2 releases
| 0.0.5 | Oct 20, 2020 |
|---|---|
| 0.0.2 | Oct 18, 2020 |
#293 in Biology
2MB
7.5K
SLoC
protein
Structural Biology in Rust
Example
Let's read a protein structure from a PDB file and draw a Ramachandran plot!
use csv::Writer; // the crate `csv` is required if you want to output csv
use protein::{
io::pdb::Parser, // the PDB parser that parses PDB file into a `Structure`
analysis::ModelAnalysis // `Structure` alone only stores data.
// Functions for analysing the `Structure` are provided by separate traits
};
use std::fs;
fn main() {
let data = fs::read("assets/4f7i.pdb").unwrap();
let (_, structure) = Parser::parse(&data).unwrap();
let (phis, psis) = structure.models[0].ramachandran();
// the `.ramachandran()` function is provided by the `ModelAnalysis` trait
let mut wtr = Writer::from_path("examples/ramachandran.csv").unwrap();
wtr.write_record(&["phi", "psi"]).unwrap();
for (&phi, &psi) in phis.iter().zip(psis.iter()) {
wtr.write_record(&[phi.to_string(), psi.to_string()])
.unwrap()
}
wtr.flush().unwrap();
}
This will produce a csv file containing two columns representing phi and psi angles. Then we can read the csv file in R and plot it (unfortunately I am not of any graphing libraries in Rust):
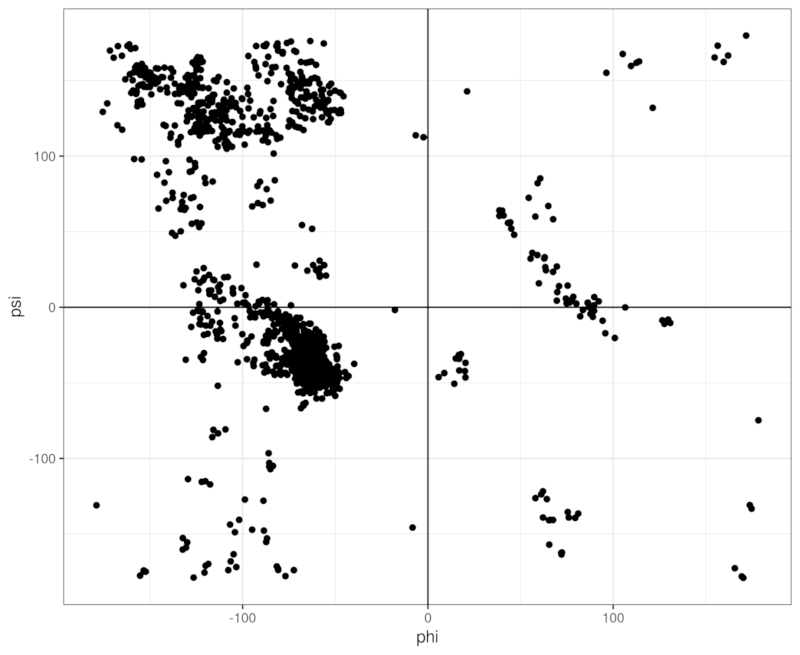
You can directly run the above example using cargo run:
cargo run --example ramachandran
Dependencies
~8.5MB
~94K SLoC