5 releases
| 0.1.4 | Nov 2, 2022 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.3 | Sep 28, 2022 |
| 0.1.2 | Sep 25, 2022 |
| 0.1.1 | Sep 23, 2022 |
| 0.1.0 | Sep 19, 2022 |
#422 in Programming languages
110KB
2K
SLoC
Mate is a library for parsing and calculating arithmetic expressions inputted as &str(string). Uses Lexer(similar to interpreted-programming languages' lexer) structure to parse string input in to token list, and Calculator structure to calculate final result from token list. Implements also a general wrapper structure that implements Lexer and Calculator inside of it. And makes it easy to calculate arithmetic expression's result directly without dealing with parsing and calculating manually.
Usage
This crate is on crates.io and can be used by adding mate-rs to your dependencies in your project's Cargo.toml.
[dependencies]
mate-rs = "0.1.4"
Example: with Mate
Mate is general wrapper structure for Lexer and Calculator.
has only one method that used to calculate result via string(&str) input.
use mate_rs::mate::Mate;
let result = Mate::calculate("6 * 7");
match result {
Ok(v) => assert_eq!(v, 42.0),
Err(_) => {
// Do something ...
}
};
Example: with Lexer and Calculator
Lexer is the main structure that parses string-input to token-list.
Calculator is the structure that used to calculate final result via Lexer's result.
use mate_rs::{calculator::Calculator, lexer::Lexer};
// Generated tokens gonna be something like:
// |
// | Token(
// | type: SUBEXP,
// | tokens: [
// | Token(
// | type: SUBEXP,
// | tokens: [
// | Token(type: NUMBER, literal: "2")
// | Token(type: PLUS, literal: "+")
// | Token(type: NUMBER, literal: "5")
// | ],
// | ),
// | Token(type: PRODUCT, literal: "*"),
// | Token(
// | type: SUBEXP,
// | tokens: [
// | Token(type: NUMBER, literal: "5")
// | Token(type: MINUS, literal: "-")
// | Token(type: NUMBER, literal: "9")
// | Token(type: PLUS, literal: "+")
// | Token(
// | type: SUBEXP,
// | tokens: [
// | Token(type: NUMBER, literal: "8")
// | Token(type: PLUS, literal: "-")
// | Token(type: NUMBER, literal: "5")
// | ],
// | ),
// | ],
// | ),
// | ],
// | ),
// | Token(type: PLUS, literal: "+")
// | Token(type: NUMBER, literal: "35")
// |
let input = "[ (2 + 5) * (5 - 9 + (8 - 5)) ] + 35";
let tokens = Lexer::lex(input.clone()).unwrap(); // should handle error case also
// Result will be calculated from tokens, by X/O/Y algorithm.
//
// ╭────────╮ ╭───────────╮ ╭────────╮
// │ NUMBER │ │ OPERATION │ │ NUMBER │
// ╰────────╯ ╰───────────╯ ╰────────╯
// ╰───╮ │ ╭───╯
// ▼ ▼ ▼
// X [+, -, *, /] Y
//
let result = Calculator::calculate(tokens, input.clone());
How it works
Mate is all about two main structures, [Lexer] and [Calculator]. [Lexer] is the structure that takes care of parsing interpretting given string expression, and [Calculator] is the structure that takes care of calculating final result via parsed tokens.
Lexer
Loops through the given input string, reads and converts each character to an [Token] structure. We've several types of main tokens and they are:
ILLEGAL- illegal character.NUMBER- number type.MINUS,PLUS,PRODUCT,DIVIDE,PERCENTAGE,POWER- operations.LPAREN,RPAREN- parentheses.LABS,LPAREN- absolute values.SUBEXP- sub expression, expressions inside of parentheses, abs, or combinations of division and multiplication.
Lexer's lex functionality converts each character to one of these tokens.
It combines multiplication or division operation related tokens into one sub-expression to keep the operation-priority right.
And nests the parentheses, absolute values and powers with a custom level-to-expression algorithm.
level-to-expression algorithm is mapping algorithm that maps concrete expression to it's nesting level.
For example if the given token list is -> (2 + 5) : (5 - 9 / (8 - 5)).
Generated result will be:

By doing that we make it easy to keep the operation-priority safe.
Calculator
Calculator takes the parsed token-list and calculates final result of it.
Uses custom X/O/Y algorithm a.k.a X/OPERATION/Y where X and Y are numbers, and O is operation.
If cannot get the X or Y takes them as zero.
╭────────╮ ╭───────────╮ ╭────────╮
│ NUMBER │ │ OPERATION │ │ NUMBER │
╰────────╯ ╰───────────╯ ╰────────╯
╰───╮ │ ╭───╯
▼ ▼ ▼
X [+, -, *, /] Y
Syntax
The syntaxt of Mate kept as easy and basic as possible. It's just plain-text mathematics syntaxt with few customizations. Let's see some examples:
Plus and Minus
2 + 5 and 2 - 5 are valid syntaxts. (in x <operation> y where x and y could be NUMBER or SUBEXP).
Multiplication, Division and Percentage
4 * 2, 4 / 2, and 4 % 2 are valid syntaxts. (in x <operation> y where x and y could be NUMBER or SUBEXP).
Also 4(10 / 2) or 4(2) is valid syntax in case of multiplication.
Power
4 ^ 2 is valid syntaxt. (in x <operation> y where x and y could be NUMBER or SUBEXP).
Also continues powers are accepted: 4 ^ 2 ^ 3 which gonna be automatically turned into 4 ^ (2 ^ 3).
Parentheses
(2 * 5) is valid syntaxt. (in x <operation> y where x and y could be NUMBER or SUBEXP).
And, nested parentheses expressions are accepted: (2 * ((5 * 2) / (9 - 5))).
Absolute-Values
[2 - 12] is valid syntaxt. (in x <operation> y where x and y could be NUMBER or SUBEXP).
And, nested absolute-value expressions are accepted: [7 - 14] * [5 - 9 / [5 - 3]].
Errors
We do not need to say anything about errors, here is some of them:
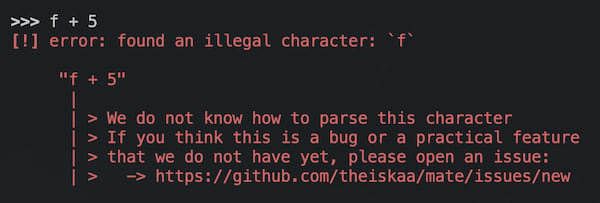
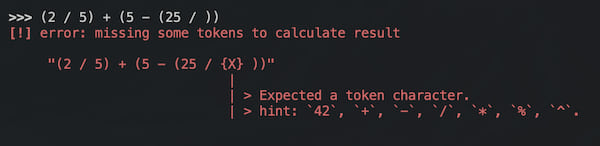
Dependencies
~2.2–3MB
~54K SLoC
