1 unstable release
| 0.1.0 | Nov 17, 2022 |
|---|
#378 in Database implementations
21 downloads per month
135KB
714 lines

No-code REST API server
Table of Contents
Using the binary
An API can be setup using the server_config.toml
Building the binary
Prerequisites
- cargo (rust package manager)
This command will build the binary:
cargo build --release --bin="rust_rest_api" --features="build-binary"
Config file
The config file uses the TOML format.
A typical config file looks like:
database="sqlite3"
database_path="database.db"
loglevel="debug"
host="127.0.0.1:3000"
# Example table
[table.people]
route = "/people"
name = "text"
age = "Integer"
Currently only database="sqlite3" is supported
database_path
Path where the database will be opened/saved to. This can be absolute or relative.
loglevel
This can be a value of:
errorwarninfodebugtraceoff
host
Specifies the IP and port that the server is run on in the format ip:port
Specifying database tables
[table.name]
This creates a table with name.
route = "/uri_to_table"
This is a required attribute for each table. The table will be accessed at the URL /uri_to_table .
field = "type"
The remaining attributes specify the structure of the table.
field is the name of a field, or column.
type is the data type of the field. In sqlite3, the following types are supported:
nullrealintegertext
A primary key id is automatically added for every table.
Command Line Options
-c --config <FILE>
Sets the path to a custom config file
-r --resetdb
Reset the database before starting server
API Format
The API uses JSON format to receive and send data.
GET Requests
Sending
Sending a GET request to a table's route will retrieve all entries.
Query strings can be used to filter the results.
/people?age=4 will translate to SQL SELECT * FROM people WHERE age=4
+ in query strings are translated to a space.
Returning
A JSON string containing an array of returned results.
Each result is an ordered array containing each field. The first field is the unique id.
Examples:
curl 127.0.0.1:3000/people
=> [[1,"john",5],[2,"jess",19],[3,"mike",56],[4,"andrew",56]]
curl 127.0.0.1:3000/people?id=2
=> [[2,"jess",19]]
curl 127.0.0.1:3000/people?age=56
=> [[3,"mike",56],[4,"andrew",56]]
POST Requests
Used to add new database entries.
Sending
A POST request must contain a JSON body. The format of the body is
{
"columns": {
"name": "john",
"age": "8"
}
}
All values in "columns" must be a string.
All fields for a table must be specified (except id).
Returning
A JSON string containing an array of the most recently added values. This is in the same format as GET returns.
Examples:
curl -X POST -d @test.json 127.0.0.1:3000/people
=> [[1,"john",8]]
curl -X POST -d @test.json 127.0.0.1:3000/people
=> [[2,"john",8]]
DELETE Requests
Used to delete database entries.
Sending
Sending a delete request to a table's route will delete the table's contents.
Query strings can be used to filter which entries are deleted.
/people?age=4 will translate to SQL DELETE FROM people WHERE age=4
+ in query strings are translated to a space.
Returning
Empty body.
If an error is encountered when deleting, HTTP error code 500/400 will be returned. It cannot be assumed the entry was deleted successfully.
Else, HTTP 200.
PATCH Requests
Used to update database entries.
Sending
A PATCH request must contain a JSON body. The format of the body is
{
"columns": {
"name": "jeff",
},
"filters": {
"age": "8"
}
}
All values in "columns" and "filters" must be a string.
This will update all columns' name to the value "jeff" for all entries that match age=8.
Returning
Empty body.
If an error is encountered when updating, HTTP error code 500/400 will be returned. It cannot be assumed any values were updated successfully.
Else, HTTP 200.
Using the library
A basic implementation (used for the binary) can be found here.
Miscellaneous
The config TOML file is parsed with:
let (config, tables) = rest_api::config_parser::read_config(optional_path)
Logging is enabled by calling:
rest_api::enable_logging(&config)
Call once only
An app is asynchronously run with:
rest_api::api_http_server::http::run_app_server(addr, app).await
This requires the parent function to be async
Flow of received HTTP requests in the app:
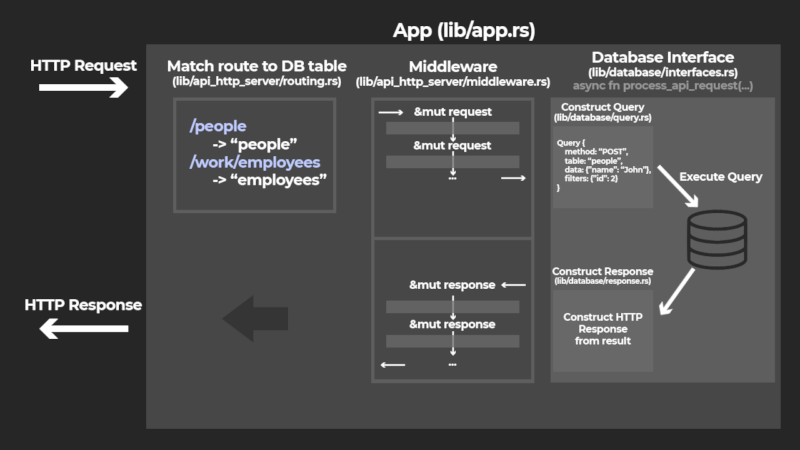
Adding middleware
The easiest way to add functionality is to create your own App with your own middleware.
This allows every request and response to be intercepted and processed.
To create a middleware, create a struct that implements the Middleware trait, as well as Sync and Send for thread safety.
Middlewares are registered when creating the App object. For reference, bin.rs shows how an app is created.
Example:
// create_auth_middleware() must return a struct that implements the Middleware + Send + Sync traits.
let auth_middleware = Box::new( create_auth_middleware() ) as Box<dyn Middleware + Send + Sync>;
let app = App {
routes,
middleware: vec![auth_middleware],
database_interface: Box::new(interface)
};
Adding a new database implementation
To support a new database type, the following things must be implemented:
Interface : Required
The interface acts as a 'bridge' between the incoming requests and the database.
It also handles other database functions such as deleting, creating and connecting.
An interface struct implements the DatabaseInterface trait.
Due to the async requirement for processing the request, the implementation of the trait must use #[async_trait::async_trait], from the async_trait crate.
The supported data types are in the SQLType enum:
pub enum SQLType {
Null,
Integer,
Real,
Text,
}
Query
The query is an optional trait that can help with converting requests to SQL. It is used in the SQLite3 interface implementation for parsing request data and safely executing SQL.
It has 2 generics <T, A>.
T is a database connection type.
A is a cursor type, returned from executing a statement.
Response Builder
The response builder is an optional trait that defines a function to convert a query result Vec<Vec<T>> (where T is a database value) into a string for a response.
The outer Vec contains the rows, and the inner Vec contains the fields in a row.
Dependencies
~9–19MB
~249K SLoC