36 releases
| 0.11.3 | Apr 30, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.11.2 | Jan 21, 2025 |
| 0.11.0 | Jun 14, 2024 |
| 0.10.2 | Feb 3, 2024 |
| 0.2.4 | Feb 9, 2023 |
#28 in Math
12,112 downloads per month
Used in 23 crates
(9 directly)
230KB
4.5K
SLoC
common_traits
A collection of traits and dependencies that can be used to write code
that is generic over numerical types. It provides also atomic floats
implemented using the integer atomic byte with the same number of bits,
and support for half precision floats via the crate half.
Additionally, there are a few traits
missing from the standard library, such as Sequence, variants
of existing library traits such as [Rng] and Hash, and macros like
invariant.
Finally, we provide traits for casting between types, such as UpcastableInto,
and fast implementation of a few primitives such FastRange and SelectInWord.
Everything is experimental and I'll change them to my needs, respecting semantic versioning. :)
Example
Mixed precision generic dot products!
use common_traits::*;
#[inline]
pub fn dot_product<MT: Number, RT: Number, A, B>(a: A, b: B) -> RT
where
A: Sequence,
B: Sequence,
A::Item: To<MT>,
B::Item: To<MT>,
MT: To<RT>,
RT: To<MT>,
{
// Ensure compatability of the vectors
invariant_eq!(a.len(), b.len());
// Compute the dot product
let mut accum = RT::ZERO;
for (a, b) in a.iter().zip(b.iter()) {
accum = (a.to()).mul_add(b.to(), accum.to()).to();
}
accum
}
let x: Vec<f32> = vec![1.0, 2.0, 3.0];
let w: Vec<u8> = vec![3, 2, 1];
// compute the dot product between f32 and u8, casting to f64 and
// accumulating as u16
let res: u16 = dot_product::<f64, _, _, _>(&x, &w);
println!("{:?}", res);
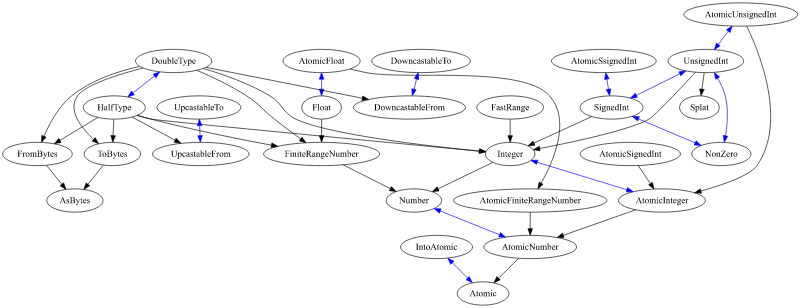
Numerical traits at a glance
The numerical traits dependancy chains is the following. Black arcs represent the traits dependancies, the blu arcs represent the possibility to access an associated type implementing that trait.
Why?
The point of making this crate public is to be able to discuss this as it covers many core missings from Rust.
The traits in this crate are similar to the ones from
num-traits
but they are more interconnected (the blue arcs in the previous graph), which allows to write generic code
(e.g., code mixing a type and its associated atomic type) more easily
and with less trait bounds.
Summary
An highlight of common_traits most noteworthy features.
Macros
This crate adds the following macros, invariant, invariant_eq, invariant_ne
which are similar to the std debug_assert macros, which get checked during debug
runs and get replaced with an unreachable_unchecked on release builds.
Structs
This crate adds emulated atomic floats through fetch_update
for the following types:
- [
f64] asAtomicF64 - [
f32] asAtomicF32 half::f16asAtomicF16half::bf16asAtomicBF16
Numerical Traits
This crate provides the following traits for numerical types:
NumberSomething that can be added, subtracted, multiplied, divided and has a Zero and a One.FiniteRangeNumberaNumberwhich has a Minimum and a Maximum.Floatfloat numbers.Integeran integer number represented as a sequence of bits.SignedInta signed integer represented in 2-complement.UnsignedIntan unsigned integer.
Atomic Numerical Traits
There are two main traits for working with atomic values:
Atomicfor values that can be read and written atomically.IntoAtomicfor values that can be converted into atomic types.
Each numerical trait has an atomic equivalent:
Miscellaneous Traits
The crate also contains a couple of extra traits:
Sequence,SequenceMut, andSequenceGrowableto abstract over slices and other sequence like types.AsBytes,ToBytesandFromBytesare traits used to convert forward and back types to bytes.NonZeroa version ofSelfwhich cannot be zero,UnsignedIntandSignedInthave an associated type implementing this.FastRangefor faster div, mod, and range operations.SelectInWordto find the position of the i-th 1 or 0 in words of memory.Splatto broadcast a smaller type on a larger type, mainly used for SWAR.- [
Rng] for a generic random number generator. Hasherwhich is likestd::hash::Hasherbut allow returing a generic type instead of anu64.SeedableHasherwhich is a standard way to initialize hashers
Conversion traits
Traits for conversion between types are also provided:
- [
To], to cast primitve values usingas. DoubleTypeandHalfTypecan be used to access bigger or smaller types in a generic way.UpcastableIntoandUpcastableFromto cast primitive values which can not lose precision.
DowncastableIntoandDowncastableFromto cast primitive values which can lose precision.
CastableIntoandCastableFromto cast primitive values which may or may not lose precision. This is the union ofDowncastableIntoandUpcastableInto.
The difference between Castable and [To] is that Castable does not
allow casting from f32 to u32 for example,
because Castable is implemented only between integers and between floats,
while [To] is implemented for all primitive types.
Features
This crate has the following features:
simd: To enableportable_simdand be able to do generic simd codeatomic_from_mut: to add theget_mut_sliceandfrom_mut_slicemethodsstd: to disable forno_stdhalf: to enable support forhalf::f16(Experimental)
Dependencies
~0.5–1MB
~22K SLoC