26 releases (13 breaking)
| 0.14.0 | Feb 6, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.13.1 | Oct 26, 2024 |
| 0.13.0 | Aug 24, 2024 |
| 0.12.1 | Jul 24, 2024 |
| 0.4.1 | Mar 22, 2023 |
#450 in Database interfaces
28 downloads per month
395KB
9K
SLoC
mtop
mtop: top for Memcached.
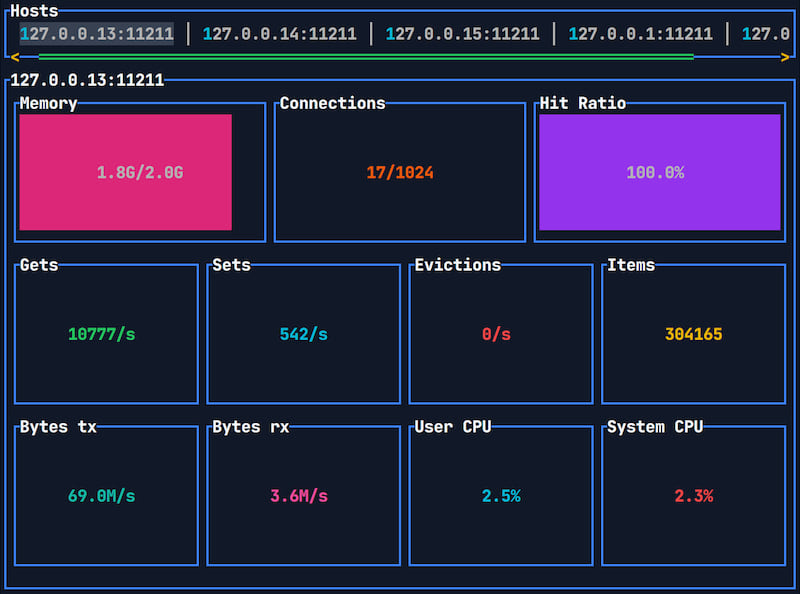
Features
- Display real-time statistics about your
memcachedservers such as- Memory usage/limit
- Per-slab memory usage
- Current/max connections
- Hit ratio
- Gets/Sets/Evictions
- Bytes transmitted and received
- Server CPU usage
- Support for easily switching between multiple servers
Install
There are multiple ways to install mtop listed below.
Binaries
Binaries are published for GNU/Linux (x86_64), Musl/Linux (x86_64), Windows (x86_64), and MacOS (x86_64 and aarch64)
for each release. Each available archive contains the mtop and mc
binaries for that platform and a few documentation files.
Docker
Docker images for GNU/Linux (amd64, arm64) are published for each release.
The docker images are built with the Dockerfile in this
repository. They do not set an entrypoint and will run mtop --help by default. The mtop and mc binaries are
placed on the PATH, in /usr/local/bin.
Cargo
mtop along with its dependencies can be downloaded and built from source using the
Rust cargo tool. Note that this requires you have a Rust toolchain installed.
To install:
cargo install mtop
To install as a completely static binary (Linux only):
cargo install --target x86_64-unknown-linux-musl mtop
To uninstall:
cargo uninstall mtop
Source
mtop along with its dependencies can be built from the latest sources on Github using
the Rust cargo tool. Note that this requires you have Git and a Rust toolchain installed.
Get the sources:
git clone https://github.com/56quarters/mtop.git && cd mtop
Install from local sources:
cargo install --path mtop
Install a completely static binary from local sources (Linux only):
cargo install --path mtop --target x86_64-unknown-linux-musl
To uninstall:
cargo uninstall mtop
Usage
mtop takes one or more Memcached host:port combinations as arguments. Statistics from
each of these servers will be collected approximately once a second. A maximum of ten
measurements from each server will be kept in memory to use for computations.
If mtop is not able to connect to the servers when starting, it will exit after printing
an error message. If mtop is not able to connect to servers or fetch statistics from
them after starting, the errors will be logged to a file. The location of this file is
/tmp/mtop/mtop.log on Unix-like systems. This log file is truncated every time mtop
starts.
Some examples of invoking mtop are given below.
Connecting to a local server
mtop localhost:11211
Connecting to multiple servers
mtop cache01.example.com:11211 cache02.example.com:11211 cache03.example.com:11211
Connecting to multiple servers with a single DNS name
A or AAAA
In this example, a DNS A lookup for memcached.local returns three DNS A records.
dig -t A memcached.local
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;memcached.local. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
memcached.local. 0 IN A 127.0.0.3
memcached.local. 0 IN A 127.0.0.2
memcached.local. 0 IN A 127.0.0.1
mtop will connect to all three servers: 127.0.0.1, 127.0.0.2, and 127.0.0.3.
mtop dns+memcached.local:11211
SRV
In this example, a DNS SRV lookup for _memcached._tcp.example.com returns three DNS SRV records.
dig -t SRV _memcached._tcp.example.com
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;_memcached._tcp.example.com. IN SRV
;; ANSWER SECTION:
_memcached._tcp.example.com. 300 IN SRV 100 100 11211 memcached01.example.com.
_memcached._tcp.example.com. 300 IN SRV 100 100 11211 memcached02.example.com.
_memcached._tcp.example.com. 300 IN SRV 100 100 11211 memcached03.example.com.
mtop will connect to all three servers, resolving their names to A or AAAA records
when connections are established: memcached01.example.com., memcached02.example.com.,
and memcached03.example.com.. Note that the port number from the SRV records are ignored,
only the port from the command line argument is used.
mtop dnssrv+_memcached._tcp.example.com:11211
Connecting to a port-forwarded Kubernetes pod
kubectl port-forward --namespace=example memcached-0 11211:11211
mtop localhost:11211
TLS connection to server
mtop --tls-enabled cache01.example.com:11211
TLS with a custom CA
mtop --tls-enabled --tls-ca memcached-ca-cert.pem cache01.example.com:11211
TLS with client authentication and a custom CA
mtop --tls-enabled --tls-ca memcached-ca-cert.pem --tls-cert memcached-client-cert.pem --tls-key memcached-client-key.pem cache01.example.com:11211
UI
Within the mtop UI, there are a few keys that control behavior.
qto quit.mto toggle between the default UI and per-slab UI.lorright-arrowto select the next host.horleft-arrowto select the previous host.jordown-arrowto select the next slab row.korup-arrowto select the previous slab row.
Limitations
No historical data
mtop displays instantaneous statistics or an average over the last 10 seconds (depending on
the particular statistic). It does not persist statistics anywhere for historical analysis. If
this is something you need, use the memcached_exporter
for Prometheus.
License
mtop is available under the terms of the GPL, version 3.
Contribution
Any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you shall be licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.
Releasing
Steps for releasing new versions of mtop are described below.
- Open and merge a PR incrementing the version of
mtopin allCargo.tomlfiles and updateCHANGELOG.md. - Update local
masterfrom Github remote. Make sure to build once with updated versions to updateCargo.lock. - Create but do not push a tag of the format
v1.2.3 - Run
cargo packageandcargo publishfor themtop-clientcrate. - Run
cargo packageandcargo publishfor themtopcrate. - Push tags to all remotes
git push --tags origin,git push --tags github
Dependencies
~19–32MB
~581K SLoC