12 releases (6 breaking)
| 0.20.0 | Aug 13, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.6.1 | Jul 21, 2024 |
| 0.6.0 | Jun 18, 2024 |
| 0.5.0 | Feb 5, 2024 |
| 0.1.1 | Jul 16, 2023 |
#1 in #instantiate-msg
25 downloads per month
555KB
6K
SLoC
CosmWasm ICA Controller Contract
This is a CosmWasm smart contract that communicates with the golang ica/host module on the counterparty chain to create and manage one interchain account. This contract can also execute callbacks based on the result of the interchain account transaction. Because this is a CosmWasm implementation of the entire ICA controller, the chain that this contract is deployed on need not have the ICA module enabled. Moreover, the counterparty chain need not have CosmWasm support. This contract uses CosmWasm v2.1 but can be deployed on chains that support CosmWasm v1.4+.
A documentation website for this contract is here.
Table of Contents
CosmWasmICA Controller Contract
Usage
The following is a brief overview of the contract's functionality. (You can also see the various ways this contract can be used in the end to end tests in the e2e directory.)
Create an interchain account
This contract provides two ways to create an interchain account:
- Using
InstantiateMsg - Using
ExecuteMsg::CreateChannel
Using InstantiateMsg
This contract only accepts MsgChannelOpenInit messages sent by itself. Relayers can never initiate a channel handshake with this contract.
InstantiateMsg always initiates the channel handshake and this is why channel_open_init_options field is not optional.
/// The message to instantiate the ICA controller contract.
#[cw_serde]
pub struct InstantiateMsg {
/// The address of the owner of the ICA application.
/// If not specified, the sender is the owner.
#[serde(skip_serializing_if = "Option::is_none")]
pub owner: Option<String>,
/// The options to initialize the IBC channel upon contract instantiation.
pub channel_open_init_options: options::ChannelOpenInitOptions,
/// The contract address that the channel and packet lifecycle callbacks are sent to.
/// If not specified, then no callbacks are sent.
#[serde(skip_serializing_if = "Option::is_none")]
pub send_callbacks_to: Option<String>,
}
Using ExecuteMsg::CreateChannel
If the channel_open_init_options field in InstantiateMsg was malformed in a way that prevents the channel handshake from succeeding, the contract owner can submit a ExecuteMsg::CreateChannel with a new channel_open_init_options.
pub enum ExecuteMsg {
/// `CreateChannel` makes the contract submit a stargate MsgChannelOpenInit to the chain.
/// This is a wrapper around [`options::ChannelOpenInitOptions`] and thus requires the
/// same fields. If not specified, then the options specified in the contract instantiation
/// are used.
CreateChannel {
/// The options to initialize the IBC channel.
/// If not specified, the options specified in the contract instantiation are used.
/// Must be `None` if the sender is not the owner.
#[serde(skip_serializing_if = "Option::is_none")]
channel_open_init_options: Option<options::ChannelOpenInitOptions>,
},
// ...
}
In case the channel was closed due to a timeout, the contract owner can submit a ExecuteMsg::CreateChannel with channel_open_init_options: None to create a channel with the same channel_open_init_options as the last channel opening.
Learn more about channel closing and reopening here.
Execute an interchain account transaction
ExecuteMsg::SendCosmosMsgs is used to commit a packet to be sent to the host chain. It accepts cosmwasm_std::CosmosMsgs to be sent to the host chain. (The contract then these messages to protobuf messages and sends them to the host chain. You can execute any custom message using CosmosMsg::Stargate).
In CosmWasm contracts, CosmosMsg are used to execute transactions on the chain that the contract is deployed on. In this contract, we use CosmosMsgs to execute transactions on the host (counterparty) chain. This is done by converting the CosmosMsgs to a protobuf ICA tx. The ICA tx is then sent to the host chain. The host chain then executes the ICA tx and sends the result back to this contract.
This execute message allows the user to submit an array of cosmwasm_std::CosmosMsg which are then converted by the contract to an atomic ICA tx.
pub enum ExecuteMsg {
// ...
/// `SendCosmosMsgs` converts the provided array of [`CosmosMsg`] to an ICA tx and sends them to the ICA host.
/// [`CosmosMsg::Stargate`] and [`CosmosMsg::Wasm`] are only supported if the [`TxEncoding`](crate::ibc::types::metadata::TxEncoding) is [`TxEncoding::Protobuf`](crate::ibc::types::metadata::TxEncoding).
///
/// **This is the recommended way to send messages to the ICA host.**
SendCosmosMsgs {
/// The stargate messages to convert and send to the ICA host.
#[serde_as(deserialize_as = "serde_with::DefaultOnNull")]
messages: Vec<CosmosMsg>,
/// The stargate queries to convert and send to the ICA host.
/// The queries are executed after the messages.
#[cfg(feature = "query")]
#[serde(skip_serializing_if = "Vec::is_empty")]
#[serde(default)]
#[serde_as(deserialize_as = "serde_with::DefaultOnNull")]
queries: Vec<cosmwasm_std::QueryRequest<cosmwasm_std::Empty>>,
/// Optional memo to include in the ibc packet.
#[serde(skip_serializing_if = "Option::is_none")]
packet_memo: Option<String>,
/// Optional timeout in seconds to include with the ibc packet.
/// If not specified, the [default timeout](crate::ibc::types::packet::DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_SECONDS) is used.
#[serde(skip_serializing_if = "Option::is_none")]
timeout_seconds: Option<u64>,
},
// ...
}
(CosmosMsg::Stargate allows the user to submit any protobuf message to the host chain.)
Here is an example execute message that delegates tokens to a validator on the host chain and then votes on a proposal (atomically).
{
"send_cosmos_msgs":{
"messages":[
{
"staking":{
"delegate":{
"validator":"validatorAddress",
"amount":{
"denom":"uatom",
"amount":"10000000"
}
}
}
},
{
"gov":{
"vote":{
"proposal_id":1,
"vote":"yes"
}
}
}
]
}
}
Querying the host chain
This contract also supports querying the host chain. To do this, you can submit a ExecuteMsg::SendCosmosMsgs with the queries field filled out. The queries are always executed after the messages, and their results are deserialized and returned in the callbacks.
This feature only works if the host (counterparty) chain is on ibc-go v7.5+. If the host chain is on an older version, then the packet will return an error acknowledgement.
Similarly to CosmosMsg, in CosmWasm contracts, QueryRequest are used to execute queries on the chain that the contract is deployed on. In this contract, we use QueryRequests to execute queries as transactions on the host (counterparty) chain. This is done by converting the QueryRequestss to a protobuf ICA tx. The ICA tx is then sent to the host chain. The host chain then executes the ICA tx and sends the result back to this contract.
Note that if both messages and queries are provided, the queries are executed after the messages.
Unlike the messages, not all query requests are supported, as query execution is not generally deterministic in CosmosSDK. See the documentation for the supported query requests here.
Execute a callback
This contract supports external contract callbacks. See src/types/callbacks.rs to learn what callbacks are supported.
This contract currently only supports sending callbacks to a single contract. You register the callback contract address during instantiation, or update it later using ExecuteMsg::UpdateCallbackAddress.
The callback contract must include the following variant in its ExecuteMsg enum:
use cosmwasm_schema::cw_serde;
use cw_ica_controller::types::callbacks::IcaControllerCallbackMsg;
#[cw_serde]
pub enum ExecuteMsg {
// ... other variants
/// The callback message from the ICA controller contract.
ReceiveIcaCallback(IcaControllerCallbackMsg),
}
Note that this crate also includes a proc-macro to add the ReceiveIcaCallback variant to the ExecuteMsg enum. This is done by adding the following macro to the callback contract:
use cosmwasm_schema::cw_serde;
use cw_ica_controller::helpers::ica_callback_execute;
#[ica_callback_execute]
#[cw_serde]
/// This is the execute message of the contract.
pub enum ExecuteMsg {
// ... other variants
}
Any contract that imports the cw-ica-controller as a library needs to disable the default-features of the cw-ica-controller crate.
This is because the default-features of the cw-ica-controller crate includes the CosmWasm entry points.
[dependencies]
cw-ica-controller = { version = "0.6.0", default-features = false }
Channel Closing and Reopening
Channel Closing
An ICA channel can be closed due to a timed out packet if the channel is ordered.
Otherwise, the channel can be closed by the user by submitting a ExecuteMsg::CloseChannel message.
Channel Reopening
If the ICA channel is closed, the contract is then able to create a new channel with the same interchain account address, and continue to use the same interchain account. To do this, you submit a ExecuteMsg::CreateChannel.
Note that the channel_open_init_options can be changed when creating a new channel.
This is useful if the user wants to change the ordering of the channel.
Demo
This project was used in the Injective Illuminate Hackathon and XION ABSTRACTATHON winner projects Tokenized Interchain Accounts, Nomos Abstraction on Xion
Injective Illuminate Hackathon
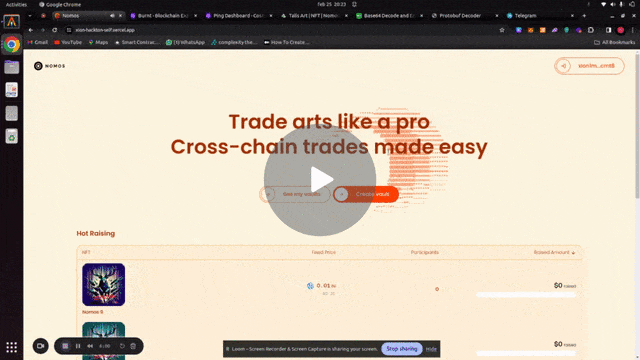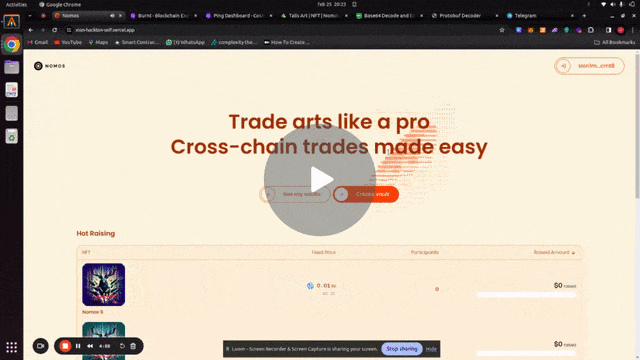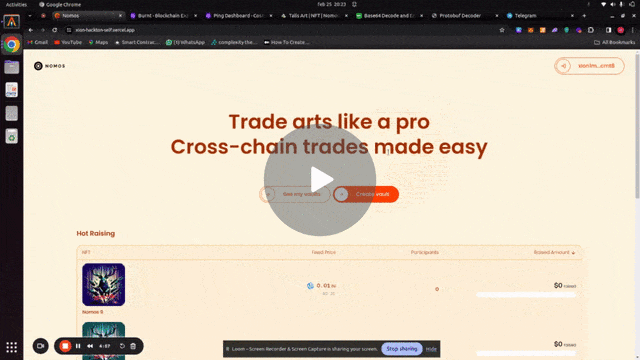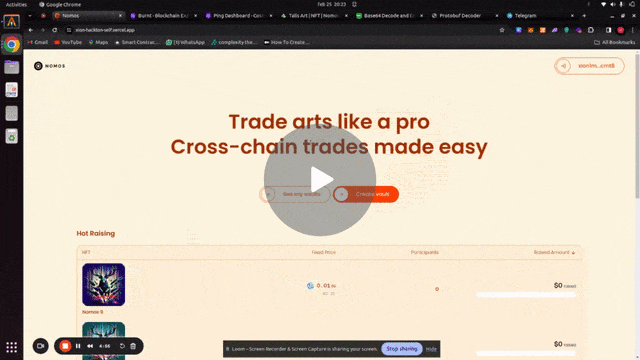
Each NFT controls an interchain account. The following is a demo of the project:
XION ABSTRACTATHON
Buying and selling and NFT from Xion on Injective using Nomos SDK and ICA controller
Building
We use cosmwasm/optimizer docker image to build the contract. This project uses just as the task runner. To install just, run the following command:
cargo install just
To build the contract, run the following command:
just build-optimize
Testing
There are two kinds of tests in this repository: unit tests and end to end tests. The unit tests are located inside the rust files in the src directory. The end to end tests are located in the e2e directory.
Unit tests
In general, the unit tests are for testing the verification functions for the handshake, and for testing that the serializers and deserializers are working correctly. To run the unit tests, run:
just unit-tests
End to end tests
The end to end tests are for testing the contract's functionality in an environment mimicking production. To see whether or not it can perform the channel handshake, send packets, and execute callbacks. We achieve this by running two local chains, one for the contract, and one for the host chain. The relayer is then used to perform the channel handshake, and send packets. The contract then executes callbacks based on the result of the packet. To learn more about the end to end tests, see the Readme in the e2e directory.
Releases
This contract follows semantic versioning, but with the following deviations:
- A major version will not be tagged until the contract is audited.
- All API breaking changes and most state-machine breaking changes will result in a minor version bump.
Limitations
This contract is not meant to be used in production. It is meant to be used as a reference implementation for how to build a CosmWasm contract that can communicate with the golang ica/host module. The following are some of the limitations of this contract:
- The contract cannot create multiple interchain accounts. It can only create one.
Acknowledgements
Much thanks to Art3mix and CyberHoward for all the helpful discussions. Also thanks to 0xekez for their work on cw-ibc-example which was a great reference for CosmWasm IBC endpoints and interchaintest.
Dependencies
~19MB
~410K SLoC