4 releases
| 0.2.0 | Jan 27, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.2 | Jun 1, 2023 |
| 0.1.1 | May 29, 2023 |
| 0.1.0 | May 29, 2023 |
#41 in #linux-process
340KB
470 lines
🌏 Somo
A human-friendly alternative to netstat or ss for socket monitoring with the ability to scan for malicious IP addresses.
⬇️ Installation:
Debian:
If you use a Debian OS go to releases and download the latest .deb release.
From crates.io:
1. Install cargo:
You can install cargo from the crates.io website.
2. Install the somo crate:
cargo install somo
🏃♀️ Running somo:
To run somo just type:
somo
Using sudo:
It can often be beneficial to run it in sudo mode since many PIDs will remain hidden otherwise. If sudo somo doesn't work, try running it using the full path:
# you can find out the path by running: "where somo"
sudo /path/to/somo
# or directly like this
sudo $(where somo)
Problems with this: it's unconvenient and ENV variables can't be accessed!
Better solution: Add it to the $PATH variable (like this).
⚙️ Features:
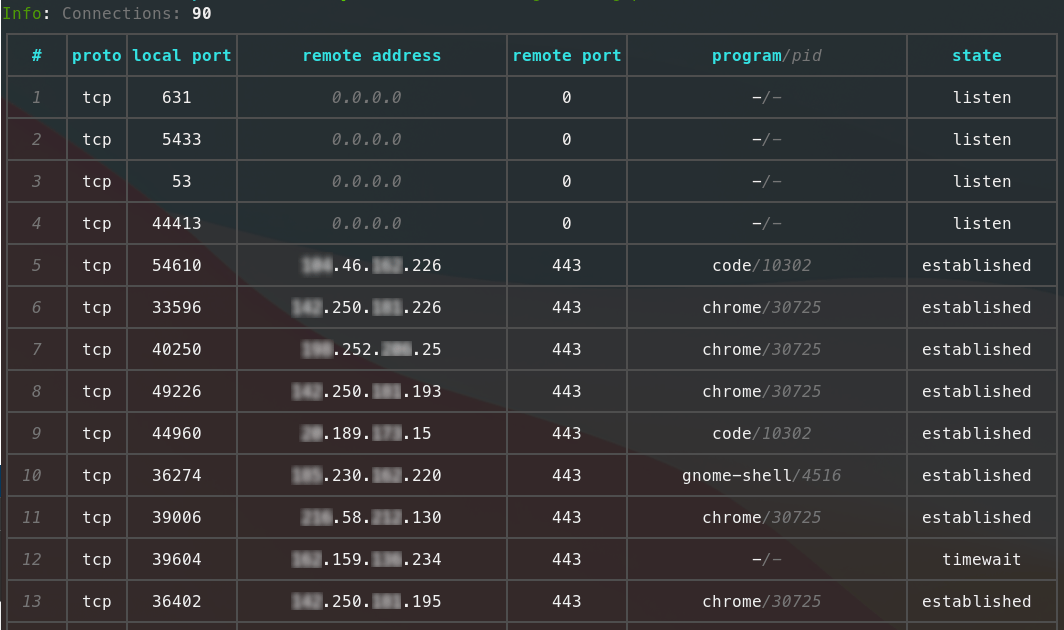
1. Pretty and easily readable table:
2. Filtering:
You can filter by remote port, local port, IP, protocol, client program, PID and connection status. Check the flag descriptions below.
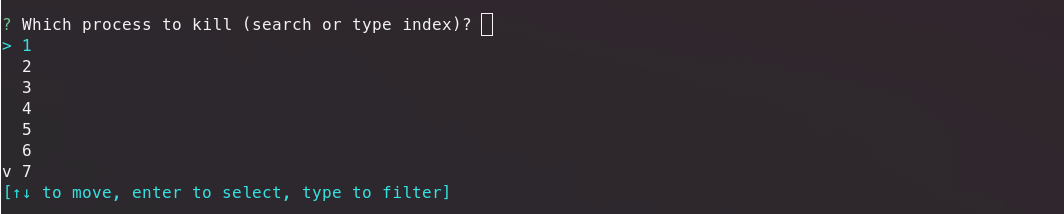
3. Process killing:
With the -k flag you can choose to kill a process after inspecting the connections using an interactive selection option.
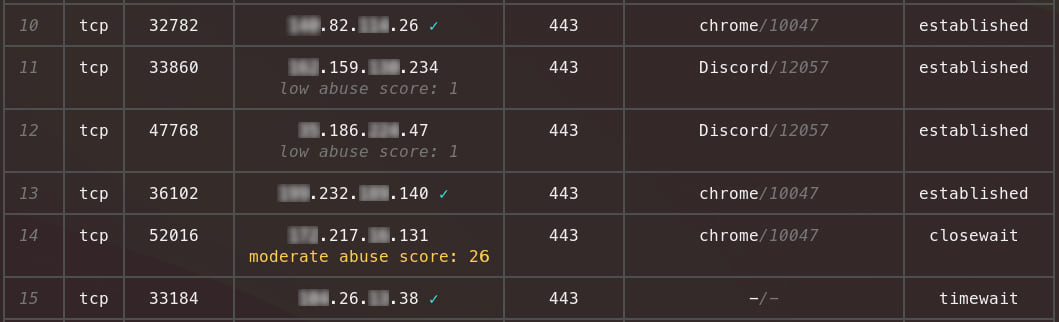
4. Checking for malicious IPs using AbuseIPDB.com:
To automatically check if any of the remote IPs you are connected to are malicious you can specify an API key for the AbuseIPDB API as an environment variable:
export ABUSEIPDB_API_KEY={your-api-key} # not session persistent
Adding the -c flag will then check for malicious IPs and notify you in the table:
🚩 Flags:
| flag | description | value |
|---|---|---|
--proto |
filter by either TCP or UDP | tcp or udp |
--ip |
filter by a remote IP | the IP address e.g 0.0.0.0 |
--port, -p |
filter by a remote port | the port number, e.g 443 |
--local-port |
filter by a local port | the port number, e.g 5433 |
--program |
filter by a client program | the program name e.g chrome |
--pid, -p |
filter by a PID | the PID number, e.g 10000 |
--open, -o |
filter by open connections | - |
--exclude-ipv6, -e |
don't list IPv6 connections | - |
--kill, -k |
interactive process killing | - |
--check, -c |
check remote IPs using AbuseIPDB (make sure the environment variable ABUSEIPDB_API_KEY is set) |
- |
Dependencies
~15–30MB
~468K SLoC