3 releases
| new 0.0.3 | May 14, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.0.2 | May 13, 2025 |
| 0.0.1 | May 12, 2025 |
#312 in Math
354 downloads per month
85KB
479 lines
rquant
A quantum computing library written entirely in rust.
It allows for qubit measurement and basic quantum logic in complex vector space. Gates can be applied to qubits in complex vector space, then those qubits can be measured to observe the outcome.
Getting Started
- Download the repo
- Open a terminal and navigate to the repo root
- Run
cargo runto see the output of the (very simple)mainfunction - Run
cargo testto run all the tests - Run
cargo doc --no-depsto generate the docs
Examples
Creating a qubit
You can create a qubit by using one of the premade qubits, or using a premade quantum position:
use rquant::{
log_info,
quantum::types::{quantum_position::QuantumPosition, qubit::Qubit},
};
fn main() {
// create a zero qubit: |0>
let zero_qubit = Qubit::zero();
log_info!("Zero qubit: {zero_qubit}");
// create an identity qubit: |1>
let identity_qubit = Qubit::one();
log_info!("Zero qubit: {identity_qubit}");
// create a custom qubit using a quantum position:
// 0+1i|0>
let custom_qubit = Qubit::new(QuantumPosition::QUARTER_TURN);
log_info!("Custom qubit: {custom_qubit}");
}
This example will produce the following output:

Applying gates to qubits
You can apply a gate to a single qubit:
use rquant::{
log_info,
quantum::types::{quantum_gate::QuantumGate, qubit::Qubit},
};
fn main() {
// use the '!' operator to apply the FLIP gate
let flipped_zero_qubit = !Qubit::zero();
log_info!("Flipped zero qubit: {flipped_zero_qubit}");
// use premade quantum gates to modify a qubit
let rotated_qubit = Qubit::one()
.apply_gate(&QuantumGate::PHASE)
.apply_gate(&QuantumGate::ROTATE);
log_info!("Rotated identity qubit: {rotated_qubit}");
}
This example will produce the following output:

Create multiple associated qubits
You can create a collection of many qubits using a qubit register:
use rquant::{
log_info,
quantum::types::{quantum_gate::QuantumGate, qubit_register::QubitRegister},
};
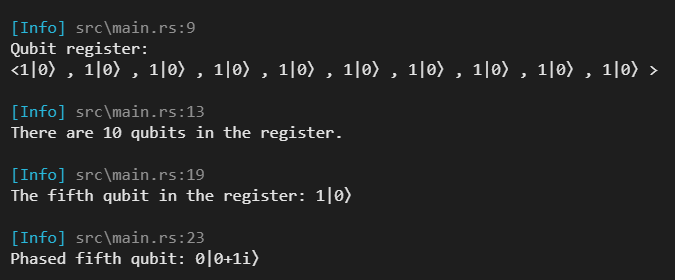
fn main() {
// create a register of 100 qubits with the |0> state
let qubit_register = QubitRegister::new(10);
log_info!("Qubit register:\n{qubit_register}");
// get the amount of qubits in the qubit register
let qubit_count = qubit_register.len();
log_info!("There are {qubit_count} qubits in the register.");
// get a (zero-indexed) qubit from the register
let fifth_qubit = qubit_register
.get(4)
.expect("There was no fifth qubit in the register.");
log_info!("The fifth qubit in the register: {fifth_qubit}");
// modify the fifth qubit by applying the PHASE gate
let phased_fifth_qubit = fifth_qubit.apply_gate(&QuantumGate::ROTATE);
log_info!("Phased fifth qubit: {phased_fifth_qubit}\n");
}
This example will produce the following output:
Run simulations on qubits
You can simulate and report on behavior on any amount of qubits:
use rquant::{
quantum::types::qubit::Qubit,
simulation::types::{simulation::Simulation, simulation_report::SimulationReport},
};
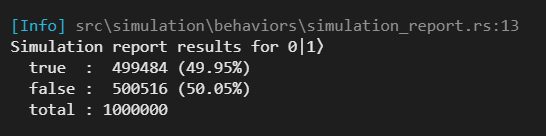
fn main() {
// create 1,000,000 superpositioned qubits, and observe
// their measurements using the report function.
Qubit::one()
.simulate_superposition(1000000)
.report(Qubit::one());
}
This example will produce the following output:
Dependencies
| Crate | Purpose |
|---|---|
| rand v0.9.1 | Used to measure qubit position |
| num-complex v0.4 | Used as the basis of quantum positions for qubits |
Dependencies
~670KB
~12K SLoC