33 releases
| 0.16.4 | Jan 4, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.16.3 | Aug 16, 2023 |
| 0.16.2 | Oct 23, 2022 |
| 0.16.0 | May 7, 2022 |
| 0.1.1 | Dec 15, 2016 |
#9 in Internationalization (i18n)
38,694 downloads per month
Used in 37 crates
(19 directly)
670KB
18K
SLoC
Whatlang
Natural language detection for Rust with focus on simplicity and performance.
Content
- Features
- Get started
- Who uses Whatlang?
- Documentation
- Supported languages
- Feature toggles
- How does it work?
- Running benchmark
- Comparison with alternatives
- Ports and clones
- Donations
- Derivation
- License
- Contributors
Features
- Supports 69 languages
- 100% written in Rust
- Lightweight, fast and simple
- Recognizes not only a language, but also a script (Latin, Cyrillic, etc)
- Provides reliability information
Get started
Example:
use whatlang::{detect, Lang, Script};
fn main() {
let text = "Ĉu vi ne volas eklerni Esperanton? Bonvolu! Estas unu de la plej bonaj aferoj!";
let info = detect(text).unwrap();
assert_eq!(info.lang(), Lang::Epo);
assert_eq!(info.script(), Script::Latin);
assert_eq!(info.confidence(), 1.0);
assert!(info.is_reliable());
}
For more details (e.g. how to blacklist some languages) please check the documentation.
Who uses Whatlang?
Whatlang is used within the following big projects as direct or indirect dependency for language recognition. You're gonna be in a great company using Whatlang:
- Sonic - fast, lightweight and schema-less search backend in Rust.
- Meilisearch - an open-source, easy-to-use, blazingly fast, and hyper-relevant search engine built in Rust.
Feature toggles
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
enum-map |
Lang and Script implement Enum trait from enum-map |
arbitrary |
Support Arbitrary |
serde |
Implements Serialize and Deserialize for Lang and Script |
dev |
Enables whatlang::dev module which provides some internal API.It exists for profiling purposes and normal users are discouraged to to rely on this API. |
How does it work?
How does the language recognition work?
The algorithm is based on the trigram language models, which is a particular case of n-grams. To understand the idea, please check the original whitepaper Cavnar and Trenkle '94: N-Gram-Based Text Categorization'.
How is is_reliable calculated?
It is based on the following factors:
- How many unique trigrams are in the given text
- How big is the difference between the first and the second(not returned) detected languages? This metric is called
ratein the code base.
Therefore, it can be presented as 2d space with threshold functions, that splits it into "Reliable" and "Not reliable" areas. This function is a hyperbola and it looks like the following one:
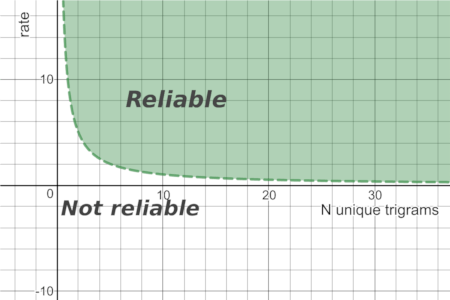
For more details, please check a blog article Introduction to Rust Whatlang Library and Natural Language Identification Algorithms.
Make tasks
make bench- run performance benchmarksmake doc- generate and open docmake test- run testsmake watch- watch changes and run tests
Comparison with alternatives
| Whatlang | CLD2 | CLD3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation language | Rust | C++ | C++ |
| Languages | 68 | 83 | 107 |
| Algorithm | trigrams | quadgrams | neural network |
| Supported Encoding | UTF-8 | UTF-8 | ? |
| HTML support | no | yes | ? |
Ports and clones
- whatlang-ffi - C bindings
- whatlanggo - whatlang clone for Go language
- whatlang-py - bindings for Python
- whatlang-rb - bindings for Ruby
- whatlangex - bindings for Elixir
Donations
You can support the project by donating NEAR tokens.
Our NEAR wallet address is whatlang.near
Derivation
Whatlang is a derivative work from Franc (JavaScript, MIT) by Titus Wormer.
License
Contributors
- greyblake Potapov Sergey - creator, maintainer.
- Dr-Emann Zachary Dremann - optimization and improvements
- BaptisteGelez Baptiste Gelez - improvements
- Vishesh Chopra - designed the logo
- Joel Natividad - support of Tagalog
- ManyTheFish - crazy optimization
- Kerollmops Clément Renault - crazy optimization
Dependencies
~2MB
~29K SLoC

