3 releases
| 0.1.2 | Apr 25, 2022 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.1 | Apr 16, 2022 |
| 0.1.0 | Apr 16, 2022 |
#549 in Graphics APIs
Used in mugltf
585KB
4.5K
SLoC
█▓▒░⡷⠂μ GL⠐⢾░▒▓█
Micro WebGL2 / WebGPU Graphics Library for Rust
Overview
mugl is a minimal, modern WebGL 2.0 / WebGPU 3D graphics abstraction layer. It provides a simplified WebGPU-style API that runs on the web using WebGL 2.0, and other platforms using native WebGPU.
Install
[dependencies]
mugl = "0.1"
Features:
backend-webgl- enables WebGL 2.0 backend for WASM. Requiresmugl/wasmnpm package for glue code. (see usage)backend-wgpu- enables WebGPU backend based onwgpustd- enablesstdsupportwasm-bindgenenableswasm-bindgenintegrationserde- enablesserdeserialize/deserialize implementations
Documentation
See Docs.rs: https://docs.rs/mugl
Usage
Examples
Several examples can be found in this repository. Use npm to run the below examples on web: npm install && npm start
| Screenshot | Source | Run Script |
|---|---|---|
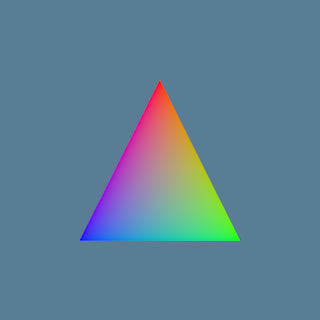 |
basic | cargo run --features backend-wgpu --example basic |
 |
instancing | cargo run --features backend-wgpu --example instancing |
 |
stencil | cargo run --features backend-wgpu --example stencil |
Hello World
Below is the minimal WASM app to draw the triangle in the basic example using the WebGL backend (See full example code here):
use mugl::{prelude::*, webgl::*};
// (Optional) Define a unique app ID to use in JS glue code. Required only when multiple WASM modules use mugl.
#[no_mangle]
pub extern "C" fn app_id() -> ContextId { ContextId::set(123); ContextId::get() }
#[no_mangle]
pub extern "C" fn render() {
app_id(); // Make sure we call ContextId::set() before any API call.
// 1. Create device from canvas of id "canvas"
let canvas = Canvas::from_id("canvas");
let device = WebGL::request_device(&canvas, WebGLContextAttribute::default(), WebGL2Features::empty())
.expect("WebGL 2.0 is unsupported");
// 2. Create buffer
let vertices: &[f32] = &[
// position color
0.0, 0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0,
0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0,
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0
];
let vertices: &[u8] = bytemuck::cast_slice(vertices);
let buffer = device.create_buffer(BufferDescriptor { usage: BufferUsage::VERTEX, size: 3 });
device.write_buffer(&buffer, 0, vertices);
// 3. Create shaders
let vertex = &device.create_shader(ShaderDescriptor {
usage: ShaderStage::VERTEX,
code: "#version 300 es
layout (location=0) in vec3 position;
layout (location=1) in vec4 color;
out vec4 vColor;
void main () {
gl_Position = vec4(position, 1);
vColor = color;
}
".into(),
});
let fragment = &device.create_shader(ShaderDescriptor {
usage: ShaderStage::FRAGMENT,
code: "#version 300 es
precision mediump float;
in vec4 vColor;
out vec4 outColor;
void main () {
outColor = vColor;
}
".into(),
});
// 4. Create pipeline
let pipeline = device.create_render_pipeline(RenderPipelineDescriptor {
vertex,
fragment,
buffers: &[VertexBufferLayout {
stride: core::mem::size_of::<[f32; 7]>() as BufferSize,
step_mode: VertexStepMode::Vertex,
attributes: &[
VertexAttribute { shader_location: 0, format: VertexFormat::F32x3, offset: 0 },
VertexAttribute { shader_location: 1, format: VertexFormat::F32x4, offset: core::mem::size_of::<[f32; 3]>() as BufferSize },
],
}],
bind_groups: &[],
targets: Default::default(),
primitive: Default::default(),
depth_stencil: Default::default(),
multisample: Default::default(),
});
// 5. Create default pass
let pass = device.create_render_pass(RenderPassDescriptor::Default {
clear_color: Some(Color(0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0)),
clear_depth: None,
clear_stencil: None,
});
// 6. Render
{
let encoder = device.render(&pass);
encoder.pipeline(&pipeline);
encoder.vertex(0, &buffer, 0);
encoder.draw(0..3, 0..1);
encoder.submit();
}
device.present();
}
To run the above WASM module, you need the dependency on mugl NPM package and the following JS glue code:
npm install --save mugl
import { set_context_memory } from "mugl/wasm";
import { memory, app_id, render } from "hello_world.wasm";
set_context_memory(app_id(), memory); // Required only if `wasm-bindgen` feature is not enabled
// 1. Create canvas with id "canvas"
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
canvas.id = "canvas";
canvas.width = canvas.height = 512;
document.body.appendChild(canvas);
// 2. Call render in WASM
render();
Dependencies
~0.3–12MB
~145K SLoC