22 releases
Uses new Rust 2024
| new 0.4.1 | May 22, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.3.4 | May 6, 2025 |
| 0.3.3 | Nov 21, 2024 |
| 0.2.18 | Dec 21, 2022 |
| 0.2.9 | Mar 17, 2022 |
#228 in Concurrency
529 downloads per month
275KB
4K
SLoC
Congee
A Rust implementation of ART-OLC concurrent adaptive radix tree. It implements the optimistic lock coupling with proper SIMD support.
It only supports (and is optimized for) fixed sized 8 byte key; due to this specialization, congee has great performance -- basic operations are faster than most hash tables, range scan is an order of magnitude faster.
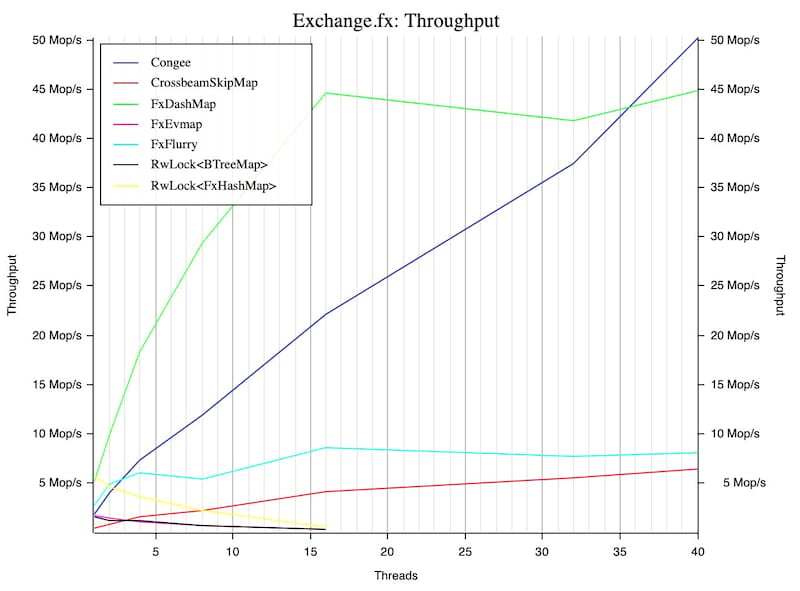
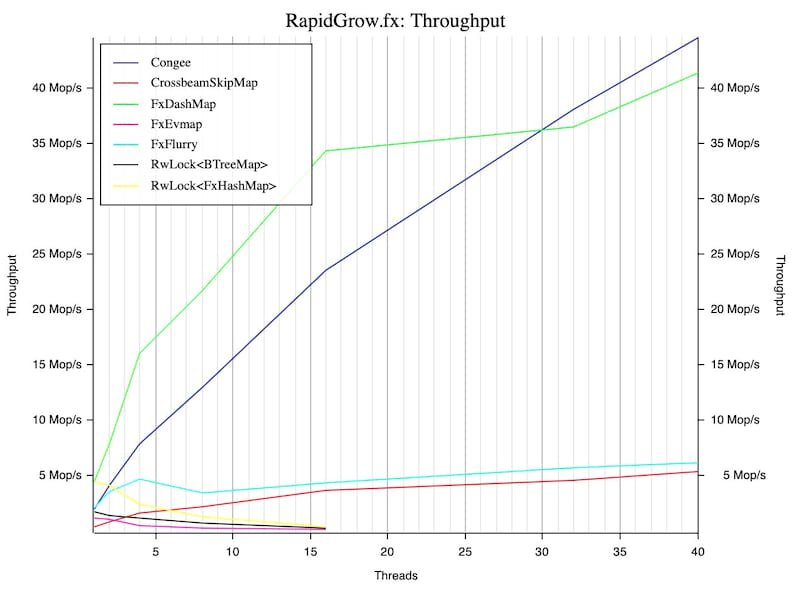
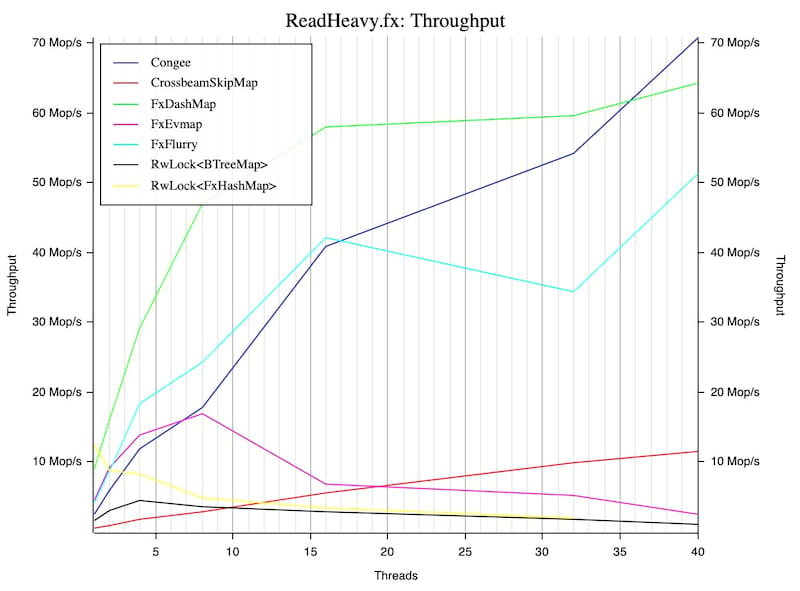
The codebase is extensively tested with {address|leak} sanitizer as well as libfuzzer. Congee's performance is continuously tracked here.
Why Congee?
- Fast performance, faster than most hash tables.
- Concurrent, super scalable, it reaches 150Mop/s on 32 cores.
- Super low memory consumption. Hash tables often have exponential bucket size growth, which often lead to low load factors. ART is more space efficient.
Why not Congee?
- Not for arbitrary key size. This library only supports 8 byte key.
Design principles
Congee aims to be a simple and reliable primitive for building database systems.
Example with CongeeArc:
use congee::CongeeArc;
use std::sync::Arc;
let art = CongeeArc::new();
let guard = art.pin(); // enter an epoch
let value = Arc::new(String::from("hello"));
art.insert(1, value.clone(), &guard).unwrap();
let retrieved = art.get(1, &guard).unwrap();
assert_eq!(retrieved.as_ref(), "hello");
// Update
art.compute_if_present(
1,
|current| Some(Arc::new(format!("{} world", current))),
&guard
);
let updated = art.get(1, &guard).unwrap();
assert_eq!(updated.as_ref(), "hello world");
let removed = art.remove(1, &guard).unwrap();
assert_eq!(removed.as_ref(), "hello world");
Example with usize KV:
use congee::Congee;
let art = Congee::default();
let guard = art.pin(); // enter an epoch
art.insert(0, 42, &guard); // insert a value
let val = art.get(&0, &guard).unwrap(); // read the value
assert_eq!(val, 42);
let mut scan_buffer = vec![(0, 0); 8];
let scan_result = art.range(&0, &10, &mut scan_buffer, &guard); // scan values
assert_eq!(scan_result, 1);
assert_eq!(scan_buffer[0], (0, 42));
Performance
Benchmarked with the conc-map-bench