9 unstable releases (4 breaking)
| 0.6.1 | Apr 25, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.6.0 | Jan 6, 2025 |
| 0.5.0 | Oct 21, 2024 |
| 0.4.0 | May 31, 2024 |
| 0.1.0 |
|
#101 in Embedded development
8,970 downloads per month
Used in sam3-hal
3.5MB
341 lines
Embedded Test
The embedded-test library provides a test harness for embedded systems (riscv, arm and xtensa). Use this library on the target together with probe-rs on the host to run integration tests on your embedded device.
probe-rs together with embedded-test provide a (libtest compatible) test runner, which will:
- Flash all the tests to the device in one go (via the
probe-rs runcommand) - Request information about all tests from the device (via semihosting SYS_GET_CMDLINE)
- In turn for each testcase:
- Reset the device
- Signal to the device (via semihosting SYS_GET_CMDLINE) which test to run
- Wait for the device to signal that the test completed successfully or with error (via semihosting SYS_EXIT)
- Report the results
Since the test runner (probe-rs run) is libtest compatible (
using libtest-mimic), you can use intellij or vscode to run individual tests
with the click of a button.
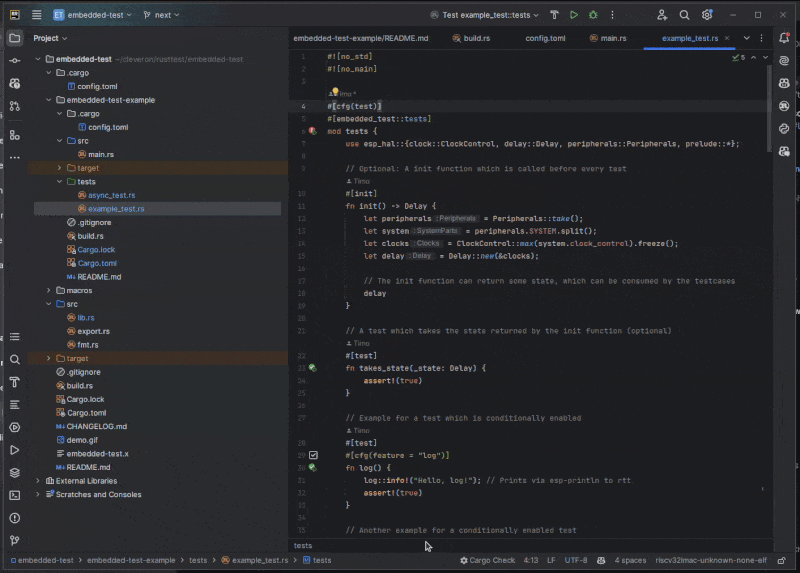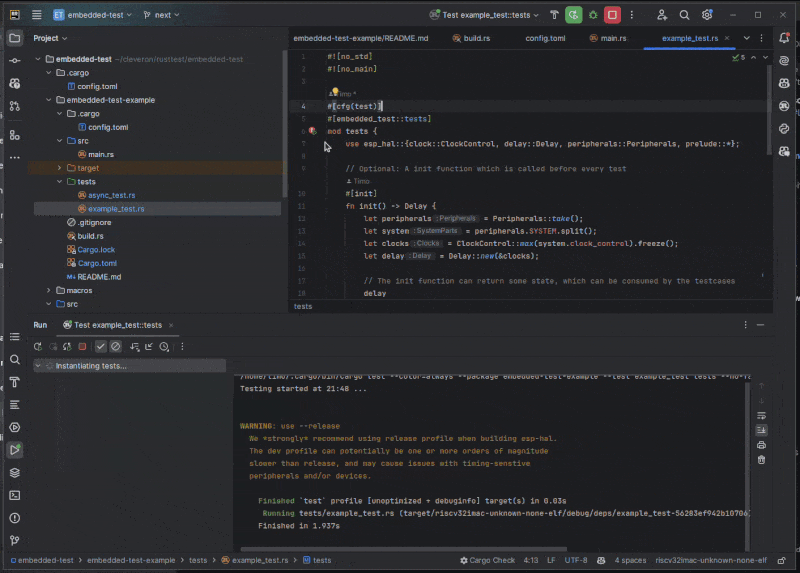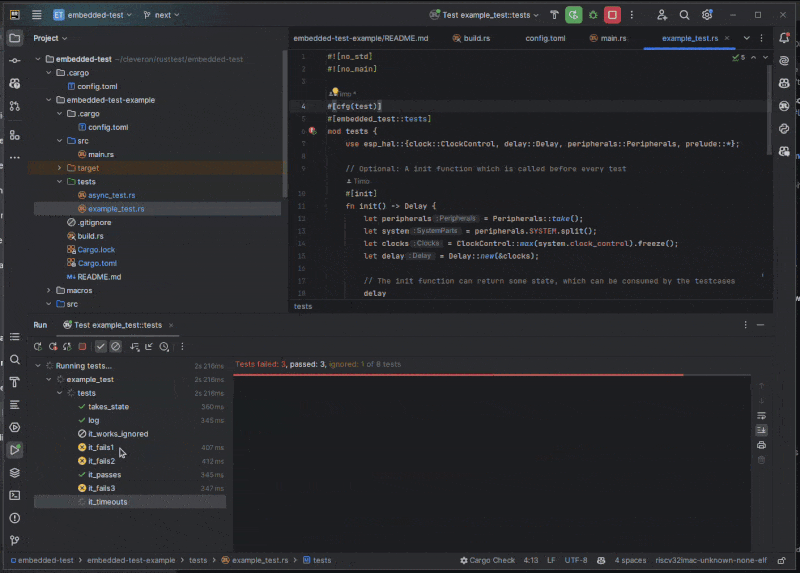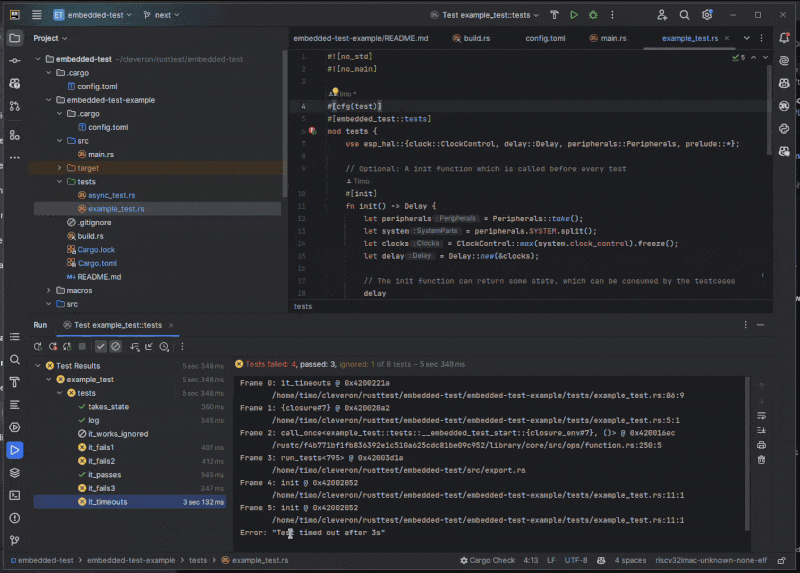
Features
- Runs each test case individually, and resets the device between each test case
- Supports an init function which will be called before each test case and can pass state to the test cases
- Supports async test and init functions (needs feature
embassy) - Support
#[should_panic],#[ignore]and#[timeout(<seconds>)]attributes for each test case
Usage
Add the following to your Cargo.toml:
[dev-dependencies]
embedded-test = { version = "0.6.0" }
[[test]]
name = "example_test"
harness = false
Install the runner on your system:
cargo install probe-rs-tools
Setup probe-rs as the runner in your .cargo/config.toml. For example:
[target.thumbv7em-none-eabihf]
runner = "probe-rs run --chip STM32F767ZITx"
# `probe-rs run` will autodetect whether the elf to flash is a normal firmware or a test binary
Add the following to your build.rs file:
fn main() {
println!("cargo::rustc-link-arg-tests=-Tembedded-test.x");
}
Then you can run your tests with cargo test --test example_test or use the button in vscode/intellij.
Having trouble setting up? Checkout out the FAQ and common Errors Wiki page.
Example Test (e.g. tests/example_test.rs)
Check the example folder for a complete example project for stm32/esp32.
#![no_std]
#![no_main]
#[cfg(test)]
#[embedded_test::tests]
mod tests {
use stm32f7xx_hal::pac::Peripherals;
// An optional init function which is called before every test
// Asyncness is optional, so is the return value
#[init]
async fn init() -> Peripherals {
Peripherals::take().unwrap()
}
// Tests can be async (needs feature `embassy`)
// Tests can take the state returned by the init function (optional)
#[test]
async fn takes_state(_state: Peripherals) {
assert!(true)
}
// Tests can be conditionally enabled (with a cfg attribute)
#[test]
#[cfg(feature = "log")]
fn log() {
rtt_target::rtt_init_log!();
log::info!("Hello, log!");
assert!(true)
}
// Tests can be ignored with the #[ignore] attribute
#[test]
#[ignore]
fn it_works_ignored() {
assert!(false)
}
// Tests can fail with a custom error message by returning a Result
#[test]
fn it_fails_with_err() -> Result<(), &'static str> {
Err("It failed because ...")
}
// Tests can be annotated with #[should_panic] if they are expected to panic
#[test]
#[should_panic]
fn it_passes() {
assert!(false)
}
// Tests can be annotated with #[timeout(<secs>)] to change the default timeout of 60s
#[test]
#[timeout(10)]
fn it_timeouts() {
loop {} // should run into the 10s timeout
}
}
Configuration features
| Feature | Default? | Description |
|---|---|---|
panic-handler |
Yes | Defines a panic-handler which will invoke semihosting::process::abort() on panic |
defmt |
No | Prints testcase exit result to defmt. You'll need to setup your defmt #[global_logger] yourself (e.g. #[embedded_test::tests(setup=rtt_target::rtt_init_defmt!())) . |
log |
No | Prints testcase exit result to log. You'll need to setup your logging sink yourself (e.g. #[embedded_test::tests(setup=rtt_target::rtt_init_log!())) |
embassy |
No | Enables async test and init functions. Note: You need to enable at least one executor feature on the embassy-executor crate unless you are using the external-executor feature. |
external-executor |
No | Allows you to bring your own embassy executor which you need to pass to the #[tests] macro (e.g. #[embedded_test::tests(executor = esp_hal::embassy::executor::thread::Executor::new())]) |
xtensa-semihosting |
No | Enables semihosting for xtensa targets. |
ariel-os |
No | Enables Ariel OS integration. |
Please also note the doc for the Attribute Macro embedded_test::tests.
License
Licensed under either of:
at your option.
Contribution
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you, as defined in the Apache-2.0 license, shall be dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.