6 releases
| 0.4.0 | Feb 18, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.0 | Nov 13, 2022 |
| 0.1.3 | May 25, 2022 |
| 0.1.2 | Jan 17, 2022 |
#689 in Game dev
367 downloads per month
135KB
722 lines
A simple implementation of the astar pathfinding algorithm from red blob games as well as "Dijkstra Maps" as described in [Dijkstra Maps Visualized]https://www.roguebasin.com/index.php/Dijkstra_Maps_Visualized
In order to use the astar pathfinder you must have a path map for it to navigate. You can define one by implementing the PathMap trait, or you can use the built-in PathMap2d.
Example
use sark_pathfinding::*;
let mut pf = Pathfinder::new();
let mut map = PathMap2d::new([10, 10]);
map.add_obstacle([3,0]);
map.add_obstacle([3,1]);
let path = pf.astar(&map, [0, 0], [5, 0]).unwrap();
assert_eq!(6, path.len());
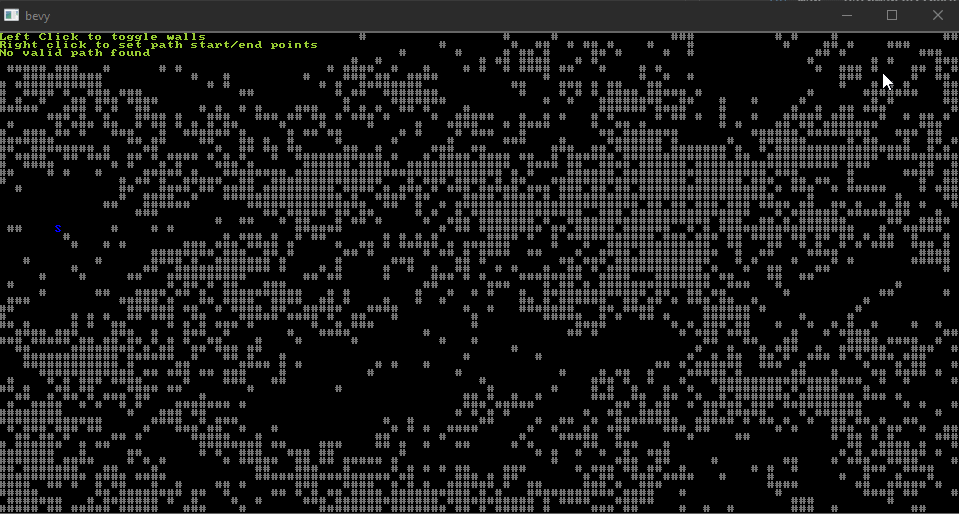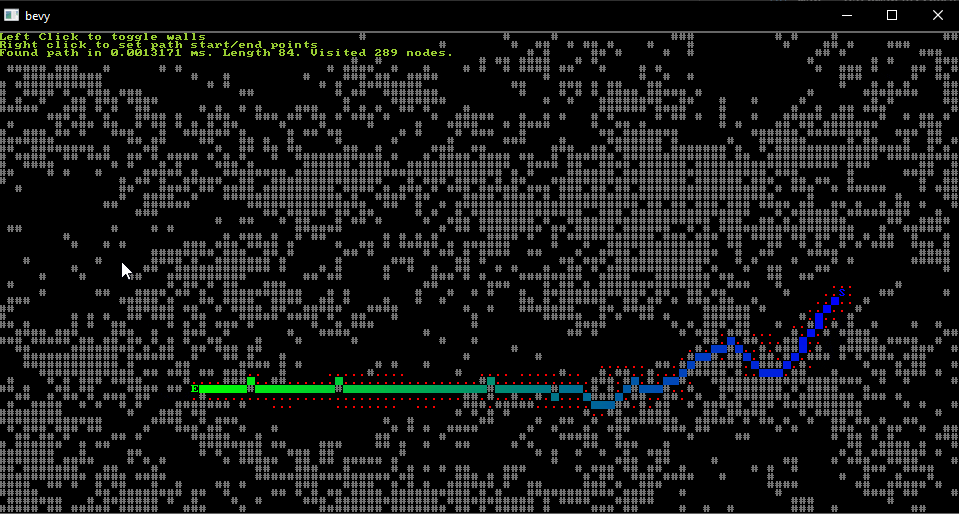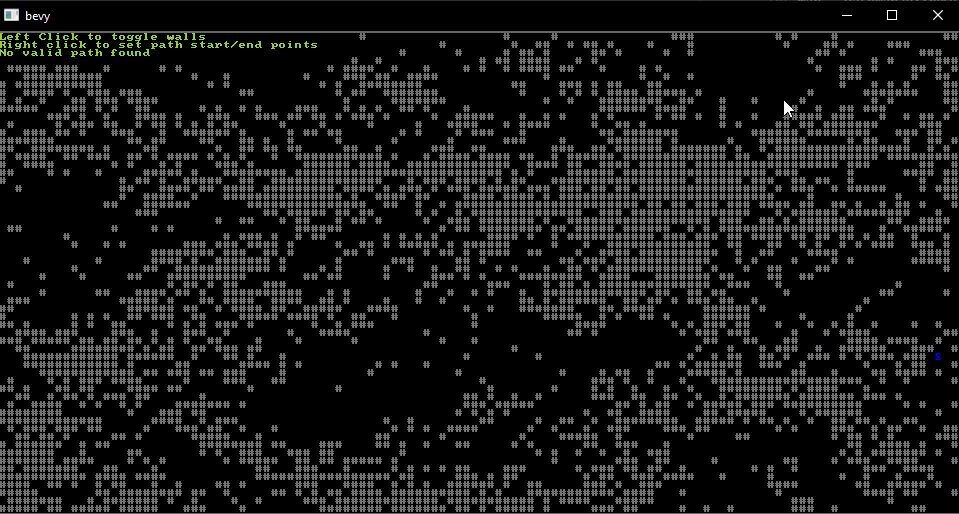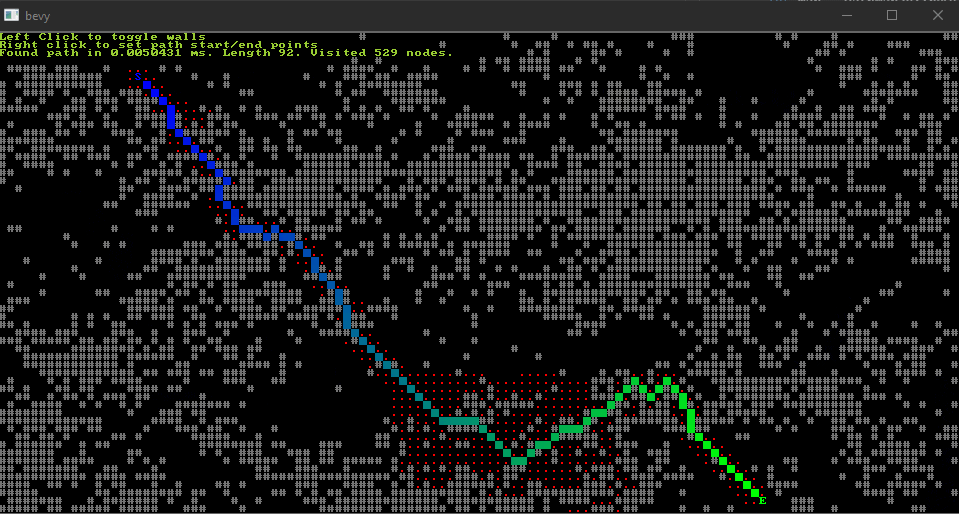 From the "astar" example.
From the "astar" example.
A DijkstraMap can be generated using a PathMap as well. The pathmap defines the obstacles and movement costs, and the 'goals' are defined in the dijkstra map.
Example
use sark_pathfinding::*;
let mut pathmap = PathMap2d::new([20,20]);
pathmap.add_obstacle([5,5]);
pathmap.add_obstacle([5,6]);
pathmap.add_obstacle([5,7]);
// Ensure the dijsktra map is defined with the same size as your pathmap.
let mut goals = DijkstraMap::new([20,20]);
goals.add_goal([10,10], 0.0);
goals.add_goal([15,15], 5.0);
goals.recalculate(&pathmap);
let next_step = goals.next_lowest([13,13], &pathmap).unwrap();
// Lower value goals are considered 'closer'.
assert_eq!([12,12], next_step.to_array());
Dependencies
~6MB
~159K SLoC