2 unstable releases
| 0.3.0 | Jun 7, 2021 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.0 | Mar 25, 2021 |
#2506 in Cryptography
361 downloads per month
Used in 14 crates
(8 directly)
120KB
2K
SLoC
Marlin
marlin is a Rust library that implements a
preprocessing zkSNARK for R1CS
with
universal and updatable SRS
This library was initially developed as part of the Marlin paper, and is released under the MIT License and the Apache v2 License (see License).
WARNING: This is an academic prototype, and in particular has not received careful code review. This implementation is NOT ready for production use.
Overview
A zkSNARK with preprocessing achieves succinct verification for arbitrary computations, as opposed to only for structured computations. Informally, in an offline phase, one can preprocess the desired computation to produce a short summary of it; subsequently, in an online phase, this summary can be used to check any number of arguments relative to this computation.
The preprocessing zkSNARKs in this library rely on a structured reference string (SRS), which contains system parameters required by the argument system to produce/validate arguments. The SRS in this library is universal, which means that it supports (deterministically) preprocessing any computation up to a given size bound. The SRS is also updatable, which means that anyone can contribute a fresh share of randomness to it, which facilitates deployments in the real world.
The construction in this library follows the methodology introduced in the Marlin paper, which obtains preprocessing zkSNARKs with universal and updatable SRS by combining two ingredients:
- an algebraic holographic proof
- a polynomial commitment scheme
The first ingredient is provided as part of this library, and is an efficient algebraic holographic proof for R1CS (a generalization of arithmetic circuit satisfiability supported by many argument systems). The second ingredient is imported from poly-commit. See below for evaluation details.
Build guide
The library compiles on the stable toolchain of the Rust compiler. To install the latest version of Rust, first install rustup by following the instructions here, or via your platform's package manager. Once rustup is installed, install the Rust toolchain by invoking:
rustup install stable
After that, use cargo (the standard Rust build tool) to build the library:
git clone https://github.com/arkworks-rs/marlin.git
cd marlin
cargo build --release
This library comes with some unit and integration tests. Run these tests with:
cargo test
Lastly, this library is instrumented with profiling infrastructure that prints detailed traces of execution time. To enable this, compile with cargo build --features print-trace.
Benchmarks
All benchmarks below are performed over the BLS12-381 curve implemented in the ark-bls12-381 library, with the asm feature activated. Benchmarks were run on a machine with an Intel Xeon 6136 CPU running at 3.0 GHz.
Running time compared to Groth16
The graphs below compare the running time, in single-thread execution, of Marlin's indexer, prover, and verifier algorithms with the corresponding algorithms of Groth16 (the state of the art in preprocessing zkSNARKs for R1CS with circuit-specific SRS) as implemented in groth16. We evaluate Marlin's algorithms when instantiated with the PC scheme from [CHMMVW20] (denoted "M-AHP w/ PC of [CHMMVW20]"), and the PC scheme from [MBKM19] (denoted "M-AHP w/ PC of [MBKM19]").
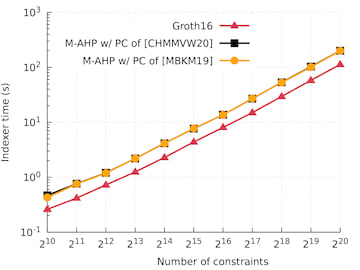
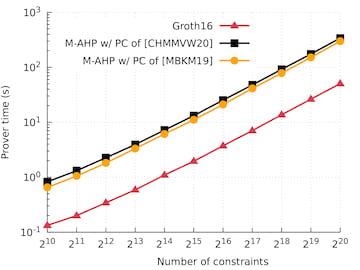
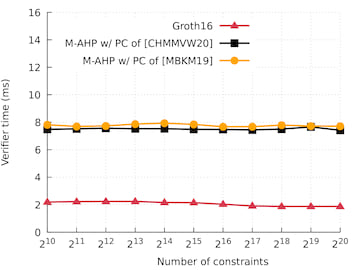
Multi-threaded performance
The following graphs compare the running time of Marlin's prover when instantiated with the PC scheme from [CHMMVW20] (left) and the PC scheme from [MBKM19] (right) when executed with a different number of threads.
![Multi-threaded scaling of Marlin AHP with the PC scheme from [CHMMVW20]](https://img.gs/czjpqfbdkz/360/https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/3220730/82859700-51bbca80-9ecc-11ea-9fe1-53a611693dd1.png)
![Multi-threaded scaling of Marlin AHP with the PC scheme from [MBKM19]](https://img.gs/czjpqfbdkz/360/https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/3220730/82859698-51233400-9ecc-11ea-8a32-37379116e828.png)
Proof size
We compare the proof size of Marlin with that of Groth16. We instantiate the Marlin SNARK with the PC scheme from [CHMMVW20], and the PC scheme from [MBKM19].
| Scheme | Proof size in bytes |
|---|---|
| Marlin AHP with PC of [CHMMVW20] | 880 |
| Marlin AHP with PC of [MBKM19] | 784 |
| [Groth16] | 192 |
License
This library is licensed under either of the following licenses, at your discretion.
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution that you submit to this library shall be dual licensed as above (as defined in the Apache v2 License), without any additional terms or conditions.
Reference paper
Marlin: Preprocessing zkSNARKs with Universal and Updatable SRS
Alessandro Chiesa, Yuncong Hu, Mary Maller, Pratyush Mishra, Psi Vesely, Nicholas Ward
EUROCRYPT 2020
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by: an Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council grant; a Google Faculty Award; the RISELab at UC Berkeley; and donations from the Ethereum Foundation and the Interchain Foundation.
Dependencies
~6–14MB
~182K SLoC