan count && xan count medias.csv
457
478
Deduplicating can also be done while sorting:
xan sort -s mediacloud_ids -u medias.csv
Computing frequency tables
xan frequency -s edito medias.csv | xan view
Displaying 3 cols from 5 rows of <stdin>
┌───┬───────┬────────────┬───────┐
│ - │ field │ value │ count │
├───┼───────┼────────────┼───────┤
│ 0 │ edito │ media │ 423 │
│ 1 │ edito │ individu │ 30 │
│ 2 │ edito │ plateforme │ 14 │
│ 3 │ edito │ agrégateur │ 10 │
│ 4 │ edito │ agence │ 1 │
└───┴───────┴────────────┴───────┘
Printing a histogram
xan frequency -s edito medias.csv | xan hist
Histogram for edito (bars: 5, sum: 478, max: 423):
media |423 88.49%|━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━|
individu | 30 6.28%|━━━╸ |
plateforme | 14 2.93%|━╸ |
agrégateur | 10 2.09%|━╸ |
agence | 1 0.21%|╸ |
Computing descriptive statistics
xan stats -s indegree,edito medias.csv | xan transpose | xan view -I
Displaying 2 cols from 14 rows of <stdin>
┌─────────────┬───────────────────┬────────────┐
│ field │ indegree │ edito │
├─────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┤
│ count │ 463 │ 478 │
│ count_empty │ 15 │ 0 │
│ type │ int │ string │
│ types │ int|empty │ string │
│ sum │ 25987 │ <empty> │
│ mean │ 56.12742980561554 │ <empty> │
│ variance │ 4234.530197929737 │ <empty> │
│ stddev │ 65.07326792108829 │ <empty> │
│ min │ 0 │ <empty> │
│ max │ 424 │ <empty> │
│ lex_first │ 0 │ agence │
│ lex_last │ 99 │ plateforme │
│ min_length │ 0 │ 5 │
│ max_length │ 3 │ 11 │
└─────────────┴───────────────────┴────────────┘
Evaluating an expression to filter a file
xan filter 'batch > 1' medias.csv | xan count
130
To access the expression language's cheatsheet, run xan help cheatsheet. To display the full list of available functions, run xan help functions.
Evaluating an expression to create a new column based on other ones
xan map 'fmt("{} ({})", name, foundation_year)' key medias.csv | xan select key | xan slice -l 10
key
Acrimed.org (2002)
24matins.fr (2006)
Actumag.info (2013)
2012un-Nouveau-Paradigme.com (2012)
24heuresactu.com (2010)
AgoraVox (2005)
Al-Kanz.org (2008)
Alalumieredunouveaumonde.blogspot.com (2012)
Allodocteurs.fr (2005)
Alterinfo.net (2005)
To access the expression language's cheatsheet, run xan help cheatsheet. To display the full list of available functions, run xan help functions.
Transform a column by evaluating an expression
xan transform name 'split(name, ".") | first | upper' medias.csv | xan select name | xan slice -l 10
name
ACRIMED
24MATINS
ACTUMAG
2012UN-NOUVEAU-PARADIGME
24HEURESACTU
AGORAVOX
AL-KANZ
ALALUMIEREDUNOUVEAUMONDE
ALLODOCTEURS
ALTERINFO
To access the expression language's cheatsheet, run xan help cheatsheet. To display the full list of available functions, run xan help functions.
Performing custom aggregation
xan agg 'sum(indegree) as total_indegree, mean(indegree) as mean_indegree' medias.csv | xan view -I
Displaying 1 col from 1 rows of <stdin>
┌────────────────┬───────────────────┐
│ total_indegree │ mean_indegree │
├────────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ 25987 │ 56.12742980561554 │
└────────────────┴───────────────────┘
To access the expression language's cheatsheet, run xan help cheatsheet. To display the full list of available functions, run xan help functions. Finally, to display the list of available aggregation functions, run xan help aggs.
Grouping rows and performing per-group aggregation
xan groupby edito 'sum(indegree) as indegree' medias.csv | xan view -I
Displaying 1 col from 5 rows of <stdin>
┌────────────┬──────────┐
│ edito │ indegree │
├────────────┼──────────┤
│ agence │ 50 │
│ agrégateur │ 459 │
│ plateforme │ 658 │
│ media │ 24161 │
│ individu │ 659 │
└────────────┴──────────┘
To access the expression language's cheatsheet, run xan help cheatsheet. To display the full list of available functions, run xan help functions. Finally, to display the list of available aggregation functions, run xan help aggs.
Available commands
- help: Get help regarding the expression language
Explore & visualize
- count (c): Count rows in file
- headers (h): Show header names
- view (v): Preview a CSV file in a human-friendly way
- flatten: Display a flattened version of each row of a file
- hist: Print a histogram with rows of CSV file as bars
- plot: Draw a scatter plot or line chart
- heatmap: Draw a heatmap of a CSV matrix
- progress: Display a progress bar while reading CSV data
Search & filter
- search: Search for (or replace) patterns in CSV data
- filter: Only keep some CSV rows based on an evaluated expression
- slice: Slice rows of CSV file
- top: Find top rows of a CSV file according to some column
- sample: Randomly sample CSV data
Sort & deduplicate
Aggregate
- frequency (freq): Show frequency tables
- groupby: Aggregate data by groups of a CSV file
- stats: Compute basic statistics
- agg: Aggregate data from CSV file
- bins: Dispatch numeric columns into bins
Combine multiple CSV files
- cat: Concatenate by row or column
- join: Join CSV files
- regex-join: Fuzzy join CSV files using regex patterns
- url-join: Join CSV files on url prefixes
- merge: Merge multiple similar already sorted CSV files
Add, transform, drop and move columns
- select: Select columns from a CSV file
- drop: Drop columns from a CSV file
- map: Create a new column by evaluating an expression on each CSV row
- transform: Transform a column by evaluating an expression on each CSV row
- enum: Enumerate CSV file by preprending an index column
- flatmap: Emit one row per value yielded by an expression evaluated for each CSV row
- fill: Fill empty cells
- blank: Blank down contiguous identical cell values
Format, convert & recombobulate
- behead: Drop header from CSV file
- rename: Rename columns of a CSV file
- input: Read unusually formatted CSV data
- fixlengths: Makes all rows have same length
- fmt: Format CSV output (change field delimiter)
- explode: Explode rows based on some column separator
- implode: Collapse consecutive identical rows based on a diverging column
- from: Convert a variety of formats to CSV
- to: Convert a CSV file to a variety of data formats
- scrape: Scrape HTML into CSV data
- reverse: Reverse rows of CSV data
- transpose (t): Transpose CSV file
Split a CSV file into multiple
Parallel operation over multiple CSV files
- parallel (p): Map-reduce-like parallel computation over multiple CSV files
Generate CSV files
- range: Create a CSV file from a numerical range
Perform side-effects
Lexicometry & fuzzy matching
- tokenize: Tokenize a text column
- vocab: Build a vocabulary over tokenized documents
- cluster: Cluster CSV data to find near-duplicates
Matrix & network-related commands
General flags and IO model
Getting help
If you ever feel lost, each command has a -h/--help flag that will print the related documentation.
If you need help about the expression language, check out the help command itself:
# Help about help ;)
xan help --help
Regarding input & output formats
All xan commands expect a "standard" CSV file, e.g. comma-delimited, with proper double-quote escaping. This said, xan is also perfectly able to infer the delimiter from typical file extensions such as .tsv, .tab, .psv, .ssv or .scsv.
If you need to process a file with a custom delimiter, you can either use the xan input command or use the -d/--delimiter flag available with all commands.
If you need to output a custom CSV dialect (e.g. using ; delimiters), feel free to use the xan fmt command.
Finally, even if most xan commands won't even need to decode the file's bytes, some might still need to. In this case, xan will expect correctly formatted UTF-8 text. Please use iconv or other utils if you need to process other encodings such as latin1 ahead of xan.
Working with headless CSV file
Even if this is good practice to name your columns, some CSV file simply don't have headers. Most commands are able to deal with those file if you give the -n/--no-headers flag.
Note that this flag always relates to the input, not the output. If for some reason you want to drop a CSV output's header row, use the xan behead command.
Regarding stdin
By default, all commands will try to read from stdin when the file path is not specified. This makes piping easy and comfortable as it respects typical unix standards. Some commands may have multiple inputs (xan join, for instance), in which case stdin is usually specifiable using the - character:
# First file given to join will be read from stdin
cat file1.csv | xan join col1 - col2 file2.csv
Note that the command will also warn you when stdin cannot be read, in case you forgot to indicate the file's path.
Regarding stdout
By default, all commands will print their output to stdout (note that this output is usually buffered for performance reasons).
In addition, all commands expose a -o/--output flag that can be use to specify where to write the output. This can be useful if you do not want to or cannot use > (typically in some Windows shells). In which case, - as a output path will mean forwarding to stdout also. This can be useful when scripting sometimes.
Gzipped files
xan is able to read gzipped files (having a .gz extension) out of the box.
Expression language reference
- Cheatsheet
- Comprehensive list of functions & operators
- Comprehensive list of aggregation functions
- Scraping DSL
Cookbook
- Merging frequency tables, three ways
- Parsing and visualizing dates with xan
- Joining files by URL prefixes
- Miscellaneous
News
For news about the tool's evolutions feel free to read:
Frequently Asked Questions
How to display a vertical bar chart?
Rotate your screen ;)
Dependencies
~66MB
~1M SLoC