6 releases
| 0.0.6 | Jan 18, 2020 |
|---|---|
| 0.0.5 | Jan 18, 2020 |
#1721 in Data structures
14KB
114 lines
ternary-tree-wasm
A WebAssembly binding to Rust ternary-tree crate.
A Ternary Search Tree (TST) is a data structure which stores key/value pairs in a tree. The key is a string, and its characters are placed in the tree nodes. Each node may have three children (hence the name): a left child, a middle child and a right child.
A search in a TST compares the current character in the key with the character of the current node:
- If both matches, the search traverses the middle child, and proceed to the next character in the key
- If the key character is less than the node one, the search simply goes through the left child, and keep looking for the same key character
- Respectively, if the key character is greater than the node one, the search simply goes through the right child
The data structure and its algorithm are explained very well in Dr.Dobb's Ternary Search Trees article.
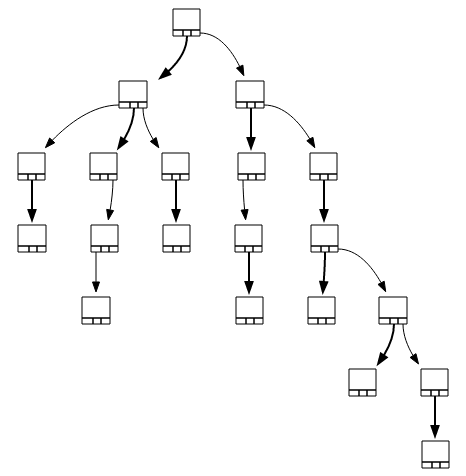
The following tree is the TST we get after inserting the following keys in order: "aba", "ab", "bc", "ac", "abc",
"a", "b", "aca", "caa", "cbc", "bac", "c", "cca", "aab", "abb", "aa" (see tst.dot produced by code below)
A checked box "☑" denotes a node which stores a value (it corresponds to the last character of a key). An empty box "☐" means that the node has no value.
A TST can be used as a map, but it allows more flexible ways to retrieve values associated with keys. This package provides four basic ways to iterate over the values of a TST:
- Apply a closure to all values stored in the tree (same as a regular map) with
tree.visit(closure, direction). See original iter doc 🦀 - Apply a closure to all values whose keys begin with some prefix (i.e. complete some prefix) with
tree.complete(prefix, closure, direction). See original iter_complete doc 🦀 - Apply a closure to all values whose keys are close to some string (Hamming distance) with
tree.neighbor(target, range, closure, direction). See original iter_neighbor doc 🦀 - Apply a closure to all values whose keys match a string with some joker (e.g. "a?c") with
tree.crossword(pattern, joker, closure, direction). See original iter_crossword doc 🦀
See the doc for a quick API walkthrough with live examples. The following lines may also give you a foretaste of this package.
//Load the package from npm through Unpkg.
//You need init, Tst and Direction.
import init, {Tst, Direction} from
"https://unpkg.com/ternary-tree-wasm/ternary_tree_wasm.js";
//Use it in an async function. Do not forget to call init.
async function run() {
await init();
//Create a new empty ternary search tree.
let tree = Tst.new();
let go = Direction;
let data = ["aba", "ab", "bc", "ac", "abc", "a", "b", "aca",
"caa", "cbc", "bac", "c", "cca", "aab", "abb", "aa"];
//Add 'matching' key value couples by deriving 'abc' strings.
for (const d of data) {
tree.insert("🗝" + d, "📦" + d);
}
let count = tree.count(); //count should be 16
//Use 'get' to retrieve the value of some key.
//value should be "📦abc"
let value = tree.get("🗝abc");
//Use 'remove' to delete a key ; if the key exists, the value
//associated with the key is returned.
value = tree.remove("🗝abc"); //value should be "📦abc"
count = tree.count(); //count should be 15
//Request for a key that does not exist returns null.
value = tree.get("🗝abc"); //value should be null
let array = [];
//Create a closure that will be called for all key value pairs
let push_all_items = function(key, value) {
array.push(`${key}=${value}`);
};
//If seeing more key value pairs is not needed, returning true
//from the closure will stop walking the tree.
let push_two_items = function(key, value) {
array.push(`${key}=${value}`);
let should_break = array.length >= 2;
return should_break;
};
//Use visit to call the closure on all key value pairs.
//Use Forward to get keys in alphabetical order and Backward to get
//them in reverse order.
tree.visit(push_all_items, go.Forward);
//array should contain all keys and values in alphabetical order :
//"🗝a=📦a","🗝aa=📦aa", [...], "🗝cbc=📦cbc","🗝cca=📦cca"
array = [];
//Use Backaward to get the last two items of the tree.
tree.visit(push_two_items, go.Backward);
//array should be "🗝cca=📦cca","🗝cbc=📦cbc"
array = [];
//Use complete with some prefix string to call the closure on all
//keys beginning with this prefix.
tree.complete("🗝ab", push_all_items, go.Forward);
//array should contain "🗝aba=📦aba", "🗝abb=📦abb"
//Note that "🗝ab=📦ab" is not present because there is nothing to
//complete (a prefix of some key can not be the whole key).
array = [];
//Use neighbor with some "target" key and a "range" to call the
//closure on all keys close to the target key (think of range as the
//number of errors allowed).
tree.neighbor("🗝abc", 1, push_all_items, go.Forward);
//array should be
//"🗝ab=📦ab", "🗝aba=📦aba", "🗝abb=📦abb", "🗝cbc=📦cbc"
array = [];
//Use crossword with some joker in the key to call the closure on
//all matching keys. You choose the joker character, and it will
//match excatly one key character.
tree.crossword("🗝?a?", "?", push_all_items, go.Forward);
//array should be "🗝aab=📦aab", "🗝bac=📦bac", "🗝caa=📦caa"
//Use pretty_print to generate a dot description of the tree.
let tree_dot = tree.pretty_print();
//tee_dot should contain a dot (from Graphviz tools) description of
//the tree.
//Use clear to remove all keys and values.
tree.clear();
count = tree.count(); //count should be 0
}
run();
License: BSD-3-Clause
Dependencies
~1–1.7MB
~30K SLoC