11 releases (2 stable)
| 1.0.1 | Dec 14, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 1.0.0 | Nov 14, 2024 |
| 0.41.0 | Nov 3, 2024 |
| 0.40.0 | Sep 1, 2024 |
| 0.37.0 | Jul 31, 2024 |
#1471 in Development tools
Used in nmd
4MB
9K
SLoC

NMD core
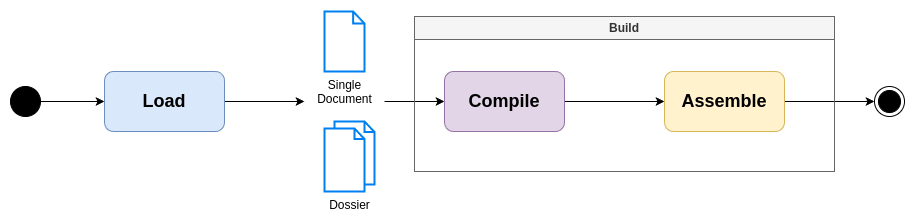
nmd-core is the core of NMD. It can be used to load and build NMD files or dossier.
If you want know more about NMD, please, you should open this link.
To get start add nmd-core to your project:
cargo add nmd-core
Documentation
Quick start
let dossier_path = PathBuf::from(".");
let codex = Codex::of_html();
let loader_configuration = LoadConfiguration::default();
let dossier = Dossier::load_dossier_from_path_buf(&dossier_path, &codex, &loader_configuration, LoadConfigurationOverLay::default()).unwrap();
let compilation_configuration = CompilationConfiguration::default();
let compiled_dossier = dossier.compile(&OutputFormat::Html, &codex, &compilation_configuration, CompilationConfigurationOverLay::default()).unwrap();
Codex
Codex contains rules to load and compile all NMD components (Dossier, Document, CompilableText, ...).
Tricky algorithms
There are two tricky algorithms in core:
- Load of
LoadBlock - Compilation of
CompilableText
Load of LoadBlock
A string raw content is segmented recursively using one-by-one all paragraph modifiers.
After tried all paragraph modifiers, unmatched segments are processed first as headers, then using fallback paragraph loading rules.
Each slice of original raw content is inserted in an independent LoadBlock, set of all blocks are used to compose documents.
Compilation of CompilableText
CompilableText (CT) can be considered as the compilable text unit in NMD. It performs low level compilation of strings using text rules inserted in Codex
CT is composed by an ordered list of parts where each part (CompilableTextPart) can be:
- Fixed if no rules can be applied on it
- Mutable if rules can act on it
In addiction, each part has a bucket (i.e. a set) of incompatible modifiers, i.e. modifiers which must not be applied on part.
Generally, CT can work starting from a random list of parts.
Suppose you have a NMD string (String or &str). It is loaded in CT through from method:
let nmd_string = "...";
let ct = CompilableText::from(nmd_string);
Internally, it is converted in a (single) mutable part:
impl From<&str> for CompilableText {
fn from(value: &str) -> Self {
Self::from(CompilableTextPart::new_compilable(
value.to_string(),
ModifiersBucket::None
))
}
}
When you run compilation on CT, every text rules are applied in order (specified in Codex) over whole parts list.
We must notice that each rule can be applied only over the mutable parts of CT. Mutable parts can be split to another by fixed parts (this is tricky!).
First of all, string of mutable parts is created to perform regex search on it.
This string composed by mutable parts is called compilable_content and for each mutable part which composes it is saved the position in compilable_content where each mutable part ends.
Then, regex search is performed over compilable_content
There are 2 while loops. The outer loop iterates over parts indices (considering all parts, even fixed parts). This loop is used to elaborate every parts considering the current match.
The inner loop still iterates over paters indices (considering all parts, even fixed parts) and it is used to find parts which are related to current match.
We must notice that a regex match can start from the middle of a mutable part. In particular for each match can be happen:
- Match is contained in a single mutable part
- Match starts in the middle of a mutable part and terminates in the middle of another mutable parts, but between these two mutable parts can be a set of fixed and other mutable parts!
In case 2, parts which "are split" by match are handled as following:
- If part is a mutable part and match start position is greater than part start, then the first part of mutable part is untouched, while the second part must be stored
- If part is a mutable part, match start is less than part start and match end is greater than part end, then the whole mutable part must be stored
- If part is a fixed part, it is stored
- If part is a mutable part and match end is greater than part end, then the first part is stored, the second is untouched
Stored parts are passed to current text rule to be processed. Rule returns list of parts, which are placed in replace of the stored part.
When a match is fully handled, algorithm passes to next match and repeat until every parts are seen (for current rules).
When every text rules are tested algorithm ends.
Important
Algorithm is "strange", it has 2 while, but it is $\approx O(n)$ because both loops iterate over the same parts vector.
NMD Syntax
Warning
NMD syntax is working in progress yet, you can contribute following contribution guidelines!
Develop
Develop check list
Known issues
- Paragraphs and text are not parsed in tables
- Nested text modifiers could be compiled wrongly (e.g.
*this is a **phrase** with some bold*.) - List with empty lines between two items
- Missed
tabas modifier - Missed style for simples quotes
- Text between two list items
Author
Nicola Ricciardi
Contributing
If you would like to contribute to the development of the NMD compiler, please follow contribution guidelines.
License
This project is licensed under the GNU General Public License v3.0 - see the LICENSE file for details.
Dependencies
~13–31MB
~419K SLoC