56 releases
| 0.21.2 | Feb 28, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.21.0 | Oct 29, 2024 |
| 0.21.0-pre.0 | Jul 30, 2024 |
| 0.20.0 | Feb 16, 2024 |
| 0.2.0 | Mar 6, 2017 |
#263 in Cargo plugins
150,595 downloads per month
Used in 13 crates
(11 directly)
355KB
7.5K
SLoC
RustSec: cargo audit
Audit your dependencies for crates with security vulnerabilities reported to the RustSec Advisory Database.
Requirements
cargo audit requires Rust 1.74 or later.
Installation
cargo audit is a Cargo subcommand and can be installed with cargo install:
$ cargo install cargo-audit --locked
Once installed, run cargo audit at the toplevel of any Cargo project.
Alpine Linux
# apk add cargo-audit
Arch Linux
# pacman -S cargo-audit
MacOS
$ brew install cargo-audit
OpenBSD
# pkg_add cargo-audit
Screenshot
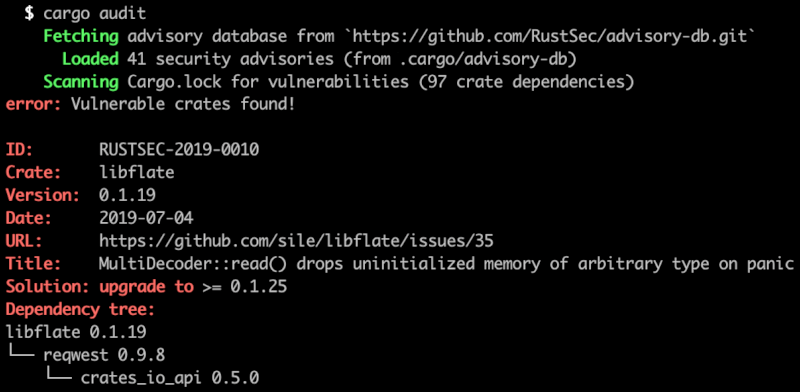
cargo audit fix subcommand
This tool supports an experimental feature to automatically update Cargo.toml
to fix vulnerable dependency requirements.
To enable it, install cargo audit with the fix feature enabled:
$ cargo install cargo-audit --locked --features=fix
Once installed, run cargo audit fix to automatically fix vulnerable
dependency requirements in your Cargo.toml:
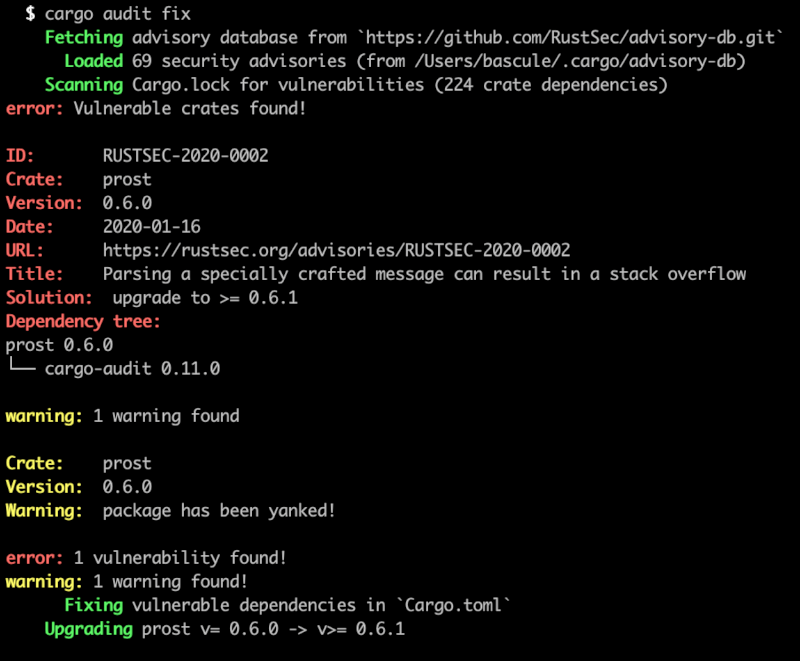
This will modify Cargo.toml in place. To perform a dry run instead, which
shows a preview of what dependencies would be upgraded, run
cargo audit fix --dry-run.
cargo audit bin subcommand
Run cargo audit bin followed by the paths to your binaries to audit them:
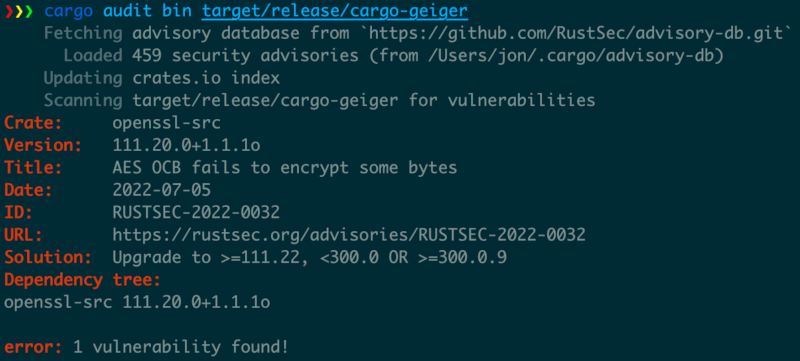
You can scan a directory recursively using fd:
fd --type=executable --exec-batch cargo audit bin
If your programs have been compiled with cargo auditable,
the audit is fully accurate because all the necessary information is embedded in the compiled binary.
For binaries that were not compiled with cargo auditable
it will recover a part of the dependency list by parsing panic messages.
This will miss any embedded C code (e.g. OpenSSL) as well as roughly half of the Rust dependencies
because the Rust compiler is very good at removing unnecessary panics,
but that's better than having no vulnerability information whatsoever.
Ignoring advisories
The first and best way to fix a vulnerability is to upgrade the vulnerable crate.
But there may be situations where an upgrade isn't available and the advisory doesn't affect your application. For example the advisory might involve a cargo feature or API that is unused.
In these cases, you can ignore advisories using the --ignore option.
$ cargo audit --ignore RUSTSEC-2017-0001
This option can also be configured via the audit.toml file.
Using cargo audit on Travis CI
To automatically run cargo audit on every build in Travis CI, you can add the following to your .travis.yml:
language: rust
cache: cargo # cache cargo-audit once installed
before_script:
- cargo install --force --locked cargo-audit
- cargo generate-lockfile
script:
- cargo audit
Using cargo audit on GitHub Action
Please use audit-check action directly.
Reporting Vulnerabilities
Report vulnerabilities by opening pull requests against the RustSec Advisory Database GitHub repo:

License
Licensed under either of:
- Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
- MIT license (LICENSE-MIT or https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
Contribution
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you shall be dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.
Dependencies
~8–19MB
~238K SLoC
