17 unstable releases (5 breaking)
| 0.7.9 | Feb 11, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.7.6 | Nov 8, 2024 |
| 0.4.0 | Jul 18, 2024 |
| 0.3.2 | Feb 20, 2024 |
#259 in Filesystem
81KB
2K
SLoC
fpick
fpick is an interactive file picker to traverse through directories tree in a terminal.
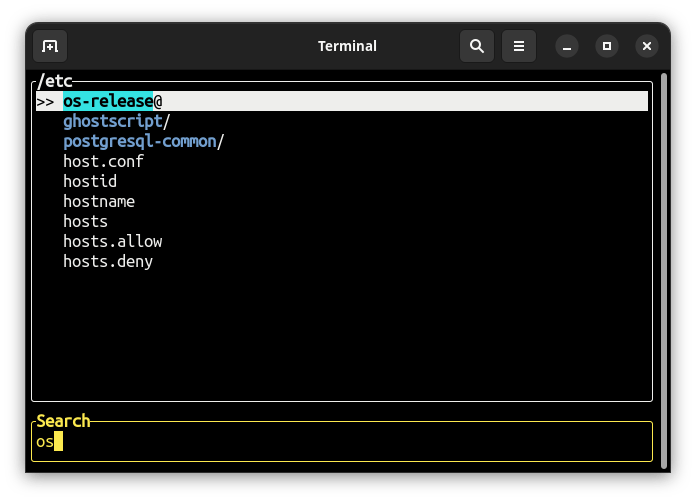
fpick returns the selected path to standard output, so you combine it with other commands:
cd "$(fpick)"
cat $(fpick)
Installation
Cargo
cargo install fpick
This will install fpick binary in Rust's Path.
Binary
Alternatively, you can download the compiled binary:
curl -L https://github.com/igrek51/fpick/releases/download/0.7.5/fpick -o ~/bin/fpick
chmod +x ~/bin/fpick
Usage
Traverse through directories
Type cd "$(fpick)" to quickly change the directory interactively:
- Start typing a name to filter the list of directories.
- Find your subdirectory with up and down arrows. Hit
Enterto go inside. - Repeat the steps until you are in the directory you are looking for.
- Hit
Enteragain (when being focused on.) to exit and change the directory.
Controls
Launch the interactive file picker by running fpick.
Navigate with keyboard:
↑and↓to move between files and directories,→to enter a directory.←to go up,- Type a phrase to filter the list of files
Enteron selected file to exit and print its path to stdout.Enteron selected directory to enter inside it.Enteron.to pick current directory.EscorCtrl + Cto exit./to go to root directory.Alt + Enteron selected file / directory to open context menu and execute an operation:- Open - open directory in file manager or a file in a default application
- Show in less
- Edit in vim
- Edit in sudo vim
- Delete file
- Delete directory
- Copy path to clipboard
- Pick absolute path - return absolute path to stdout.
- Pick relative path - return relative path to stdout.
CLI arguments
See fpick --help for options.
Usage:
fpick [OPTIONS]to select a file in a current directory and return its pathfpick [OPTIONS] <PATH>to select a file starting from a specified directory
Options:
--relative,--rel,-r- Print selected path as relative to the starting directory--version- Print version--help,-h- Print usage
Examples
You can use it in combination with other commands, for example to print the selected file:
cat $(fpick)
Tired of typing ls and cd, over and over again,
just to find a file in a deeply nested directory tree?
Use fpick to navigate through directories interactively:
cd "$(fpick)"
Set alias for quick access:
alias cfp='cd "$(fpick)"'
Move file by interactively picking the source and destination:
mv "$(fpick)" "$(fpick)"
Dependencies
~9–19MB
~256K SLoC