98 releases (62 stable)
Uses new Rust 2024
| 3.4.1 | May 6, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 3.3.1 | Apr 29, 2025 |
| 2.2.0 | Mar 31, 2025 |
| 1.10.0 | Feb 2, 2025 |
| 0.5.0 | Nov 16, 2023 |
#41 in Algorithms
65,900 downloads per month
Used in 84 crates
(5 directly)
430KB
10K
SLoC
iOverlay
The iOverlay library provides high-performance boolean operations on polygons, including union, intersection, difference, and xor. It is designed for applications that require precise polygon operations, such as computer graphics, CAD systems, and geographical information systems (GIS). By supporting both integer (i32) and floating-point (f32, f64) APIs, iOverlay offers flexibility and precision across diverse use cases.
For detailed performance benchmarks, check out the Performance Comparison
Read full documentation
⚠️ Version 3.0.0 Direction Change Notice
Starting from v3.0.0, the default output contour direction has changed:
- Outer contours are now counter-clockwise
- Holes are clockwise
This aligns with the standard mathematical convention and improves compatibility across other libraries.
🔧 Note: Output direction is fully configurable — you can still override it if needed.
Table of Contents
- Features
- Demo
- Getting Started
- Boolean Operations
- Custom Point Type Support
- Slicing & Clipping
- Buffering
- Versioning Policy
Features
- Boolean Operations: union, intersection, difference, and exclusion.
- Polyline Operations: clip and slice.
- Polygons: with holes, self-intersections, and multiple contours.
- Simplification: removes degenerate vertices and merges collinear edges.
- Buffering: offsets paths and polygons.
- Fill Rules: even-odd, non-zero, positive and negative.
- Data Types: Supports i32, f32, and f64 APIs.
Demo
Getting Started
Add the following to your Cargo.toml:
[dependencies]
i_overlay = "^3.0"
Boolean Operations
Simple Example
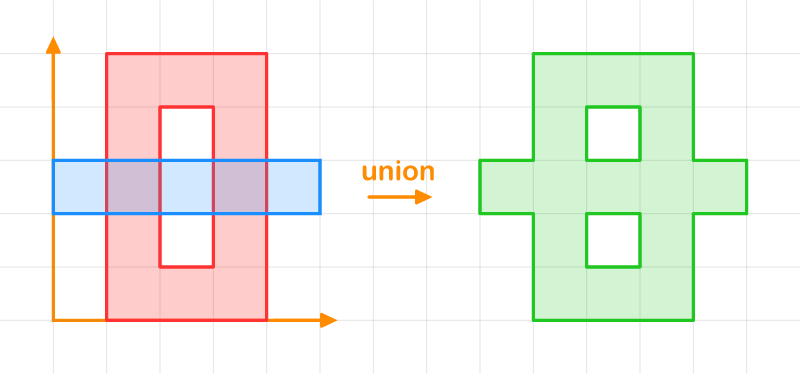 Here's an example of performing a union operation between two polygons:
Here's an example of performing a union operation between two polygons:
// Define the subject "O"
let subj = [
// main contour
vec![
[1.0, 0.0],
[4.0, 0.0],
[4.0, 5.0],
[1.0, 5.0], // the contour is auto closed!
],
// hole contour
vec![
[2.0, 1.0],
[2.0, 4.0],
[3.0, 4.0],
[3.0, 1.0], // the contour is auto closed!
],
];
// Define the clip "-"
let clip = [
// main contour
[0.0, 2.0],
[5.0, 2.0],
[5.0, 3.0],
[0.0, 3.0], // the contour is auto closed!
];
let result = subj.overlay(&clip, OverlayRule::Union, FillRule::EvenOdd);
println!("result: {:?}", result);
The result is a vec of shapes:
[
// first shape
[
// main contour (counterclockwise order)
[
[0.0, 3.0], [0.0, 2.0], [1.0, 2.0], [1.0, 0.0], [4.0, 0.0], [4.0, 2.0], [5.0, 2.0], [5.0, 3.0], [4.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0], [1.0, 5.0], [1.0, 3.0]
],
// first hole (clockwise order)
[
[2.0, 1.0], [2.0, 2.0], [3.0, 2.0], [3.0, 1.0]
],
// second hole (clockwise order)
[
[2.0, 3.0], [2.0, 4.0], [3.0, 4.0], [3.0, 3.0]
]
]
// ... other shapes if present
]
The overlay function returns a Vec<Shapes>:
Vec<Shape>: A collection of shapes.Shape: Represents a shape made up of:Vec<Contour>: A list of contours.- The first contour is the outer boundary (counterclockwise), and subsequent contours represent holes (clockwise).
Contour: A sequence of points (Vec<P: FloatPointCompatible>) forming a closed contour.
Note: By default, outer boundaries are counterclockwise and holes are clockwise—unless main_direction is set. More information about contours.
Overlay Rules
| A,B | A ∪ B | A ∩ B | A - B | B - A | A ⊕ B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Custom Point Type Support
iOverlay allows users to define custom point types, as long as they implement the FloatPointCompatible trait.
#[derive(Clone, Copy, Debug)]
struct CustomPoint {
x: f32,
y: f32,
}
impl FloatPointCompatible<f32> for CustomPoint {
fn from_xy(x: f32, y: f32) -> Self {
Self { x, y }
}
fn x(&self) -> f32 {
self.x
}
fn y(&self) -> f32 {
self.y
}
}
let subj = [
CustomPoint { x: 0.0, y: 0.0 },
CustomPoint { x: 0.0, y: 3.0 },
CustomPoint { x: 3.0, y: 3.0 },
CustomPoint { x: 3.0, y: 0.0 },
];
let clip = [
CustomPoint { x: 1.0, y: 1.0 },
CustomPoint { x: 1.0, y: 2.0 },
CustomPoint { x: 2.0, y: 2.0 },
CustomPoint { x: 2.0, y: 1.0 },
];
let result = subj.overlay(&clip, OverlayRule::Difference, FillRule::EvenOdd);
println!("result: {:?}", result);
Slicing & Clipping
Slicing a Polygon with a Polyline
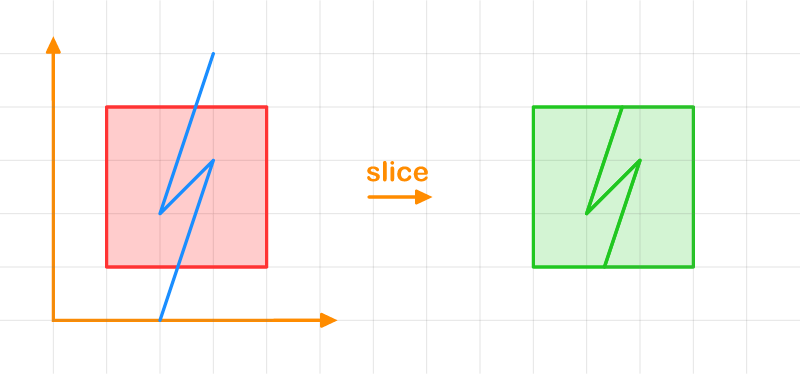
let polygon = [
[1.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 4.0],
[4.0, 4.0],
[4.0, 1.0],
];
let slicing_line = [
[3.0, 5.0],
[2.0, 2.0],
[3.0, 3.0],
[2.0, 0.0],
];
let result = polygon.slice_by(&slicing_line, FillRule::NonZero);
println!("result: {:?}", result);
Clipping a Polyline by a Polygon
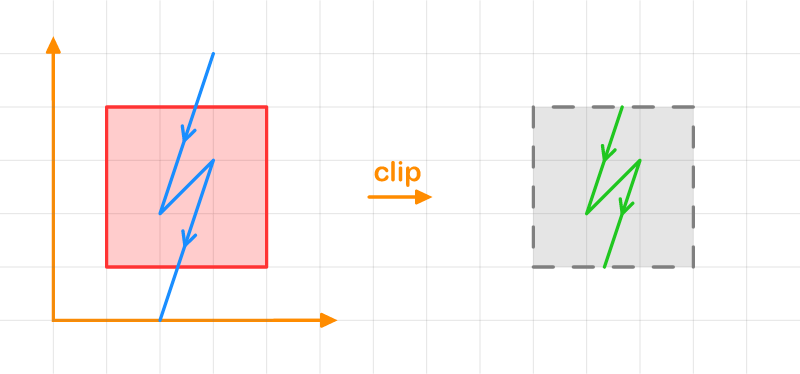
let polygon = [
[1.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 4.0],
[4.0, 4.0],
[4.0, 1.0],
];
let string_line = [
[3.0, 5.0],
[2.0, 2.0],
[3.0, 3.0],
[2.0, 0.0],
];
let clip_rule = ClipRule { invert: false, boundary_included: false };
let result = string_line.clip_by(&polygon, FillRule::NonZero, clip_rule);
println!("result: {:?}", result);
Buffering
Offseting a Path
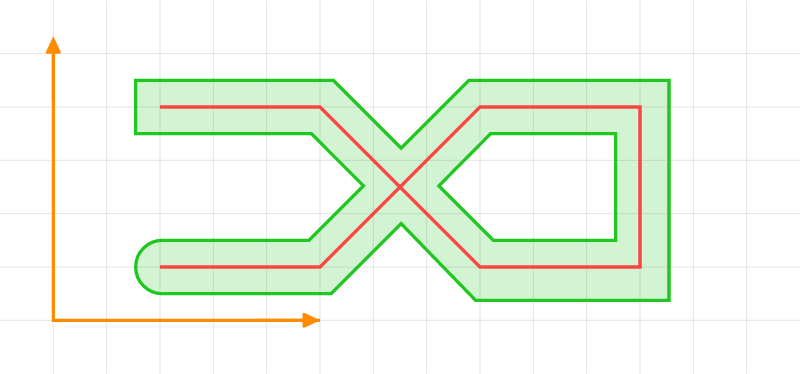
let path = [
[ 2.0, 1.0],
[ 5.0, 1.0],
[ 8.0, 4.0],
[11.0, 4.0],
[11.0, 1.0],
[ 8.0, 1.0],
[ 5.0, 4.0],
[ 2.0, 4.0],
];
let style = StrokeStyle::new(1.0)
.line_join(LineJoin::Miter(1.0))
.start_cap(LineCap::Round(0.1))
.end_cap(LineCap::Square);
let shapes = path.stroke(style, false);
println!("result: {:?}", shapes);
Offseting a Polygon
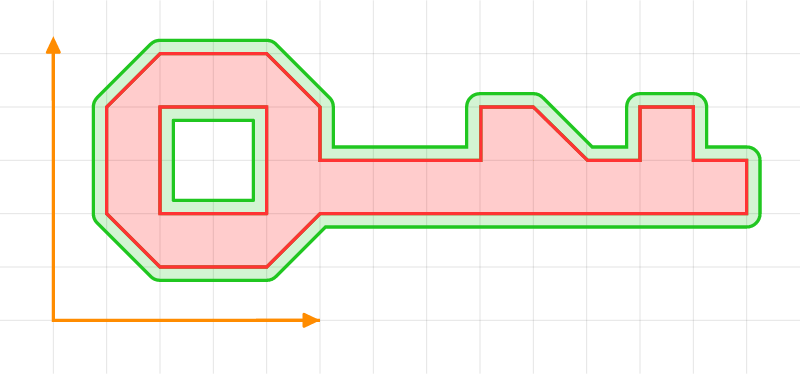
let shape = vec![
vec![
[2.0, 1.0],
[4.0, 1.0],
[5.0, 2.0],
[13.0, 2.0],
[13.0, 3.0],
[12.0, 3.0],
[12.0, 4.0],
[11.0, 4.0],
[11.0, 3.0],
[10.0, 3.0],
[9.0, 4.0],
[8.0, 4.0],
[8.0, 3.0],
[5.0, 3.0],
[5.0, 4.0],
[4.0, 5.0],
[2.0, 5.0],
[1.0, 4.0],
[1.0, 2.0]
],
vec![
[2.0, 4.0],
[4.0, 4.0],
[4.0, 2.0],
[2.0, 2.0]
],
];
let style = OutlineStyle::new(0.2).line_join(LineJoin::Round(0.1));
let shapes = shape.outline(style);
println!("shapes: {:?}", &shapes);
Note:
-
Offsetting a polygon works reliably only with valid polygons. Ensure that:
- No self-intersections.
- Outer boundaries are counterclockwise, holes are clockwise—unless
main_directionis set.
If polygon validity cannot be guaranteed, it is recommended to apply the simplify_shape operation before offsetting.
More information on contour orientation. -
Using
LineJoin::Bevelwith a large offset may produce visual artifacts.
LineCap
| Butt | Square | Round | Custom |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
LineJoin
| Bevel | Mitter | Round |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Versioning Policy
This crate follows a pragmatic versioning approach:
PATCH updates (e.g., 1.8.1 → 1.8.2): Guaranteed to be backward-compatible, containing only bug fixes or small improvements.
MINOR updates (e.g., 1.8.0 → 1.9.0): Typically backward-compatible but may include changes to experimental or less commonly used APIs.
MAJOR updates (e.g., 1.x.x → 2.x.x): Reserved for significant breaking changes or major redesigns.
To minimize disruption, consider pinning dependencies when relying on specific versions.
Dependencies
~0.9–2.4MB
~59K SLoC
