12 releases
| 0.2.7 | Mar 26, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.6 | Jan 21, 2025 |
| 0.2.3 | Dec 24, 2024 |
| 0.2.1 | Nov 23, 2024 |
| 0.1.0 | Aug 17, 2024 |
#1512 in Network programming
171 downloads per month
300KB
7K
SLoC


What is WireMan?
WireMan is a terminal-based gRPC client with a user-friendly interface. It reads .proto files from a config file and keeps a history of requests.
WireMan is an ideal choice for developers testing gRPC endpoints directly from the terminal.
Quick Start
If you prefer a quick overview, you can check out the official website.
Or follow the guide below.
Prerequisites
- Rust: [Minimum required Rust version is 1.70] (Installation Guide)
Installation
Install with cargo
cargo install wireman
Install with brew
brew install preiter93/wireman/wireman
Download Binary
You can download the latest wireman binary from the releases page.
Install manually
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/preiter93/wireman.git -
Build in release mode:
cd wireman cargo build --release -
Copy the binary to your PATH, e.g.:
cp target/release/wireman /usr/local/binAlternatively, you can create an alias to the binary in your
.bashrcor.zshrcfile:echo "alias wireman='CURRENT_DIRECTORY/target/release/wireman'" >> ~/.zshrc
Demo
Setup/Configuration
-
Set the
WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIRenvironment variable to specify the directory where your configuration file will be located:export WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIR=~/.config/wireman
This step is optional. By default, wireman will be installed to ~/.config/wireman.
-
Follow the setup steps:
wireman init -
The previos step creates a
wireman.tomlfile in your configuration directory. Here's an example configuration:includes = [ '$HOME/my-project/services', '$HOME/my-project/protos' ] files = [ 'order/api.proto', 'price/api.proto' ] [server] default_address = "http://localhost:50051" default_auth_header = "Bearer $(getToken.sh)" [history] directory = "$WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIR/history" # Optional. Defaults to $WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIR/history. autosave = true # Optional. Autosaves history on request. Defaults to true. disabled = false # Optional. History is enabled by default. [logging] directory = "$WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIR" # Optional. Defaults to $WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIR. level = "Debug" # Optional. Defaults to Debug. # [ui] # skin = "$WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIR/skins/dracula.toml" # Optional. Set a UI theme.Replace with the appropriate values for your project.
-
At last, you can now verify the setup configuration
wireman check
Usage
-
After adding the protos in the config, start
wireman. -
Basic key mappings are displayed in the footer of each page. For extended help, press
?and close with?orEsc. If you want to close the app entirely, typeCtrl+c. -
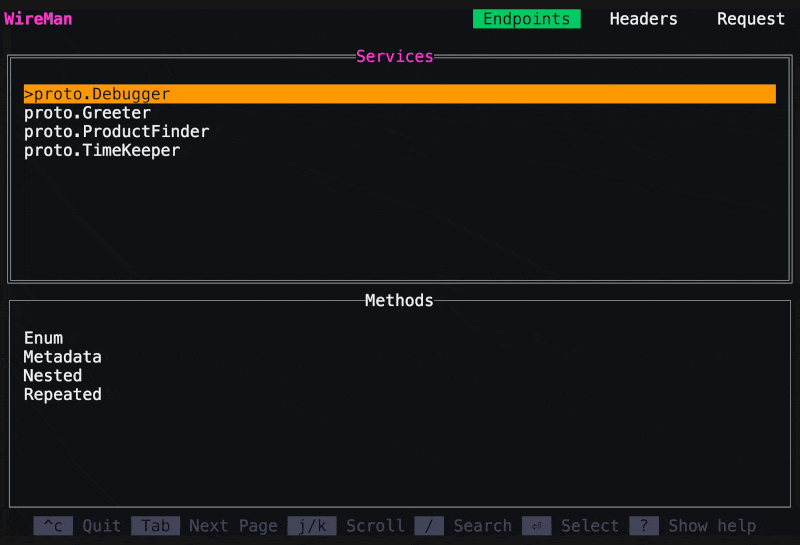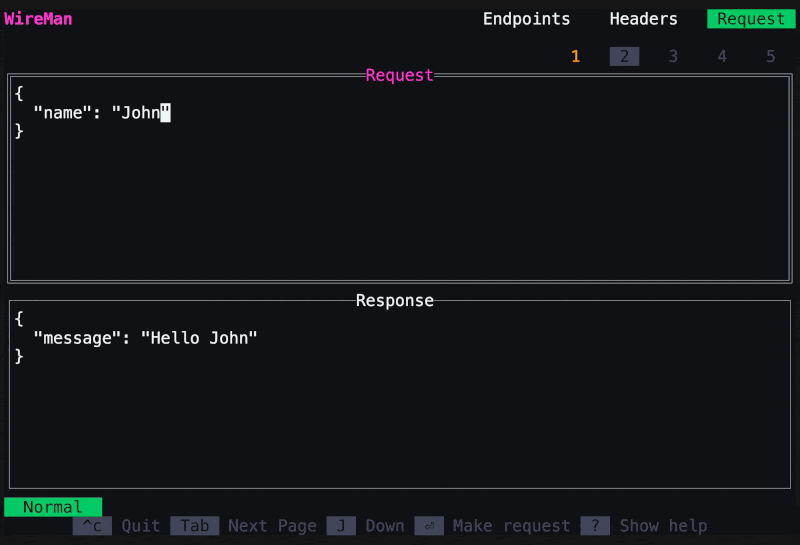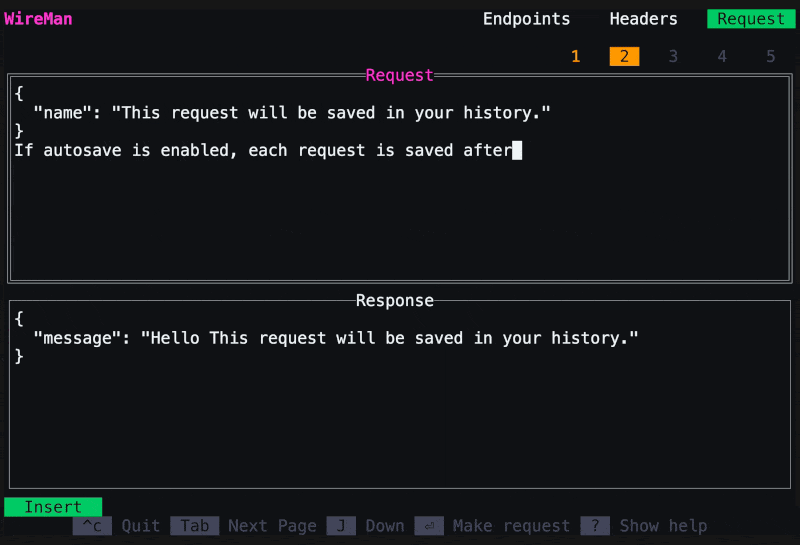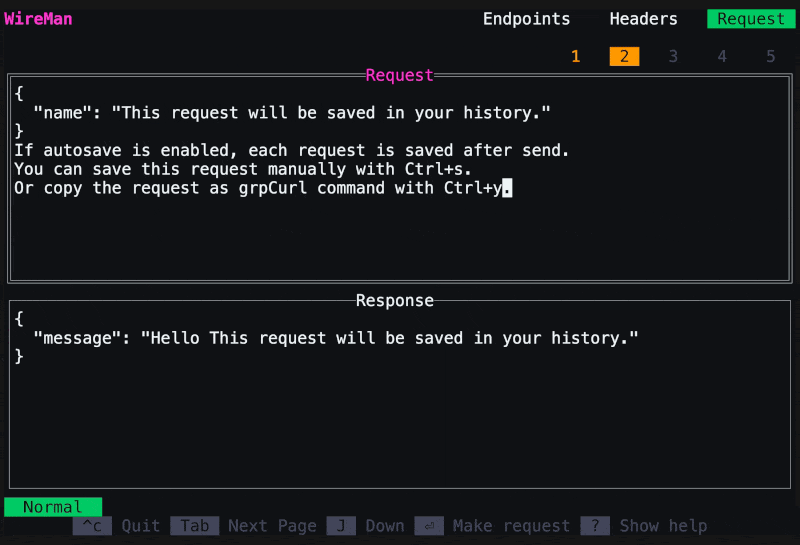
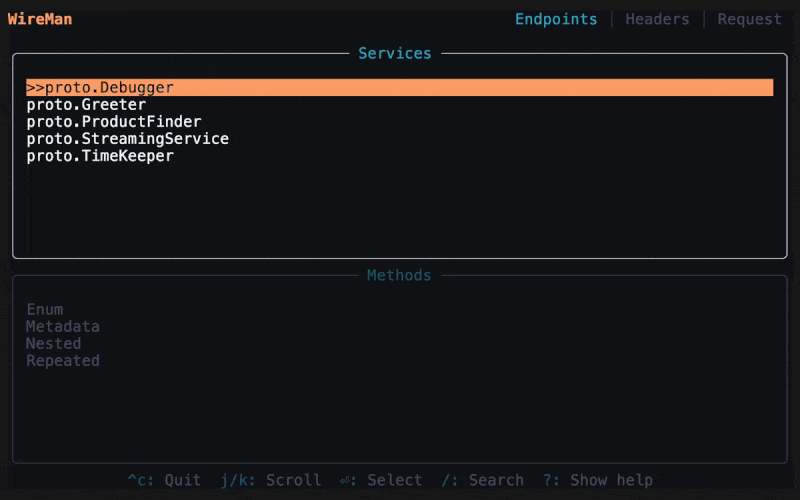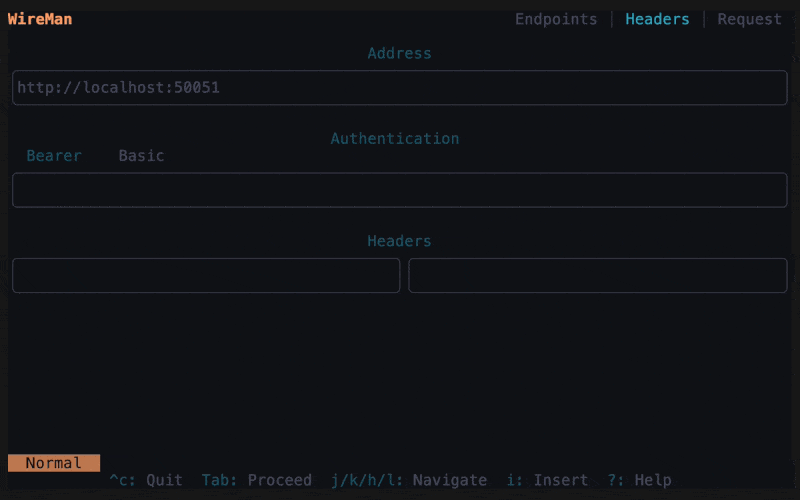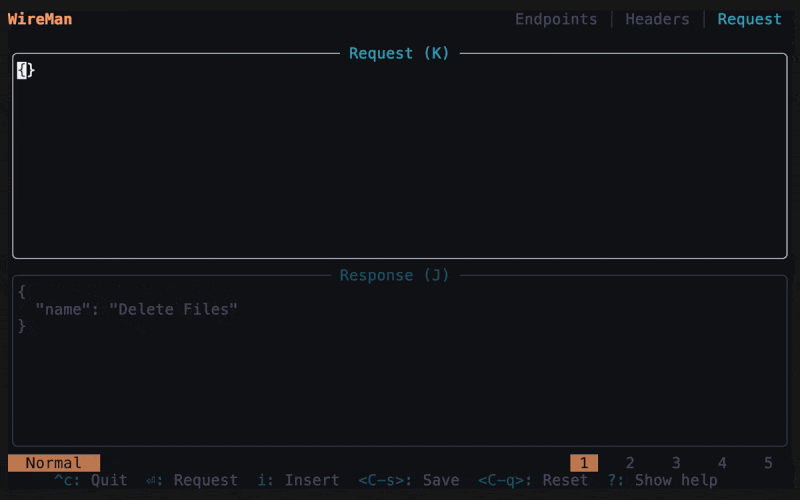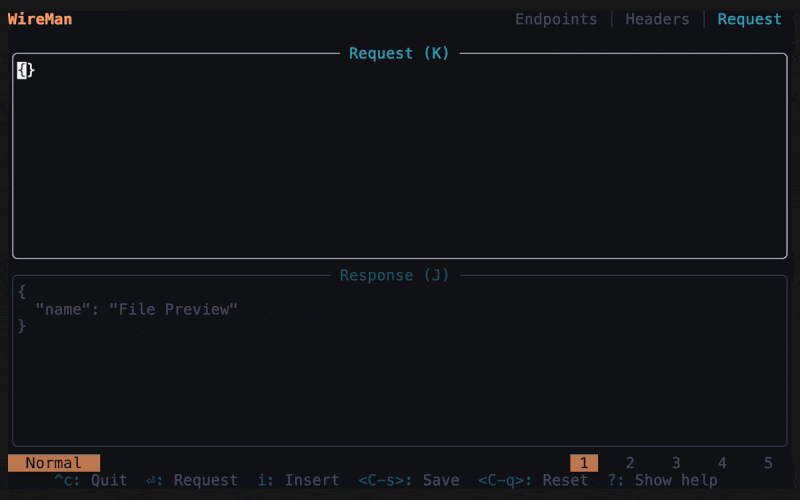
The first page of Wireman will list your grpc services and their methods. You can navigate with
up/downorj/k, select withEnteror unselect withEsc, then clickTab. -
The second page is the message screen. Edit your request message, you can format it with
Ctrl+f. Then click tab. The navigation of the editor is vim-inspired: useh,j,k,lfor motion, go into insert mode withi, and escape insert mode withEsc. For more details, refer to edtui. -
The third page is the config screen where you can edit the address or metadata. Wireman allows for using bash scripts to get your tokens. Place the name of your script in the bearer token field, which must be in your PATH, between
$(). For example, if you have a bash script namedgetToken.shthat prints the Bearer tokeney..., you would use$(getToken.sh)(the script output should not include the word 'Bearer', as it is automatically added). Additional headers can be added withCtrl+aand deleted withCtrl+d. Go to the request page with Shift+Tab or click tab twice. -
Now you can make the request by clicking Enter. You can save it with
Ctrl+s. Saved requests are stored in spots 1 to 5. Switch to a spot by clicking the respective number. You can restore the default request withCtrl+d, which deletes the history. You can also cancel a request with Esc. Switch between request and response withJ/K.To copy the request or response clickY. Or follow step 6. -
If you want to get the current request as a gRPCurl command, click
Ctrl+yon the request tab, and it's copied to your clipboard.
Command line flags
Commands
-
check
Runs a health check and displays configuration details. -
init
Sets up wireman by creating a default configuration file.
Options
-
-c, --config <CONFIG>
Specifies an optional path to a configuration file. If not provided, wireman uses the default configuration path. -
-l, --local-protos
Uses local protobuf files instead of the files and includes which specified in the configuration.
Troubleshooting
Wireman logs important information and errors to assist in troubleshooting. By default, logs are stored in $WIREMAN_CONFIG_DIR/wireman.log.Make sure to check this log file if you encounter any unexpected behavior or errors while using the application.
If you are unable to resolve the issue on your own or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to open an issue.
Custom Skins
Wireman allows users to customize the appearance of the UI by adding custom skins. To do this, simply specify the desired skin file in the wireman.toml file config:
[ui]
skin = "path_to_file/custom_skin.toml"
For a collection of pre-made themes, check out the Wireman themes repository.
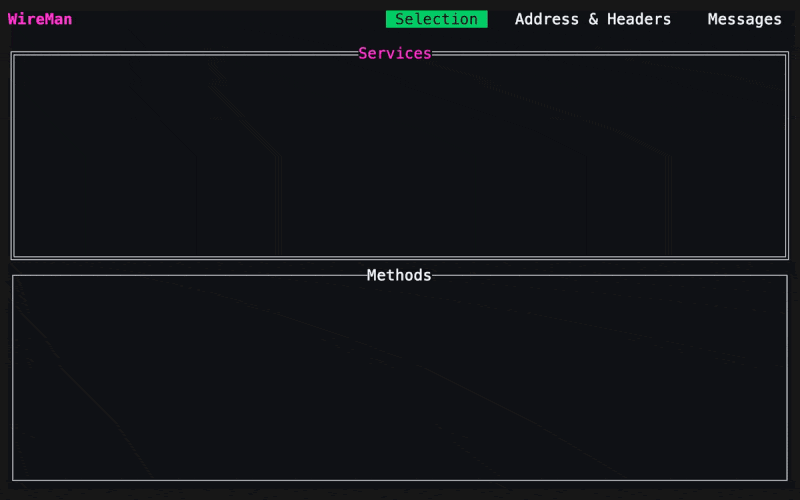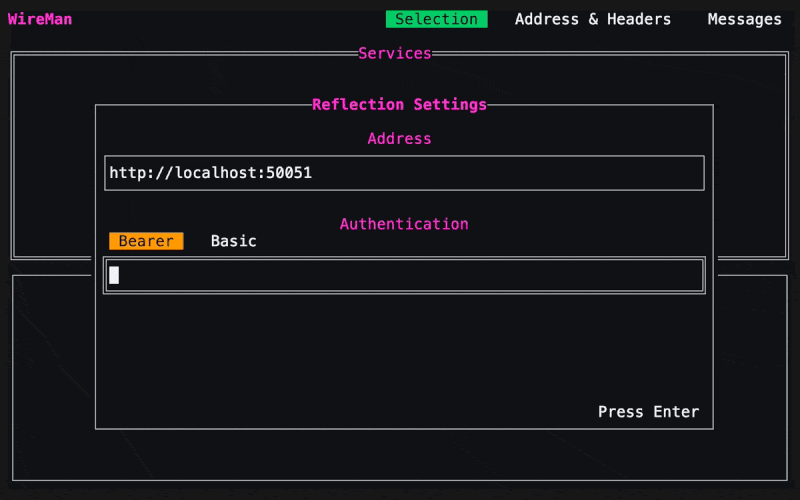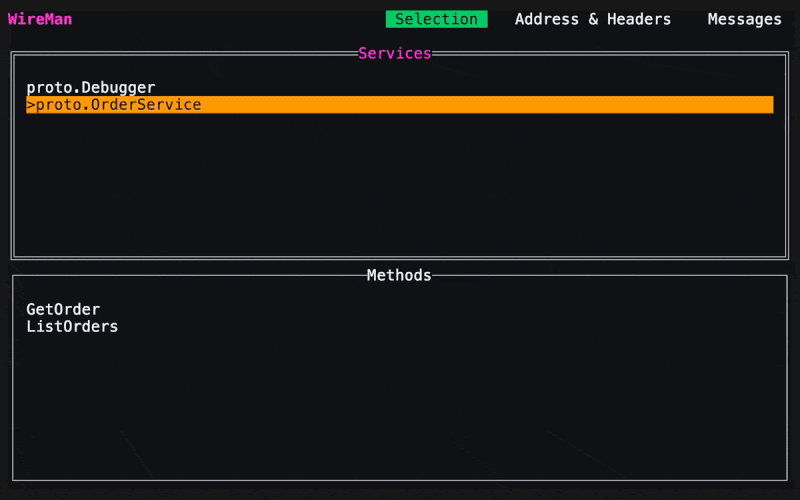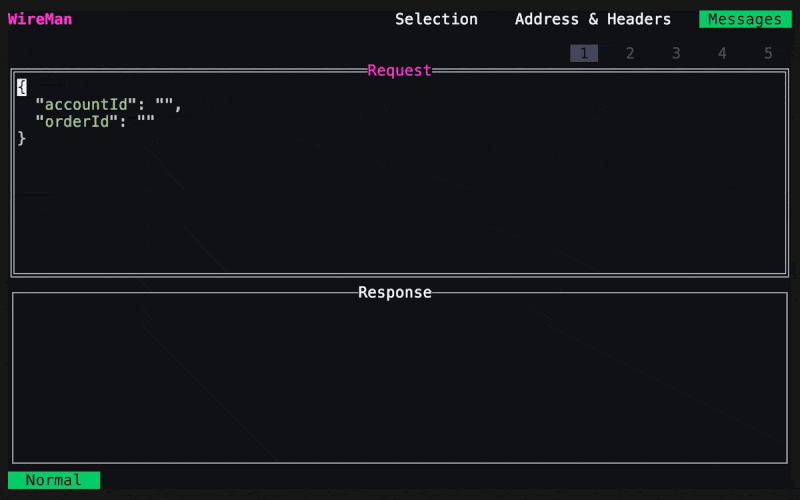
Server Reflection
Wireman also supports server reflection of gRPC servers. To activate reflection mode, press Ctrl + r on the selection tab, enter the host along with optional authentication headers, and then press Enter. To switch back from reflection mode to file mode press Ctrl + r again.
Server Side Streaming
Wireman supports server-side streaming. For example, if you have an endpoint like this:
rpc ListFeatures (ListFeaturesReq) returns (stream ListFeaturesResp) {}
Wireman automatically detects whether the endpoint is server-side streaming and handles it accordingly.
Edit Configuration in-app
You can manage your configuration directly within the app:
- Navigate to the services page.
- Type
Ctrl-eto edit the configuration. - Save your changes with
Ctrl-s.
Features
- Unary gRPC
- Set host address
- Set authentication headers
- Request History
- Defaults of repeated/nested fields
- Yank/Paste from clipboard
- Yank request as grpcurl command
- Vim like editor feeling
- Show loading indicator
- Metadata headers
- Provide installation help
- Custom themes
- Server reflection
- Edit config file in app
- Server side Streaming
- Supports wayland
Dependencies
~36–52MB
~757K SLoC