3 unstable releases
Uses old Rust 2015
| 0.2.1 | Aug 20, 2017 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.0 | Aug 20, 2017 |
| 0.1.0 | Jul 14, 2017 |
#2405 in Algorithms
105KB
1.5K
SLoC
revonet
Rust implementation of real-coded genetic algorithm for solving optimization problems and training of neural networks. The latter is also known as neuroevolution.
Features:
- real-coded Evolutionary Algorithm
- NeuroEvolutionary tuning of weights of Neural Network with fixed structure
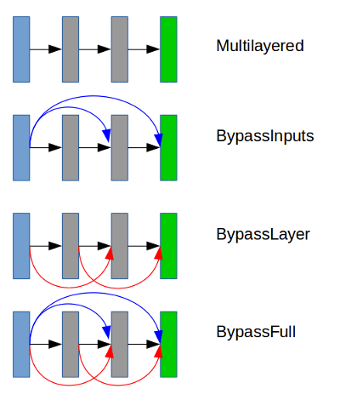
- supports several feed-forward architectures
- automatically computes statistics for single and multiple runs for EA and NE
- EA settings and results can be saved to json
- allows defining user-specified objective functions for EA and NE (see examples below)
Examples
Real-coded genetic algorithm
let pop_size = 20u32; // population size.
let problem_dim = 10u32; // number of optimization parameters.
let problem = RosenbrockProblem{}; // objective function.
let gen_count = 10u32; // generations number.
let settings = GASettings::new(pop_size, gen_count, problem_dim);
let mut ga: GA<RosenbrockProblem> = GA::new(settings, &problem); // init GA.
let res = ga.run(settings).expect("Error during GA run"); // run and fetch the results.
// get and print results of the current run.
println!("\n\nGA results: {:?}", res);
// make multiple runs and get combined results.
let res = ga.run_multiple(settings, 10 as u32).expect("Error during multiple GA runs");
println!("\n\nResults of multple GA runs: {:?}", res);
Run evolution of NN weights to solve regression problem
let (pop_size, gen_count, param_count) = (20, 20, 100); // gene_count does not matter here as NN structure is defined by a problem.
let settings = EASettings::new(pop_size, gen_count, param_count);
let problem = SymbolicRegressionProblem::new_f();
let mut ne: NE<SymbolicRegressionProblem> = NE::new(&problem);
let res = ne.run(settings).expect("Error: NE result is empty");
println!("result: {:?}", res);
println!("\nbest individual: {:?}", res.best);
Creating multilayered neural network with 2 hidden layers with sigmoid activation and with linear output nodes.
const INPUT_SIZE: usize = 20;
const OUTPUT_SIZE: usize = 2;
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng(); // needed for weights initialization when NN is built.
let mut net: MultilayeredNetwork = MultilayeredNetwork::new(INPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE);
net.add_hidden_layer(30 as usize, ActivationFunctionType::Sigmoid)
.add_hidden_layer(20 as usize, ActivationFunctionType::Sigmoid)
.build(&mut rng, NeuralArchitecture::Multilayered); // `build` finishes creation of neural network.
let (ws, bs) = net.get_weights(); // `ws` and `bs` are `Vec` arrays containing weights and biases for each layer.
assert!(ws.len() == 3); // number of elements equals to number of hidden layers + 1 output layer
assert!(bs.len() == 3); // number of elements equals to number of hidden layers + 1 output layer
Creating custom optimization problem for GA
// Dummy problem returning random fitness.
pub struct DummyProblem;
impl Problem for DummyProblem {
// Function to evaluate a specific individual.
fn compute<T: Individual>(&self, ind: &mut T) -> f32 {
// use `to_vec` to get real-coded representation of an individual.
let v = ind.to_vec().unwrap();
let mut rng: StdRng = StdRng::from_seed(&[0]);
rng.gen::<f32>()
}
}
Creating custom problem for NN evolution
// Dummy problem returning random fitness.
struct RandomNEProblem {}
impl RandomNEProblem {
fn new() -> RandomNEProblem {
RandomNEProblem{}
}
}
impl NeuroProblem for RandomNEProblem {
// return number of NN inputs.
fn get_inputs_num(&self) -> usize {1}
// return number of NN outputs.
fn get_outputs_num(&self) -> usize {1}
// return NN with random weights and a fixed structure. For now the structure should be the same all the time to make sure that crossover is possible. Likely to change in the future.
fn get_default_net(&self) -> MultilayeredNetwork {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
let mut net: MultilayeredNetwork = MultilayeredNetwork::new(self.get_inputs_num(), self.get_outputs_num());
net.add_hidden_layer(5 as usize, ActivationFunctionType::Sigmoid)
.build(&mut rng, NeuralArchitecture::Multilayered);
net
}
// Function to evaluate performance of a given NN.
fn compute_with_net<T: NeuralNetwork>(&self, nn: &mut T) -> f32 {
let mut rng: StdRng = StdRng::from_seed(&[0]);
let mut input = (0..self.get_inputs_num())
.map(|_| rng.gen::<f32>())
.collect::<Vec<f32>>();
// compute NN output using random input.
let mut output = nn.compute(&input);
output[0]
}
}
Dependencies
~1–2MB
~40K SLoC