6 stable releases
| 1.0.5 | Dec 20, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 1.0.3 | Jun 13, 2023 |
| 1.0.2 | Jun 12, 2023 |
| 1.0.0 | Jun 11, 2023 |
#328 in Algorithms
37 downloads per month
22KB
230 lines
tiny_sort binary-size optimized sort implementations
The tiny_sort crate provides two sort implementations tiny_sort::stable::sort and tiny_sort::unstable::sort. The crate is no_std and both versions can be disabled via features, by setting default-features = false. tiny_sort::stable::sort requires alloc, tiny_sort::unstable::sort doesn't. In addition to fn sort<T: Ord>(v: &mut [T]), both sort implementations also provide fn sort_by<T, F: FnMut(&T, &T) -> Ordering>(v: &mut [T], mut compare: F) to sort with a custom comparison function.
Use these sort implementations if you care about binary-size more than you care about performance. Otherwise use slice::sort and slice::sort_unstable.
A closer look at the implementations.
stable::sort
The stable sort is a branchless mergesort. This means:
- Guaranteed O(N * log(N)) worst case perf
- No adaptiveness
- Branch miss-prediction not affected by outcome of comparison function
- Allocates N auxiliary memory.
unstable::sort
The unstable sort is a branchless heapsort. This means:
- Guaranteed O(N * log(N)) worst case perf
- No adaptiveness
- Branch miss-prediction not affected by outcome of comparison function
Benchmarks
Setup
Linux 6.3
rustc 1.76.0-nightly (f704f3b93 2023-12-19)
clang version 15.0.7
gcc (GCC) 13.1.1 20230429
AMD Ryzen 9 5900X 12-Core Processor (Zen3 micro-architecture)
CPU boost enabled.
Contestants:
- rust_tinymergesort_stable | This crate' `stable::sort`
- rust_std_stable | `slice::sort` https://github.com/rust-lang/rust (1)
- cpp_std_gnu_stable | libstdc++ `std::sort_stable` (2)
- cpp_std_libcxx_stable | libc++ `std::sort_stable` (3)
- rust_tinyheapsort_unstable | This crate' `unstable::sort`
- rust_std_unstable | `slice::sort_unstable` https://github.com/rust-lang/rust (1)
- cpp_std_gnu_unstable | libstdc++ `std::sort` (2)
- cpp_std_libcxx_unstable | libc++ `std::sort` (3)
Footnotes:
- Vendored ca. mid 2022.
- Built with gcc.
- Built with clang.
Binary-size
A minimal program is compiled with --release, lto = "thin" and opt-level = "s" for the Rust code and -Os for the header only C++ code. The C++ code is compiled with gcc. And the resulting binary is stripped with strip.
#[inline(never)]
fn instantiate_sort<T: Ord + std::fmt::Display>(mut v: Vec<T>) {
tiny_sort::unstable::sort(&mut v);
// side-effect
println!("{}", v[v.len() - 1]);
}
fn main() {
use std::env;
let len = env::args().len();
// The vec pattern is hard to predict for the compiler.
// And the len is unknown by design.
// Plus instantiate_sort is forced to inline never which means it has to be
// compiled in a way that could accept all possible layout of v.
instantiate_sort((0..len as u64).rev().collect());
}
The baseline with the sort uncommented is: 292_864 bytes. The values below are the stripped binary size subtracted from the baseline.
- rust_tinymergesort_stable | 528 bytes
- rust_std_stable | 2928 bytes
- cpp_std_gnu_stable | 5528 bytes
- cpp_std_libxx_stable | 4368 bytes
- rust_tinyheapsort_unstable | 320 bytes
- rust_std_unstable | 3848 bytes
- cpp_std_gnu_unstable | 2128 bytes
- cpp_std_libcxx_unstable | 1272 bytes
Run-time
A rough estimate what kind of performance you can get with these sort implementations. If you care about performance use slice::sort and slice::sort_unstable.
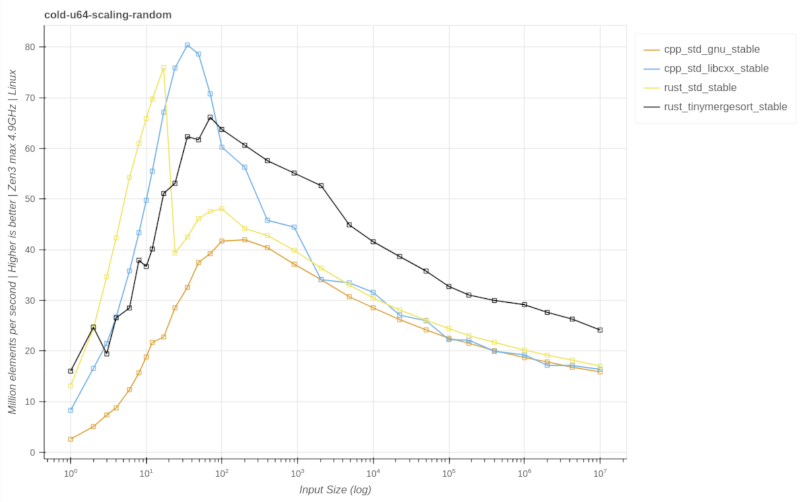
stable::sort
hot-u64-10k
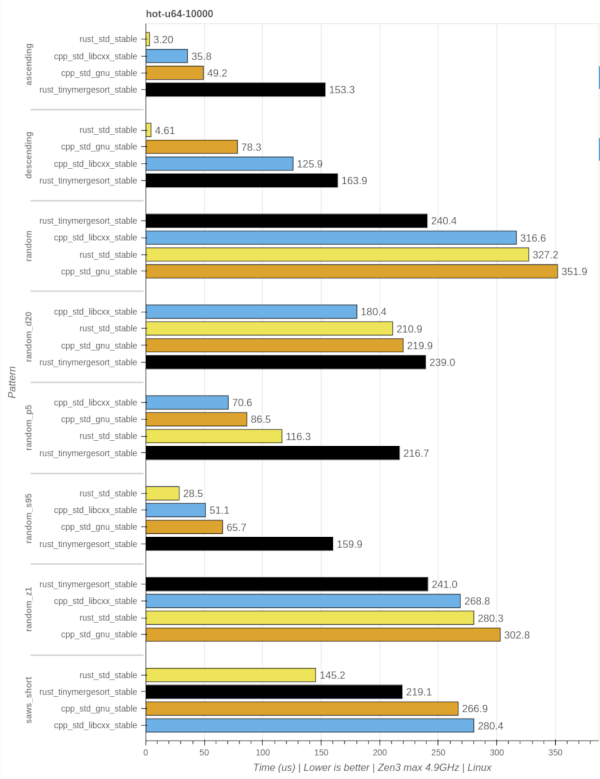
cold-u64-scaling-random
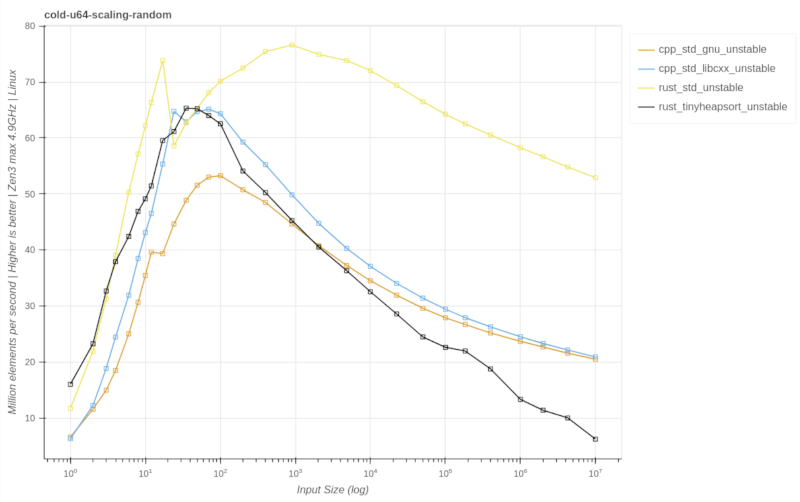
unstable::sort
hot-u64-10k
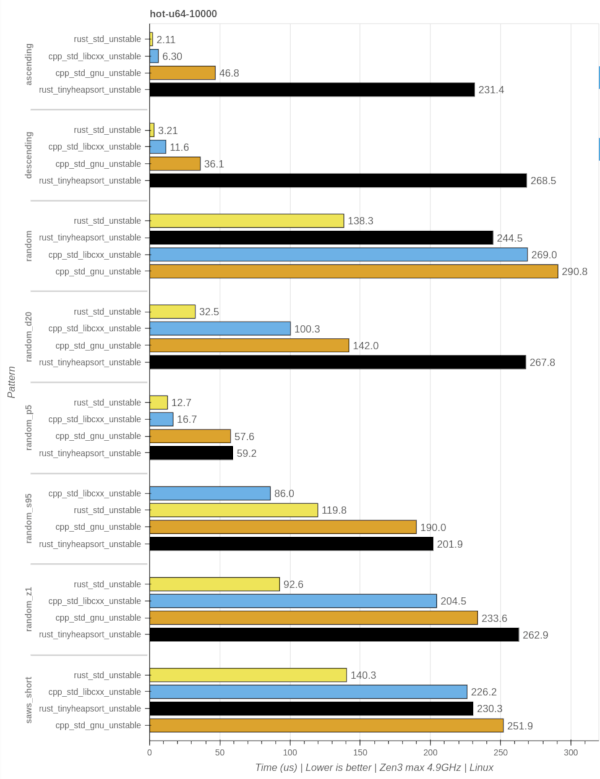
cold-u64-scaling-random
Min required rustc version
The minimum required rustc version is 1.51.
The minimum versions are best-effort and may change with any new major release.
Contributing
Please respect the CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md when contributing.
Versioning
We use SemVer for versioning. For the versions available, see the tags on this repository.
Authors
- Lukas Bergdoll - Initial work - Voultapher
See also the list of contributors who participated in this project.
License
This project is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 - see the LICENSE.md file for details.