13 releases
| 0.10.0 | Mar 11, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 0.9.0 | May 9, 2022 |
| 0.8.6 | Feb 27, 2022 |
| 0.8.2 | Oct 5, 2021 |
| 0.1.1 | Mar 12, 2020 |
#194 in Science
42 downloads per month
94KB
1.5K
SLoC
nanoq 
Ultra-fast quality control and summary reports for nanopore reads
Overview
v0.10.0
Purpose
Nanoq implements ultra-fast read filters and summary reports for high-throughput nanopore reads.
Citation
We would appreciate a citation if you are using nanoq for research. Please see here for some suggestions how you could give back to the community if you are using nanoq for industry applications 🙏
Steinig and Coin (2022). Nanoq: ultra-fast quality control for nanopore reads. Journal of Open Source Software, 7(69), 2991, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02991
Performance
Nanoq is as fast as seqtk-fqchk for summary statistics of small datasets (e.g. Zymo - 100,000 reads) and slightly faster on large datasets (e.g. Zymo - 3.5 million reads, 1.3x - 1.5x). In fast mode (no quality scores), nanoq is ~2-3x faster than rust-bio-tools and seqkit stats for summary statistics and other commonly used read summary or filtering methods (up to 297x-442x). Memory consumption is consistent and tends to be lower than other tools (~5-10x).
Tests
Nanoq comes with high test coverage for your peace of mind.
cargo test
Install
Cargo
cargo install nanoq
Conda
Explicit version (for some reason defaults to old version)
conda install -c conda-forge -c bioconda nanoq=0.10.0
Binaries
Precompiled binaries for Linux and MacOS are attached to the latest release.
VERSION=0.10.0
RELEASE=nanoq-${VERSION}-x86_64-unknown-linux-musl.tar.gz
wget https://github.com/esteinig/nanoq/releases/download/${VERSION}/${RELEASE}
tar xf nanoq-${VERSION}-x86_64-unknown-linux-musl.tar.gz
nanoq-${VERSION}-x86_64-unknown-linux-musl/nanoq -h
Usage
Nanoq accepts a file (-i) or stream (stdin) of reads in fast{a,q}.{gz,bz2,xz} format and outputs reads to file (-o) or stream (stdout).
nanoq -i test.fq.gz -o reads.fq
cat test.fq.gz | nanoq > reads.fq
Read filters
Reads can be filtered by minimum read length (-l), maximum read length (-m), minimum average read quality (-q) or maximum average read quality (-w).
nanoq -i test.fq -l 1000 -m 10000 -q 10 -w 15 > reads.fq
Read trimming
A fixed number of bases can be trimmed from the start (-S) or end (-E) of reads:
nanoq -i test.fq -S 100 -E 100 > reads.fq
Read report
Read summaries are produced when using the stats flag (-s, report to stdout, no read output to stdout) or when specifying a report file (-r):
nanoq -i test.fq -s
nanoq -i test.fq -r report.txt > reads.fq
For report types and configuration see the output section.
Fast mode
⚠️ When using fast mode
-fread quality scores are not computed (output of quality fields:NaN)
Read qualities may be excluded from filters and statistics to speed up read iteration (-f).
nanoq -i test.fq.gz -f -s
Compression
Output compression is inferred from file extensions (gz, bz2, lzma).
nanoq -i test.fq -o reads.fq.gz
Output compression can be specified manually with -O and -c.
nanoq -i test.fq -O g -c 9 -o reads.fq.gz
Online runs
Nanoq can be used to check on active sequencing runs and barcoded samples.
find /data/nanopore/run -name "*.fastq" -print0 | xargs -0 cat | nanoq -s
for i in {01..12}; do
find /data/nanopore/run -name barcode${i}.fastq -print0 | xargs -0 cat | nanoq -s
done
Parameters
nanoq 0.10.0
Filters and summary reports for nanopore reads
USAGE:
nanoq [FLAGS] [OPTIONS]
FLAGS:
-f, --fast Ignore quality values if present
-h, --help Prints help information
-H, --header Header for summary output
-j, --json Summary report in JSON format
-s, --stats Summary report only [stdout]
-V, --version Prints version information
-v, --verbose Verbose output statistics [multiple, up to -vvv]
OPTIONS:
-c, --compress-level <1-9> Compression level to use if compressing output [default: 6]
-i, --input <input> Fast{a,q}.{gz,xz,bz}, stdin if not present
-m, --max-len <INT> Maximum read length filter (bp) [default: 0]
-w, --max-qual <FLOAT> Maximum average read quality filter (Q) [default: 0]
-l, --min-len <INT> Minimum read length filter (bp) [default: 0]
-q, --min-qual <FLOAT> Minimum average read quality filter (Q) [default: 0]
-o, --output <output> Output filepath, stdout if not present
-O, --output-type <u|b|g|l> u: uncompressed; b: Bzip2; g: Gzip; l: Lzma
-r, --report <FILE> Summary read statistics report output file
-t, --top <INT> Number of top reads in verbose summary [default: 5]
-L, --read-lengths <FILE> Output read lengths of surviving reads to file
-Q, --read-qualities <FILE> Output read qualities of surviving reads to file
-S, --trim-start <INT> Trim bases from the start of each read [default: 0]
-E, --trim-end <INT> Trim bases from the end of each read [default: 0]
Output
Read lengths and qualities
Files with read lengths (--read-lengths/-L) and qualities (--read-qualities/-Q) of the surviving reads can be output:
nanoq -i test.fq -Q rq.txt -L rl.txt > reads.fq
Summary reports
Summary reports are output to file explicitly using --report/-r:
nanoq -i test.fq -r report.txt > reads.fq
nanoq -i test.fq -r report.txt -s
When using the --stats/-s flag read output is suppressed and summary is directed to stdout:
nanoq -i test.fq -s > report.txt
Report format is minimal by default:
100000 400398234 5154 44888 5 4003 3256 8.90 9.49
- number of reads
- number of base pairs
- N50 read length
- longest read
- shorted reads
- mean read length
- median read length
- mean read quality
- median read quality
A machine readable header can be added using the -H flag:
nanoq -i test.fq -s -H
Extended summaries analogous to NanoStat can be obtained using multiple -v flags (up to -vvv), including the top (-t) read lengths and qualities:
-v- verbose read summary (top block as below)-vv- like-vwith read length and/or quality thresholds-vvv- like-vvwith top ranking read lengths and/or qualities
nanoq -i test.fq -f -s -t 5 -vvv
Nanoq Read Summary
====================
Number of reads: 100000
Number of bases: 400398234
N50 read length: 5154
Longest read: 44888
Shortest read: 5
Mean read length: 4003
Median read length: 3256
Mean read quality: NaN
Median read quality: NaN
Read length thresholds (bp)
> 200 99104 99.1%
> 500 96406 96.4%
> 1000 90837 90.8%
> 2000 73579 73.6%
> 5000 25515 25.5%
> 10000 4987 05.0%
> 30000 47 00.0%
> 50000 0 00.0%
> 100000 0 00.0%
> 1000000 0 00.0%
Top ranking read lengths (bp)
1. 44888
2. 40044
3. 37441
4. 36543
5. 35630
JSON formatted extended output (equivalent to -vvv) can be output to --report (-r) or stdout (-s) using the --json/-j flag:
nanoq -i test.fq --json -f -r report.json > reads.fq
nanoq -i test.fq --json -f -s > report.json
{
"reads": 100000,
"bases": 400398234,
"n50": 5154,
"longest": 44888,
"shortest": 5,
"mean_length": 4003,
"median_length": 3256,
"mean_quality": null,
"median_quality": null,
"length_thresholds": {
"200": 99104,
"500": 96406,
"1000": 90837,
"2000": 73579,
"5000": 25515,
"10000": 4987,
"30000": 47,
"50000": 0,
"100000": 0,
"1000000": 0
},
"quality_thresholds": {
"5": 0,
"7": 0,
"10": 0,
"12": 0,
"15": 0,
"20": 0,
"25": 0,
"30": 0
},
"top_lengths": [
44888, 40044, 37441, 36543, 35630
],
"top_qualities": []
}
Note that in this example no read qualities are computed; quality thresholds are therefore all zero.
Benchmarks
Benchmarks evaluate processing speed and memory consumption of a basic read length filter and summary statistics on the even Zymo mock community (GridION) with comparisons to rust-bio-tools, seqtk fqchk, seqkit stats, NanoFilt, NanoStat and Filtlong. Time to completion and maximum memory consumption were measured using /usr/bin/time -f "%e %M", speedup is relative to the slowest command in the set. We note that summary statistics from rust-bio-tools and seqkit stats do not compute read quality scores and are therefore comparable to nanoq-fast.
Tasks:
stats: basic read set summariesfilter: minimum read length filter (into/dev/null)
Tools:
rust-bio-tools 0.28.0nanostat 1.5.0nanofilt 2.8.0filtlong 0.2.1seqtk 1.3-r126seqkit 2.0.0nanoq 0.8.2
Commands used for stats task:
nanostat(fq + fq.gz) -->NanoStat --fastq test.fq --threads 1rust-bio(fq) -->rbt sequence-stats --fastq < test.fqrust-bio(fq.gz) -->zcat test.fq.gz | rbt sequence-stats --fastqseqtk-fqchk(fq + fq.gz) -->seqtk fqchkseqkit stats(fq + fq.gz) -->seqkit stats -j1nanoq(fq + fq.gz) -->nanoq --input test.fq --statsnanoq-fast(fq + fq.gz) -->nanoq --input test.fq --stats --fast
Commands used for filter task:
filtlong(fq + fq.gz) -->filtlong --min_length 5000 test.fq > /dev/nullnanofilt(fq) -->NanoFilt --fastq test.fq --length 5000 > /dev/nullnanofilt(fq.gz) -->gunzip -c test.fq.gz | NanoFilt --length 5000 > /dev/nullnanoq(fq + fq.gz) -->nanoq --input test.fq --min-len 5000 > /dev/nullnanoq-fast(fq + fq.gz) -->nanoq --input test.fq --min-len 5000 --fast > /dev/null
Files:
zymo.fq: uncompressed (100,000 reads, ~400 Mbp)zymo.fq.gz: compressed (100,000 reads, ~400 Mbp)zymo.full.fq: uncompressed (3,491,078 reads, ~14 Gbp)
Data preparation:
wget "https://nanopore.s3.climb.ac.uk/Zymo-GridION-EVEN-BB-SN.fq.gz"
zcat Zymo-GridION-EVEN-BB-SN.fq.gz > zymo.full.fq
head -400000 zymo.full.fq > zymo.fq && gzip -k zymo.fq
Elapsed real time and maximum resident set size:
/usr/bin/time -f "%e %M"
Task and command execution:
Commands were run in replicates of 10 with a mounted benchmark data volume in the provided Docker container. An additional cold start iteration for each command was not considered in the final benchmarks.
for i in {1..11}; do
for f in /data/*.fq; do
/usr/bin/time -f "%e %M" nanoq -f- s -i $f 2> benchmark
tail -1 benchmark >> nanoq_stat_fq
done
done
Benchmark results
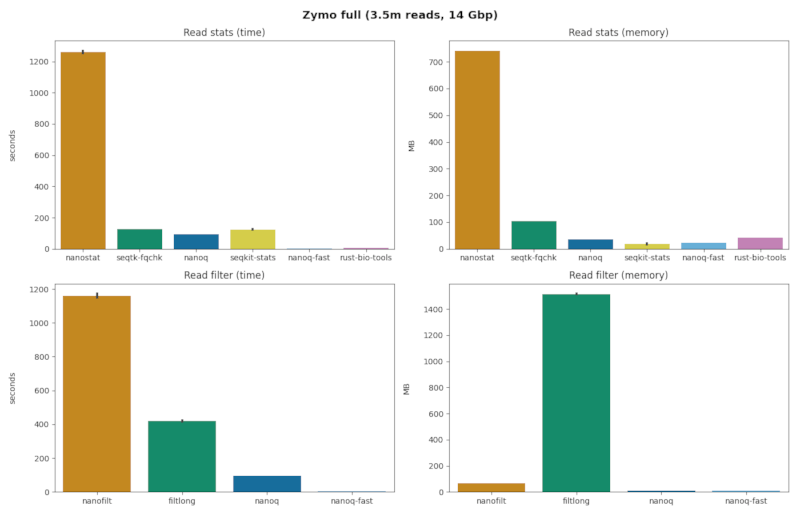
stats + zymo.full.fq
| command | mb (sd) | sec (sd) | reads / sec | speedup | quality scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nanostat | 741.4 (0.09) | 1260. (13.9) | 2,770 | 01.00 x | true |
| seqtk-fqchk | 103.8 (0.04) | 125.9 (0.15) | 27,729 | 10.01 x | true |
| seqkit-stats | 18.68 (3.15) | 125.3 (0.91) | 27,861 | 10.05 x | false |
| nanoq | 35.83 (0.06) | 94.51 (0.43) | 36,938 | 13.34 x | true |
| rust-bio | 43.20 (0.08) | 06.54 (0.05) | 533,803 | 192.7 x | false |
| nanoq-fast | 22.18 (0.07) | 02.85 (0.02) | 1,224,939 | 442.1 x | false |
filter + zymo.full.fq
| command | mb (sd) | sec (sd) | reads / sec | speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nanofilt | 67.47 (0.13) | 1160. (20.2) | 3,009 | 01.00 x |
| filtlong | 1516. (5.98) | 420.6 (4.53) | 8,360 | 02.78 x |
| nanoq | 11.93 (0.06) | 94.93 (0.45) | 36,775 | 12.22 x |
| nanoq-fast | 08.05 (0.05) | 03.90 (0.30) | 895,148 | 297.5 x |
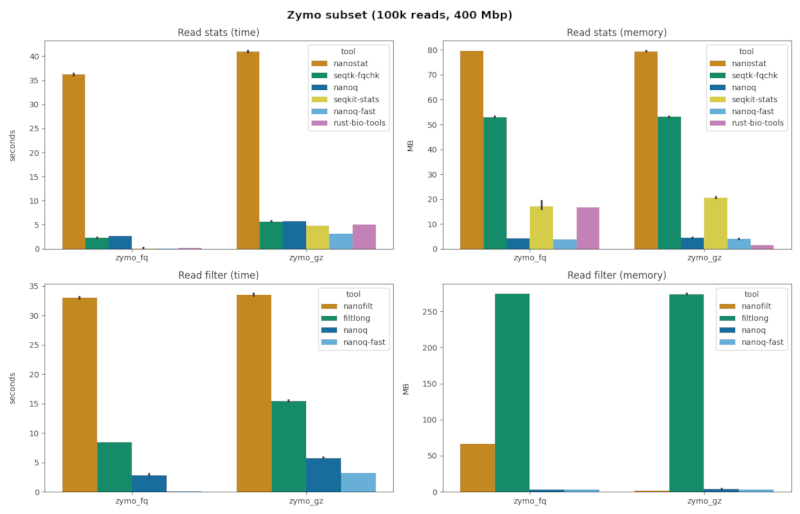
stats + zymo.fq
| command | mb (sd) | sec (sd) | reads / sec | speedup | quality scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nanostat | 79.64 (0.14) | 36.22 (0.27) | 2,760 | 01.00 x | true |
| nanoq | 04.26 (0.09) | 02.69 (0.02) | 37,147 | 13.46 x | true |
| seqtk-fqchk | 53.01 (0.05) | 02.28 (0.06) | 43,859 | 15.89 x | true |
| seqkit-stats | 17.07 (3.03) | 00.13 (0.00) | 100,000 | 36.23 x | false |
| rust-bio | 16.61 (0.08) | 00.22 (0.00) | 100,000 | 36.23 x | false |
| nanoq-fast | 03.81 (0.05) | 00.08 (0.00) | 100,000 | 36.23 x | false |
stats + zymo.fq.gz
| command | mb (sd) | sec (sd) | reads / sec | speedup | quality scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nanostat | 79.46 (0.22) | 40.98 (0.31) | 2,440 | 01.00 x | true |
| nanoq | 04.44 (0.09) | 05.74 (0.04) | 17,421 | 07.14 x | true |
| seqtk-fqchk | 53.11 (0.05) | 05.70 (0.08) | 17,543 | 07.18 x | true |
| rust-bio | 01.59 (0.06) | 05.06 (0.04) | 19,762 | 08.09 x | false |
| seqkit-stats | 20.54 (0.41) | 04.85 (0.02) | 20,619 | 08.45 x | false |
| nanoq-fast | 03.95 (0.07) | 03.15 (0.02) | 31,746 | 13.01 x | false |
filter + zymo.fq
| command | mb (sd) | sec (sd) | reads / sec | speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nanofilt | 66.29 (0.15) | 33.01 (0.24) | 3,029 | 01.00 x |
| filtlong | 274.5 (0.04) | 08.49 (0.01) | 11,778 | 03.89 x |
| nanoq | 03.61 (0.04) | 02.81 (0.28) | 35,587 | 11.75 x |
| nanoq-fast | 03.26 (0.06) | 00.12 (0.01) | 100,000 | 33.01 x |
filter + zymo.fq.gz
| command | mb (sd) | sec (sd) | reads / sec | speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nanofilt | 01.57 (0.07) | 33.48 (0.35) | 2,986 | 01.00 x |
| filtlong | 274.2 (0.04) | 16.45 (0.09) | 6,079 | 02.04 x |
| nanoq | 03.68 (0.06) | 05.77 (0.04) | 17,331 | 05.80 x |
| nanoq-fast | 03.45 (0.07) | 03.20 (0.02) | 31,250 | 10.47 x |
Dependencies
Nanoq uses needletail for read operations and niffler for output compression.
Etymology
Avoided name collision with nanoqc and dropped the c to arrive at nanoq [nanɔq] which coincidentally means 'polar bear' in Native American (Eskimo-Aleut, Greenlandic). If you find nanoq useful for your work consider a small donation to the Polar Bear Fund, RAVEN or Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami
Contributions
We welcome any and all suggestions or pull requests. Please feel free to open an issue in the repository on GitHub.
Dependencies
~8MB
~132K SLoC