32 releases
| 0.9.0 | Apr 26, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.8.4 | Aug 14, 2024 |
| 0.8.3 | Apr 28, 2024 |
| 0.8.2 | Jan 14, 2024 |
| 0.0.1 | Jul 7, 2020 |
#76 in Command line utilities
240 downloads per month
211MB
6.5M
SLoC
diffsitter
Disclaimer
diffsitter is very much a work in progress and nowhere close to production
ready (yet). Contributions are always welcome!
Summary
diffsitter creates semantically meaningful diffs that ignore formatting
differences like spacing. It does so by computing a diff on the AST (abstract
syntax tree) of a file rather than computing the diff on the text contents of
the file.
diffsitter uses the parsers from the
tree-sitter project to parse
source code. As such, the languages supported by this tool are restricted to the
languages supported by tree-sitter.
diffsitter supports the following languages:
- Bash
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Go
- Java
- OCaml
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- Rust
- Typescript/TSX
- HCL
Examples
Take the following files:
fn main() {
let x = 1;
}
fn add_one {
}
fn
main
()
{
}
fn addition() {
}
fn add_two() {
}
The standard output from diff will get you:
1,2c1,12
< fn main() {
< let x = 1;
---
> fn
>
>
>
> main
>
> ()
>
> {
> }
>
> fn addition() {
5c15
< fn add_one {
---
> fn add_two() {
You can see that it picks up the formatting differences for the main
function, even though they aren't semantically different.
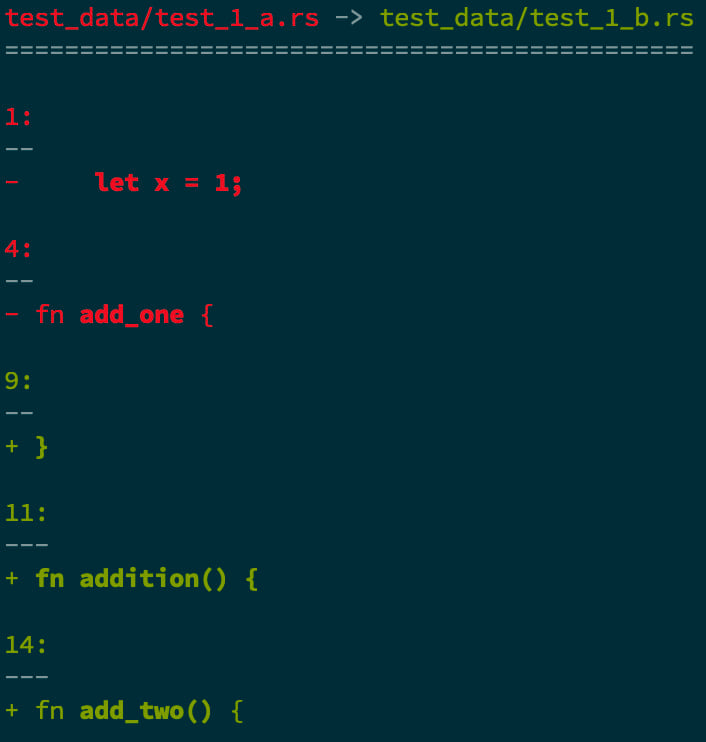
Check out the output from diffsitter:
test_data/short/rust/a.rs -> test_data/short/rust/b.rs
======================================================
9:
--
+ }
11:
---
+ fn addition() {
1:
--
- let x = 1;
14:
---
+ fn add_two() {
4:
--
- fn add_one {
Note: the numbers correspond to line numbers from the original files.
You can also filter which tree sitter nodes are considered in the diff through the config file.
Since it uses the AST to calculate the difference, it knows that the formatting
differences in main between the two files isn't a meaningful difference, so
it doesn't show up in the diff.
diffsitter has some nice (terminal aware) formatting too:
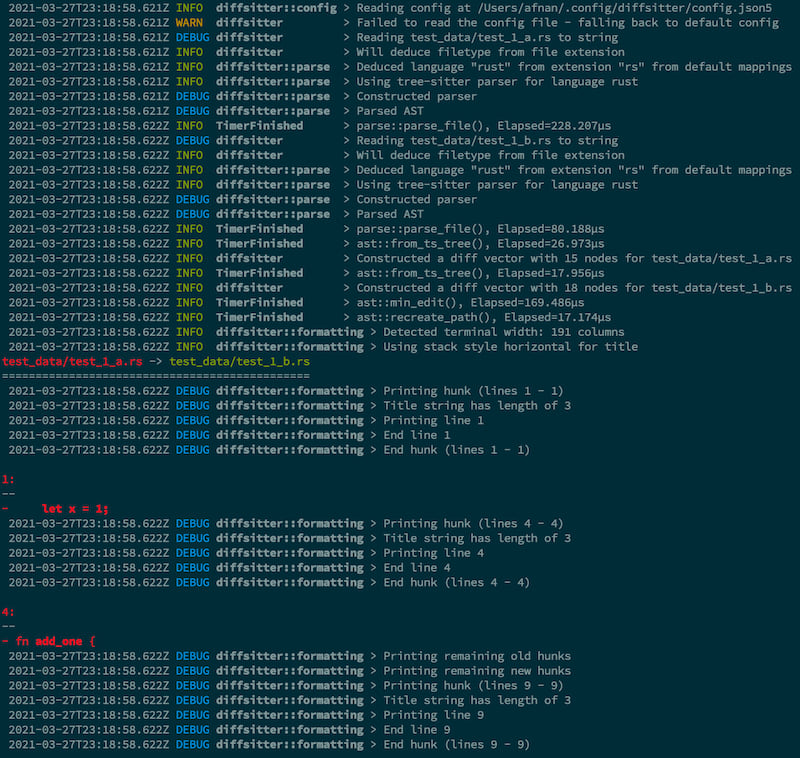
It also has extensive logging if you want to debug or see timing information:
Node filtering
You can filter the nodes that are considered in the diff by setting
include_nodes or exclude_nodes in the config file. exclude_nodes always
takes precedence over include_nodes, and the type of a node is the kind
of a tree-sitter node. The kind directly corresponds to whatever is reported
by the tree-sitter API, so this example may occasionally go out of date.
This feature currently only applies to leaf nodes, but we could exclude nodes recursively if there's demand for it.
"input-processing": {
// You can exclude different tree sitter node types - this rule takes precedence over `include_kinds`.
"exclude_kinds": ["string_content"],
// You can specifically allow only certain tree sitter node types
"include_kinds": ["method_definition"],
}
Installation

Published binaries
This project uses Github actions to build and publish binaries for each tagged release. You can download binaries from there if your platform is listed. We publish nightly releases as well as tagged stable releases.
Cargo
You can build from source with cargo using the following command:
cargo install diffsitter --bin diffsitter
If you want to generate completion files and other assets you can install the
diffsitter_completions binary with the following command:
cargo install diffsitter --bin diffsitter_completions
Homebrew
You can use my tap to install diffsitter:
brew tap afnanenayet/tap
brew install diffsitter
# brew install afnanenayet/tap/diffsitter
Arch Linux (AUR)
@samhh has packaged diffsitter for arch on the AUR. Use your favorite AUR
helper to install diffsitter-bin.
Alpine Linux
Install package diffsitter from the Alpine Linux repositories (on v3.16+ or Edge):
apk add diffsitter
Tree-sitter grammars are packaged separately (search for tree-sitter-*).
You can install individual packages you need or the virtual package tree-sitter-grammars to install all of them.
Building with Docker
We also provide a Docker image that builds diffsitter using the standard Rust base image. It separates the compilation stage from the run stage, so you can build it and run with the following command (assuming you have Docker installed on your system):
docker build -t diffsitter .
docker run -it --rm --name diffsitter-interactive diffsitter
Usage
For detailed help you can run diffsitter --help (diffsitter -h provides
brief help messages).
You can configure file associations and formatting options for diffsitter
using a config file. If a config is not supplied, the app will use the default
config, which you can see with diffsitter dump-default-config. It will
look for a config at ${XDG_HOME:-$HOME}/.config/diffsitter/config.json5 on
macOS and Linux, and the standard directory for Windows. You can also refer to
the sample config.
You can override the default config path by using the --config flag or set
the DIFFSITTER_CONFIG environment variable.
Note: the tests for this crate check to make sure the provided sample config is a valid config.
Git integration
To see the changes to the current git repo in diffsitter, you can add
the following to your repo's .git/config and run git difftool.
[diff]
tool = diffsitter
[difftool]
prompt = false
[difftool "diffsitter"]
cmd = diffsitter "$LOCAL" "$REMOTE"
Shell Completion
You can generate shell completion scripts using the binary using the
gen-completion subcommand. This will print the shell completion script for a
given shell to STDOUT.
You should use the help text for the most up to date usage information, but general usage would look like this:
diffsitter gen-completion bash > completion.bash
We currently support the following shells (via clap_complete):
- Bash
- Zsh
- Fish
- Elvish
- Powershell
Dependencies
diffsitter is usually compiled as a static binary, so the tree-sitter
grammars/libraries are baked into the binary as static libraries. There is an
option to build with support for dynamic libraries which will look for shared
library files in the user's default library path. This will search for
library files of the form libtree-sitter-{lang}.{ext}, where lang is the
language that the user is trying to diff and ext is the platform-specific
extension for shared library files (.so, .dylib, etc). The user can
override the dynamic library file for each language in the config as such:
{
"grammar": {
// You can specify the dynamic library names for each language
"dylib-overrides": {
// with a filename
"rust": "libtree-sitter-rust.so",
// with an absolute path
"c": "/usr/lib/libtree-sitter-c.so",
// with a relative path
"cpp": "../libtree-sitter-c.so",
},
}
}
The above excerpt was taken from the sample config.
Questions, Bugs, and Support
If you notice any bugs, have any issues, want to see a new feature, or just have a question, feel free to open an issue or create a discussion post.
If you file an issue, it would be preferable that you include a minimal example
and/or post the log output of diffsitter (which you can do by adding the
-d/--debug flag).
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md.
Similar Projects
Dependencies
~15–31MB
~510K SLoC