2 releases (1 stable)
| 1.0.0 | Apr 16, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.4.0 | Oct 6, 2023 |
#26 in Biology
207 downloads per month
435KB
1.5K
SLoC
kractor
kraken extractor
Kractor extracts sequencing reads based on taxonomic classifications obtained
via Kraken2. It consumes paired or unpaired fastq[.gz/.bz] files as input
alongisde a Kraken2 standard output. It can optionally consume a Kraken2 report to extract all taxonomic parents and
children of a given taxid. Fast and multithreaded by default, it outputs fast[q/a] files, that can optionally be
compressed. Memory usage
is minimal, averaging ~4.5MB while processing a 17GB fastq file.
The end result is a fast[q/a] file containing all reads classified as the specified taxon.
Kractor significantly enhances processing speed compared to KrakenTools for both paired and unpaired reads. Paired reads are processed approximately 21x quicker for compressed fastqs and 10x quicker for uncompressed. Unpaired reads are approximately 4x faster for both compressed and uncompressed inputs.
For additional details, refer to the benchmarks
Motivation
Inspired by KrakenTools.
The main motivation was to enchance speed when parsing, extracting, and writing a large volume of reads - and also to learn rust.
Installation
Binaries:
Precompiled binaries for Linux, MacOS and Windows are attached to the latest release 1.0.0
Docker:
A docker image is available on Docker Hub
Cargo:
Requires cargo
cargo install kractor
Build from source:
Install rust toolchain:
To install please refer to the rust documentation: docs
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Sam-Sims/Kractor
Build and add to path:
cd Kractor
cargo build --release
export PATH=$PATH:$(pwd)/target/release
All executables will be in the directory Kractor/target/release.
Usage
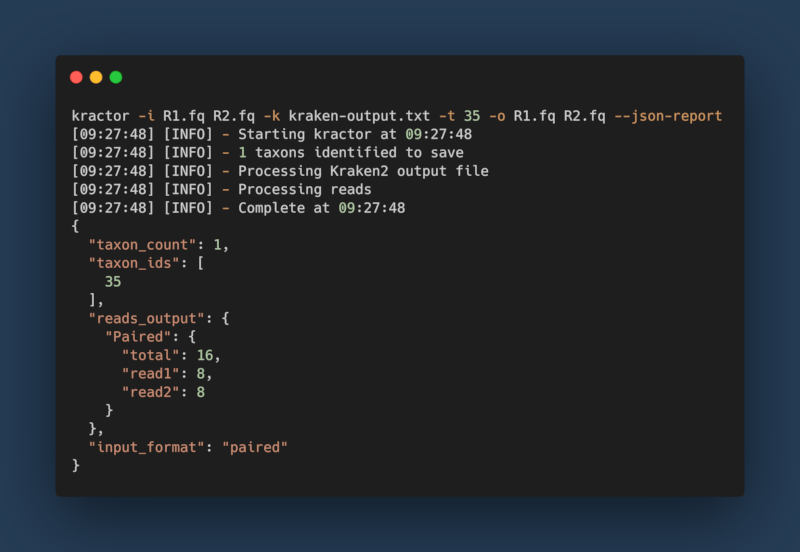
Basic Usage:
kractor -k <kraken_output> -i <fastq_file> -t <taxonomic_id> -o <output_file> --json-report > kractor_report.json
Or, if you have paired-end illumina reads:
kractor -k <kraken_output> -i <R1_fastq_file> -i <R2_fastq_file> -t <taxonomic_id> -o <R1_output_file> -o <R2_output_file>
If you want to extract all children of a taxon:
kractor -k <kraken_output> -r <kraken_report> -i <fastq_file> -t <taxonomic_id> --children -o <output_file>
Arguments:
Required:
Input
-i, --input
This option will specify the input files containing the reads you want to extract from. They can be compressed - (gz,
bz2). Paired end reads can be specified by:
Using --input twice: -i <R1_fastq_file> -i <R2_fastq_file>
Using --input once but passing both files: -i <R1_fastq_file> <R2_fastq_file>
This means that bash wildcard expansion works: -i *.fastq
Output
-o, --output
This option will specify the output files containing the extracted reads. The order of the output files is assumed to be the same as the input.
By default the compression will be inferred from the output file extension for supported file types (gz, bz). If the
output type cannot be inferred, plaintext will be output.
Kraken Output
-k, --kraken
This option will specify the path to the Kraken2 output containing taxonomic classification of read IDs.
Taxid
-t, --taxid
This option will specify the taxon ID for reads you want to extract.
Optional:
Output type
-O, --output-type
This option will manually set the compression mode used for the output file and will override the type inferred from the output path.
Valid values are:
gzto output gzbz2to output bz2noneto not apply compresison
Compression level
-l, --level
This option will set the compression level to use if compressing the output. Should be a value between 1-9 with 1 being the fastest but largest file size and 9 is for slowest, but best file size. By default this is set at 2 as it is a good trade off for speed/filesize.
Output fasta
--output-fasta
This option will output a fasta file, with read ids as headers.
Kraken Report
-r, --report
This option specifies the path to the report file generated by Kraken2. If you want to use --parents or --children
then is argument is required.
Parents
--parents
This will extract reads classified at all taxons between the root and the specified --taxid.
Children
--children
This will extract all the reads classified as decendents or subtaxa of --taxid (Including the taxid).
Exclude
--exclude
This will output every read except those matching the taxid. Works with --parents and --children
Skip report
--json-report
This will output a json report that to stdout upon programme completion.
Version
- 1.0.0
Dependencies
~13–26MB
~386K SLoC