28 releases (14 breaking)
| 0.23.5 | Sep 8, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.23.3 | Aug 27, 2024 |
| 0.19.3 | Jul 30, 2024 |
#92 in Biology
475KB
8K
SLoC
Spiking Neural Networks
spiking_neural_networks is a package focused on designing neuron models
with neurotransmission and calculating dynamics between neurons over time.
Neuronal dynamics are made using traits so they can be expanded via the
type system to add new dynamics for different neurotransmitters, receptors
or neuron models. Currently implements system for spike trains, spike time depedent
plasticity, basic attractors, reward modulated dynamics,
and dynamics for neurons connected in a lattice.
See below for examples and how to add custom models.
Quick Examples
Morris-Lecar Model with Static Input
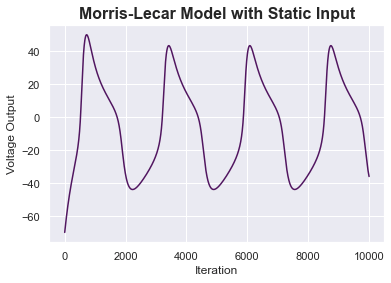
Coupled Izhikevich Neurons
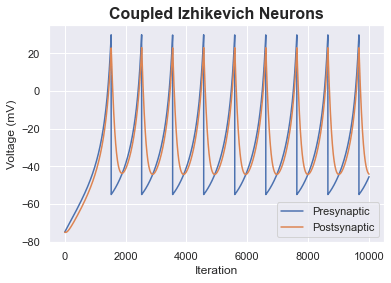
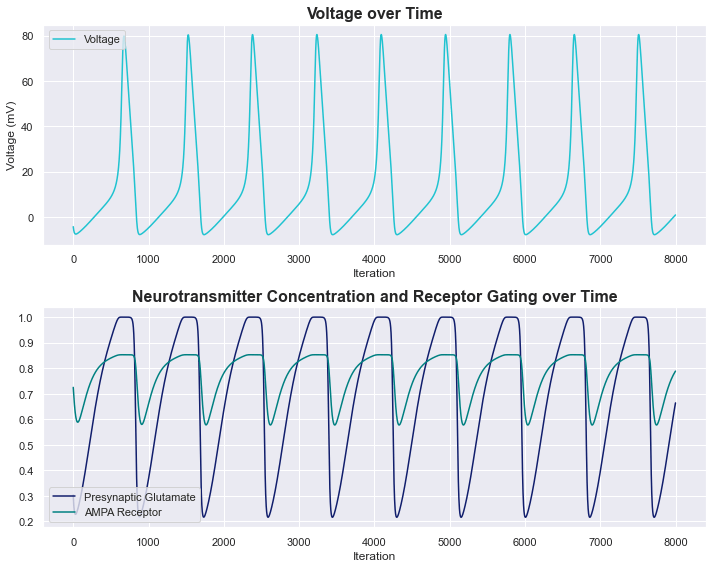
Hodgkin Huxley Model with Neurotransmission
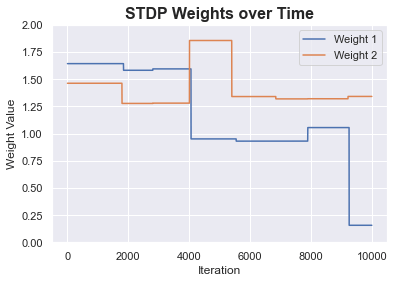
Spike Time Dependent Plasticity Weights over Time
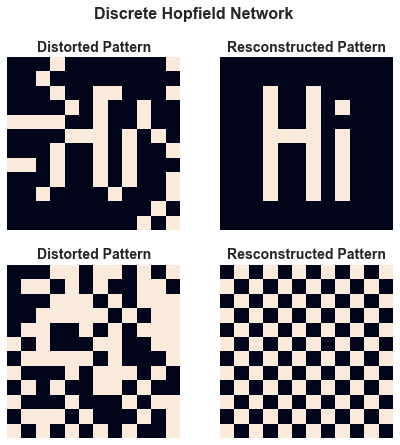
Hopfield Network Pattern Reconstruction
Lattice

Example Code
See examples folder for more examples.
Interacting lattices of neurons with inhibitory and excitatory input
extern crate spiking_neural_networks;
use rand::Rng;
use spiking_neural_networks::{
neuron::{
integrate_and_fire::IzhikevichNeuron,
plasticity::STDP,
Lattice, LatticeNetwork, AverageVoltageHistory
},
graph::AdjacencyMatrix,
error::SpikingNeuralNetworksError,
};
/// Creates two pools of neurons, one inhibitory and one excitatory, and connects them,
/// writes the average voltage history over time of each pool to .csv files to the
/// current working directory
fn main() -> Result<(), SpikingNeuralNetworksError> {
let base_neuron = IzhikevichNeuron::default_impl();
// creates smaller inhbitory lattice to stabilize excitatory feedback
let mut inh_lattice: Lattice<_, AdjacencyMatrix<_, _>, AverageVoltageHistory, STDP, _> = Lattice::default();
inh_lattice.populate(&base_neuron, 4, 4);
inh_lattice.connect(&|x, y| x != y, Some(&|_, _| -1.));
inh_lattice.apply(|n| {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
n.current_voltage = rng.gen_range(n.v_init..=n.v_th);
});
inh_lattice.update_grid_history = true;
// creates larger excitatory lattice
let mut exc_lattice: Lattice<_, AdjacencyMatrix<_, _>, AverageVoltageHistory, STDP, _> = Lattice::default();
exc_lattice.set_id(1);
exc_lattice.populate(&base_neuron, 7, 7);
exc_lattice.connect(&|x, y| x != y, Some(&|_, _| 1.));
exc_lattice.apply(|n| {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
n.current_voltage = rng.gen_range(n.v_init..=n.v_th);
});
exc_lattice.update_grid_history = true;
// sets up network
let mut network = LatticeNetwork::default_impl();
network.parallel = true;
network.add_lattice(inh_lattice)?;
network.add_lattice(exc_lattice)?;
network.connect(0, 1, &|_, _| true, Some(&|_, _| -1.))?;
network.connect(1, 0, &|_, _| true, None)?;
network.set_dt(1.);
network.run_lattices(1_000)?;
Ok(())
}
Coupling neurons with spike time dependent plasticity
use std::collections::HashMap;
extern crate spiking_neural_networks;
use spiking_neural_networks::{
neuron::{
integrate_and_fire::IzhikevichNeuron,
iterate_and_spike::{
IterateAndSpike, GaussianParameters,
ApproximateNeurotransmitter, NeurotransmitterType},
spike_train::{DeltaDiracRefractoriness, PresetSpikeTrain},
plasticity::STDP,
Lattice, LatticeNetwork, SpikeTrainGridHistory, SpikeTrainLattice
},
error::SpikingNeuralNetworksError,
};
/// Tests STDP dynamics over time given a set of input firing rates to a postsynaptic neuron
/// and updates the weights between the spike trains and given postsynaptic neuron, returns
/// the voltage and weight history over time
pub fn test_stdp<N, T>(
firing_rates: &[f32],
postsynaptic_neuron: &T,
iterations: usize,
stdp_params: &STDP,
weight_params: &GaussianParameters,
electrical_synapse: bool,
chemical_synapse: bool,
) -> Result<(HashMap<String, Vec<f32>>, Vec<Vec<Vec<Option<f32>>>>), SpikingNeuralNetworksError>
where
N: NeurotransmitterType,
T: IterateAndSpike<N=N>,
{
type SpikeTrainType<N> = PresetSpikeTrain<N, ApproximateNeurotransmitter, DeltaDiracRefractoriness>;
// sets up line of spike trains depending on number of firing rates
let mut spike_train_lattice: SpikeTrainLattice<
N,
SpikeTrainType<N>,
SpikeTrainGridHistory,
> = SpikeTrainLattice::default();
let preset_spike_train = PresetSpikeTrain::default();
spike_train_lattice.populate(&preset_spike_train, firing_rates.len(), 1);
spike_train_lattice.apply_given_position(
&(|pos: (usize, usize), spike_train: &mut SpikeTrainType<N>| {
spike_train.firing_times = vec![firing_rates[pos.0]];
})
);
spike_train_lattice.update_grid_history = true;
spike_train_lattice.set_id(0);
// generates postsynaptic neuron
let mut lattice = Lattice::default_impl();
lattice.populate(&postsynaptic_neuron.clone(), 1, 1);
lattice.plasticity = *stdp_params;
lattice.do_plasticity = true;
lattice.update_grid_history = true;
lattice.set_id(1);
// connects spike trains to neuron and runs
let lattices = vec![lattice];
let spike_train_lattices = vec![spike_train_lattice];
let mut network = LatticeNetwork::generate_network(lattices, spike_train_lattices)?;
network.connect(
0, 1, &(|_, _| true), Some(&(|_, _| weight_params.get_random_number()))
)?;
network.update_connecting_graph_history = true;
network.electrical_synapse = electrical_synapse;
network.chemical_synapse = chemical_synapse;
network.run_lattices(iterations)?;
// track postsynaptic voltage over time
// track spike trains over time
// track weights over time
let mut output_hashmap: HashMap<String, Vec<f32>> = HashMap::new();
output_hashmap.insert(
String::from("postsynaptic_voltage"),
network.get_lattice(&1).unwrap().grid_history
.history
.iter()
.map(|i| i[0][0])
.collect(),
);
let spike_train_history = &network.get_spike_train_lattice(&0).unwrap()
.grid_history.history;
for i in 0..firing_rates.len() {
output_hashmap
.entry(format!("presynaptic_voltage_{}", i))
.or_insert_with(Vec::new)
.extend(spike_train_history.iter().map(|step| step[i][0]).collect::<Vec<f32>>());
}
Ok((output_hashmap, network.get_connecting_graph().history.clone()))
}
Custom IterateAndSpike implementation
use spiking_neural_networks::neuron::iterate_and_spike_traits::IterateAndSpikeBase;
use spiking_neural_networks::neuron::iterate_and_spike::{
GaussianFactor, GaussianParameters, IsSpiking, Timestep,
CurrentVoltage, GapConductance, IterateAndSpike,
LastFiringTime, NeurotransmitterConcentrations, LigandGatedChannels,
ReceptorKinetics, NeurotransmitterKinetics, Neurotransmitters,
ApproximateNeurotransmitter, ApproximateReceptor,
IonotropicNeurotransmitterType,
};
use spiking_neural_networks::neuron::ion_channels::{
BasicGatingVariable, IonChannel, TimestepIndependentIonChannel,
};
/// A calcium channel with reduced dimensionality
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]
pub struct ReducedCalciumChannel {
/// Conductance of calcium channel (nS)
pub g_ca: f32,
/// Reversal potential (mV)
pub v_ca: f32,
/// Gating variable steady state
pub m_ss: f32,
/// Tuning parameter
pub v_1: f32,
/// Tuning parameter
pub v_2: f32,
/// Current output
pub current: f32,
}
impl TimestepIndependentIonChannel for ReducedCalciumChannel {
fn update_current(&mut self, voltage: f32) {
self.m_ss = 0.5 * (1. + ((voltage - self.v_1) / self.v_2).tanh());
self.current = self.g_ca * self.m_ss * (voltage - self.v_ca);
}
fn get_current(&self) -> f32 {
self.current
}
}
/// A potassium channel based on steady state calculations
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]
pub struct KSteadyStateChannel {
/// Conductance of potassium channel (nS)
pub g_k: f32,
/// Reversal potential (mV)
pub v_k: f32,
/// Gating variable
pub n: f32,
/// Gating variable steady state
pub n_ss: f32,
/// Gating decay
pub t_n: f32,
/// Reference frequency
pub phi: f32,
/// Tuning parameter
pub v_3: f32,
/// Tuning parameter
pub v_4: f32,
/// Current output
pub current: f32
}
impl KSteadyStateChannel {
fn update_gating_variables(&mut self, voltage: f32) {
self.n_ss = 0.5 * (1. + ((voltage - self.v_3) / self.v_4).tanh());
self.t_n = 1. / (self.phi * ((voltage - self.v_3) / (2. * self.v_4)).cosh());
}
}
impl IonChannel for KSteadyStateChannel {
fn update_current(&mut self, voltage: f32, dt: f32) {
self.update_gating_variables(voltage);
let n_change = ((self.n_ss - self.n) / self.t_n) * dt;
self.n += n_change;
self.current = self.g_k * self.n * (voltage - self.v_k);
}
fn get_current(&self) -> f32 {
self.current
}
}
/// An implementation of a leak channel
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]
pub struct LeakChannel {
/// Conductance of leak channel (nS)
pub g_l: f32,
/// Reversal potential (mV)
pub v_l: f32,
/// Current output
pub current: f32
}
impl TimestepIndependentIonChannel for LeakChannel {
fn update_current(&mut self, voltage: f32) {
self.current = self.g_l * (voltage - self.v_l);
}
fn get_current(&self) -> f32 {
self.current
}
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone, IterateAndSpikeBase)]
pub struct MorrisLecarNeuron<T: NeurotransmitterKinetics, R: ReceptorKinetics> {
/// Membrane potential (mV)
pub current_voltage: f32,
/// Voltage threshold (mV)
pub v_th: f32,
/// Initial voltage value (mV)
pub v_init: f32,
/// Controls conductance of input gap junctions
pub gap_conductance: f32,
/// Calcium channel
pub ca_channel: ReducedCalciumChannel,
/// Potassium channel
pub k_channel: KSteadyStateChannel,
/// Leak channel
pub leak_channel: LeakChannel,
/// Membrane capacitance (nF)
pub c_m: f32,
/// Timestep in (ms)
pub dt: f32,
/// Whether the neuron is spiking
pub is_spiking: bool,
/// Whether the voltage was increasing in the last step
pub was_increasing: bool,
/// Last timestep the neuron has spiked
pub last_firing_time: Option<usize>,
/// Parameters used in generating noise
pub gaussian_params: GaussianParameters,
/// Postsynaptic neurotransmitters in cleft
pub synaptic_neurotransmitters: Neurotransmitters<IonotropicNeurotransmitterType, T>,
/// Ionotropic receptor ligand gated channels
pub ligand_gates: LigandGatedChannels<R>,
}
impl<T: NeurotransmitterKinetics, R: ReceptorKinetics> MorrisLecarNeuron<T, R> {
/// Updates channel states based on current voltage
pub fn update_channels(&mut self) {
self.ca_channel.update_current(self.current_voltage);
self.k_channel.update_current(self.current_voltage, self.dt);
self.leak_channel.update_current(self.current_voltage);
}
/// Calculates change in voltage given an input current
pub fn get_dv_change(&self, i: f32) -> f32 {
(i - self.leak_channel.current - self.ca_channel.current - self.k_channel.current)
* (self.dt / self.c_m)
}
// checks if neuron is currently spiking but seeing if the neuron is increasing in
// reference to the last inputted voltage and if it is above a certain
// voltage threshold, if it is then the neuron is considered spiking
// and `true` is returned, otherwise `false` is returned
fn handle_spiking(&mut self, last_voltage: f32) -> bool {
let increasing_right_now = last_voltage < self.current_voltage;
let threshold_crossed = self.current_voltage > self.v_th;
let is_spiking = threshold_crossed && self.was_increasing && !increasing_right_now;
self.is_spiking = is_spiking;
self.was_increasing = increasing_right_now;
is_spiking
}
}
impl<T: NeurotransmitterKinetics, R: ReceptorKinetics> IterateAndSpike for MorrisLecarNeuron<T, R> {
type N = IonotropicNeurotransmitterType;
fn get_neurotransmitter_concentrations(&self) -> NeurotransmitterConcentrations<Self::N> {
self.synaptic_neurotransmitters.get_concentrations()
}
// updates voltage and adaptive values as well as the
// neurotransmitters, receptor current is not factored in,
// and spiking is handled and returns whether it is currently spiking
fn iterate_and_spike(&mut self, input_current: f32) -> bool {
self.update_channels();
let last_voltage = self.current_voltage;
self.current_voltage += self.get_dv_change(input_current);
self.synaptic_neurotransmitters.apply_t_changes(self.current_voltage, self.dt);
self.handle_spiking(last_voltage)
}
// updates voltage and adaptive values as well as the
// neurotransmitters, receptor current is factored in and receptor gating
// is updated spiking is handled at the end of the method and
// returns whether it is currently spiking
fn iterate_with_neurotransmitter_and_spike(
&mut self,
input_current: f32,
t_total: &NeurotransmitterConcentrations<Self::N>,
) -> bool {
self.ligand_gates.update_receptor_kinetics(t_total, self.dt);
self.ligand_gates.set_receptor_currents(self.current_voltage, self.dt);
self.update_channels();
let last_voltage = self.current_voltage;
let receptor_current = -self.ligand_gates.get_receptor_currents(self.dt, self.c_m);
self.current_voltage += self.get_dv_change(input_current) + receptor_current;
self.synaptic_neurotransmitters.apply_t_changes(self.current_voltage, self.dt);
self.handle_spiking(last_voltage)
}
}
Custom NeurotransmitterKinetics implementation
use spiking_neural_networks::neuron::iterate_and_spike::NeurotransmitterKinetics;
/// An approximation of neurotransmitter kinetics that sets the concentration to the
/// maximal value when a spike is detected (input `voltage` is greater than `v_th`) and
/// slowly through exponential decay that scales based on the `decay_constant` and `dt`
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]
pub struct ExponentialDecayNeurotransmitter {
/// Maximal neurotransmitter concentration (mM)
pub t_max: f32,
/// Current neurotransmitter concentration (mM)
pub t: f32,
/// Voltage threshold for detecting spikes (mV)
pub v_th: f32,
/// Amount to decay neurotransmitter concentration by
pub decay_constant: f32,
}
// used to determine when voltage spike occurs
fn heaviside(x: f32) -> f32 {
if x > 0. {
1.
} else {
0.
}
}
// calculate change in concentration
fn exp_decay(x: f32, l: f32, dt: f32) -> f32 {
-x * (dt / -l).exp()
}
impl NeurotransmitterKinetics for ExponentialDecayNeurotransmitter {
fn apply_t_change(&mut self, voltage: f32, dt: f32) {
let t_change = exp_decay(self.t, self.decay_constant, dt);
// add change and account for spike
self.t += t_change + (heaviside(voltage - self.v_th) * self.t_max);
self.t = self.t_max.min(self.t.max(0.)); // clamp values
}
fn get_t(&self) -> f32 {
self.t
}
fn set_t(&mut self, t: f32) {
self.t = t;
}
}
Custom ReceptorKinetics implementation
use spiking_neural_networks::neuron::iterate_and_spike::{
ReceptorKinetics, AMPADefault, GABAaDefault, GABAbDefault, NMDADefault,
};
/// Receptor dynamics approximation that sets the receptor
/// gating value to the inputted neurotransmitter concentration and
/// then exponentially decays the receptor over time
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]
pub struct ExponentialDecayReceptor {
/// Maximal receptor gating value
pub r_max: f32,
/// Receptor gating value
pub r: f32,
/// Amount to decay neurotransmitter concentration by
pub decay_constant: f32,
}
// calculate change in receptor gating variable over time
fn exp_decay(x: f32, l: f32, dt: f32) -> f32 {
-x * (dt / -l).exp()
}
impl ReceptorKinetics for ExponentialDecayReceptor {
fn apply_r_change(&mut self, t: f32, dt: f32) {
// calculate and apply change
self.r += exp_decay(self.r, self.decay_constant, dt) + t;
self.r = self.r_max.min(self.r.max(0.)); // clamp values
}
fn get_r(&self) -> f32 {
self.r
}
fn set_r(&mut self, r: f32) {
self.r = r;
}
}
// automatically generate defaults so `LigandGatedChannels`
// can use default receptor settings in construction
macro_rules! impl_exp_decay_receptor_default {
($trait:ident, $method:ident) => {
impl $trait for ExponentialDecayReceptor {
fn $method() -> Self {
ExponentialDecayReceptor {
r_max: 1.0,
r: 0.,
decay_constant: 2.,
}
}
}
};
}
impl_exp_decay_receptor_default!(Default, default);
impl_exp_decay_receptor_default!(AMPADefault, ampa_default);
impl_exp_decay_receptor_default!(GABAaDefault, gabaa_default);
impl_exp_decay_receptor_default!(GABAbDefault, gabab_default);
impl_exp_decay_receptor_default!(NMDADefault, nmda_default);
Dependencies
~8MB
~158K SLoC