4 releases
| 0.1.3 | May 5, 2020 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.2 | Sep 24, 2019 |
| 0.1.1 | Sep 18, 2019 |
| 0.1.0 | Sep 18, 2019 |
#104 in Profiling
15,239 downloads per month
Used in 7 crates
(5 directly)
22KB
161 lines
coz-rs
Rust support for the coz Causal Profiler
Usage
First, follow the instructions in coz to install the coz command.
Next, coz is a profiler that, for the best results, typically requires
source-level modifications of your code. To do this first add this to your
Cargo.toml
[dependencies]
coz = "0.1"
Then you'll want to either add throughput or latency tracepoints. More information on this can be found upstream. If you have something you'd wish would execute more often, you can add:
fn main() {
loop {
// ...
// For example you wish this `loop` executed more iterations
coz::progress!(); // equivalent of `COZ_PROGRESS`
}
}
Note that coz::progress!("name") is the equivalent of COZ_PROGRESS_NAMED as
well.
If you'd like to profile the latency of an operation you can instead use:
// Boy I wish this function executed more quickly...
fn foo() {
coz::begin!("foo");
// ...
coz::end!("foo");
}
After you've instrumented your code, you need to also ensure that you're
compiling with DWARF debug information. To do this you'll want to configure
Cargo.toml again:
[profile.release]
debug = 1
Next up you'll build your application with cargo build --release, and then
finally you can run it with coz run --- ./target/release/$your_binary.
Caveats
Known caveats so far to generate a report that collects information are:
-
Rust programs by default segfault when run with
cozwith an issue related to plasma-umass/coz#110. Rust programs set up asigaltstackto run segfault handlers to print "you ran out of stack", but this alternate stack is too small to run theSIGPROFhandler thatcozinstalls. To handle this this crate provides acoz::thread_init()function which will increase thesigaltstacksize that Rust installs by default to something large enough to runcoz. If you see segfaults, or corrupt reports, you may wish to manually callcoz::thread_init()instead of waiting for this crate to automatically call it for you. -
Debug information looks to be critical to get a report from
coz. Make sure that your program is compiled with at least line-table information (debug = 1) to ensure you get the best experience usingcoz. -
Currently
cozonly works on Linux, and while this crate should compile on all platforms it only actually does something on Linux.
Examples
You can find an example toy program at examples/toy.rs in this repository, and
we can execute it with coz:
$ cargo build --release
$ coz run --- ./target/release/examples/toy
...
[profiler.cpp:75] Starting profiler thread
$
That should generate profile.coz in the current directory, which if you plot
that should look something like this:
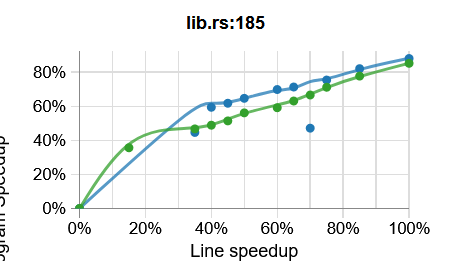
Note that I'm still learning myself the best sorts of applications to run on as
well as the best sorts of questions to ask coz and where to put
latency/throughput points. If you've got ideas or good examples, please feel
free to add them here!
Dependencies
~90KB