9 stable releases
Uses new Rust 2024
| new 2.1.0 | Apr 6, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 2.0.0 | Mar 18, 2025 |
| 1.4.0 | Mar 3, 2025 |
| 1.3.0 | Jan 30, 2025 |
| 1.0.0 | Nov 30, 2024 |
#57 in Configuration
283 downloads per month
135KB
3.5K
SLoC
envfetch
Lightweight cross-platform CLI tool for working with environment variables
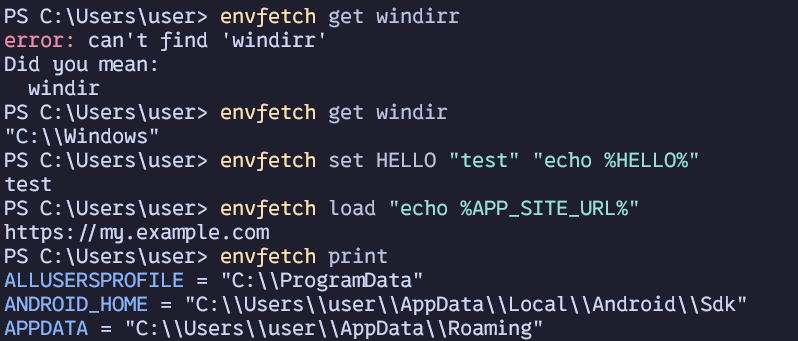
Features
- Print list of all environment variables
- Get value of variable by name
- Show similar variables if given variable not found
- Set variable (temporary and permanent)
- Delete variable (temporary and permanent)
- Load variables from dotenv-style file (temporary and permanent)
- Add string to the end of variable (temporary and permanent)
- Set and delete multiple variables at once
- Interactive mode
- Basic support
- Export variables
- Configuration support
Get started
Installing
Read about installing envfetch in the Wiki.
Using
Read in Wiki.
Configuration
Read in this Wiki page
Contributing and building from source
Read in this Wiki page
See Also
- codewars-api-rs - Rust library for Codewars API
- conemu-progressbar-go - Progress bar for ConEmu for Go
- terminal-go - Go library for working with ANSI/VT terminal sequences
- zapret-discord-youtube - Zapret build for Windows for fixing Discord and YouTube in Russia or other services
Dependencies
~11–22MB
~330K SLoC