1 unstable release
| 0.1.1 | Nov 17, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.0 |
|
#594 in Algorithms
65KB
149 lines
Reveler - 中文文档
This repository implements a cryptographic commitment scheme based on optimized FFT and hashing functions, designed for efficient commitment generation and verification. The scheme uses Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) for matrix multiplication and BlueHash-based hashing for commitment verification.
Overview
This library provides two main functions:
- Commitment Generation (
commit): This function generates a cryptographic commitment based on input parameters. - Commitment Verification (
verify): This function verifies the validity of a commitment using a random challenge.
The cryptographic commitment uses a combination of FFT-based matrix multiplication and a multi-round BlueHash hashing algorithm to ensure both randomness and security.
Commitment Generation
The commit function computes the commitment using the following steps:
-
Matrix Generation: Random matrices
AandBare generated using thegenerate_paramsfunction. These matrices will be used in the FFT-based matrix multiplication.The matrices ( A ) and ( B ) are of size ( N \times N ), where ( N = 256 ). Each element is randomly chosen from the range ( [0, Q) ), where ( Q = 65535 ).
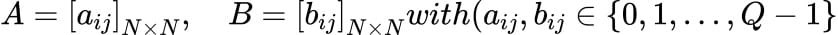
-
FFT Matrix Multiplication: For each row ( a_i ) from matrix ( A ) and ( b_i ) from matrix ( B ), we perform an FFT-based matrix multiplication:
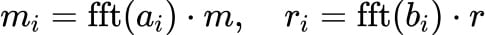
Where represents element-wise multiplication of the FFT-transformed rows and the vectors ( m ) and ( r ), respectively.
-
Commitment Point Calculation: The sum of the FFT results for each row is calculated as:
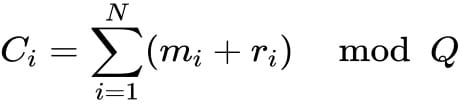
This results in a commitment point:
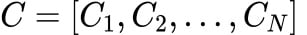
-
Commitment Hashing: The commitment point ( C ) is then hashed using the BlueHash algorithm. The BlueHash algorithm applies multiple rounds of hashing for added randomness and security:

The final commitment hash is obtained after 3 rounds of BlueHash.
The commitment is returned as a struct containing both the commitment point ( C ) and its hash ( H(C) ).
Verification
The verify function checks the validity of a commitment. It recomputes the commitment hash from the commitment point and compares it to the stored commitment hash:
![]()
Where ( C' ) is the commitment point being verified. If the recomputed hash ( H(C') ) matches the original hash, the commitment is valid.
Mathematical Foundations
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) for Matrix Multiplication
The commitment generation relies heavily on FFT-based matrix multiplication. Given two matrices ( A ) and ( B ), the rows of these matrices are transformed into frequency space using FFT. The transformation is given by:
![]()
Where ( \mathcal{F} ) represents the FFT transformation.
The matrix multiplication in frequency space is done by element-wise multiplication of the FFT results, which is computationally more efficient than directly multiplying the matrices in the time domain.
BlueHash Algorithm
The BlueHash algorithm is used for hashing the commitment point to generate the final commitment hash. It applies multiple rounds of hashing to increase the entropy and randomness of the hash.
![]()
Where ( H(C) ) is the final hash after 3 rounds of the BlueHash algorithm.
Code Structure
The project consists of three main modules:
- fft: Implements FFT-based matrix multiplication for commitment generation.
- Functions:
fft_matrix_multiply
- Functions:
- utils: Contains utility functions for random number generation, matrix creation, and BlueHash-based hashing.
- Functions:
get_optimal_thread_count,hash_to_commitment,generate_params
- Functions:
- commitment: Implements the commitment structure and the core
commitandverifyfunctions.- Functions:
commit,verify,RevelerCommit
- Functions:
Example Code
fn main() {
let (a, b) = generate_params();
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
let m: Vec<u64> = (0..N).map(|_| rng.gen_range(0..Q)).collect();
let r: Vec<u64> = (0..N).map(|_| rng.gen_range(0..Q)).collect();
let commitment = commit(&a, &b, &m, &r);
println!("Commitment: {:?}", commitment);
let is_valid = verify(&commitment);
println!("Is commitment valid? {}", is_valid);
}
Donations
 |
 |
 |
|---|
Dependencies
~11–21MB
~303K SLoC