5 stable releases
| new 1.3.0 | May 13, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 1.2.1 | Apr 15, 2025 |
| 1.2.0 | Apr 3, 2025 |
| 1.1.0 | Dec 4, 2024 |
| 1.0.0 | Nov 19, 2024 |
#1830 in Command line utilities
156 downloads per month
415KB
3K
SLoC
daikoku
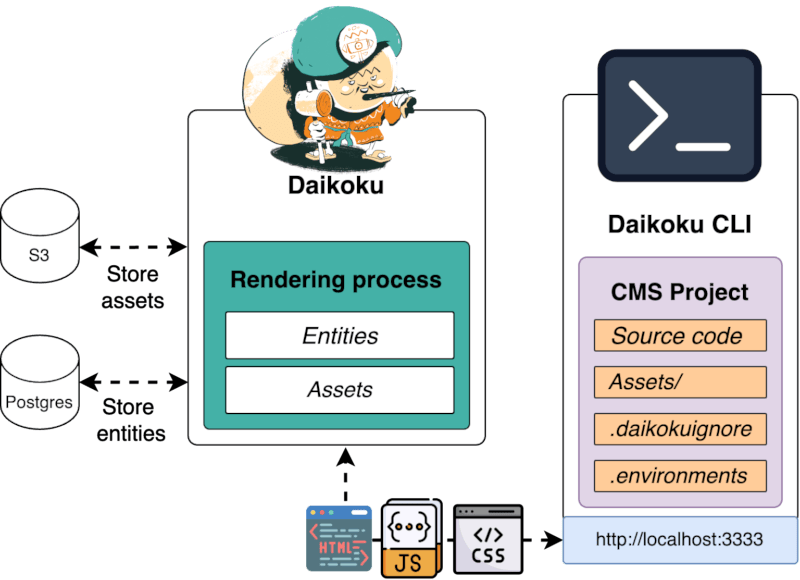
Reference Documentation
The reference documentation is available at https://maif.github.io/daikoku/docs/cli
Dependencies
~31–53MB
~885K SLoC