4 releases
Uses old Rust 2015
| 0.1.3 | Aug 11, 2016 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.2 | Apr 26, 2016 |
| 0.1.1 | Apr 22, 2016 |
| 0.1.0 | Apr 19, 2016 |
#195 in #hex
22KB
711 lines
Rorschach
Pretty print binary blobs based on common layout definition.
Example
use rorschach::{Definition, Field, LittleEndian};
use rorschach::formatter::{self, Color};
let def = Definition::default()
.field(Field::named("sequence")
.is::<u32>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(255).normal()))
.field(Field::named("buttons")
.bytes(3)
.binary()
.style(Color::Fixed(3).normal()))
.field(Field::named("trigger.left")
.is::<u8>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(255).on(Color::Fixed(63)).underline()))
.field(Field::named("trigger.right")
.is::<u8>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(255).on(Color::Fixed(63))))
.field(Field::padding()
.bytes(3))
.field(Field::named("pad.left.x")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(255).on(Color::Fixed(27)).underline()))
.field(Field::named("pad.left.y")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(27).normal()))
.field(Field::named("pad.right.x")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(255).on(Color::Fixed(36)).underline()))
.field(Field::named("pad.right.y")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(36).normal()))
.field(Field::padding()
.bytes(12))
.field(Field::named("acceleration.pitch")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(124).normal()))
.field(Field::named("acceleration.yaw")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(160).normal()))
.field(Field::named("acceleration.roll")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(196).normal()))
.field(Field::named("orientation.pitch")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(57).normal()))
.field(Field::named("orientation.yaw")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(93).normal()))
.field(Field::named("orientation.roll")
.is::<i16>(LittleEndian)
.style(Color::Fixed(129).normal()))
.field(Field::padding()
.bytes(16));
Structured
The structured formatter takes inspiration from the ASCII art tables often used in network related RFCs.
formatter::Structured::default()
.header(true)
.style(Default::default())
.format(&def, buffer, io::stdout())
.unwrap()
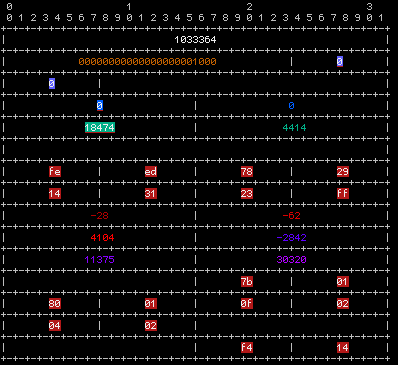
Inline
The inline formatter is the simplest formatter, it just prints the bytes as hexadecimal one after another, but it does support coloring which can help reversing formats.
formatter::Inline::default()
.newline(true)
.split(4)
.style(Default::default())
.format(&def, buffer, io::stdout())
.unwrap()
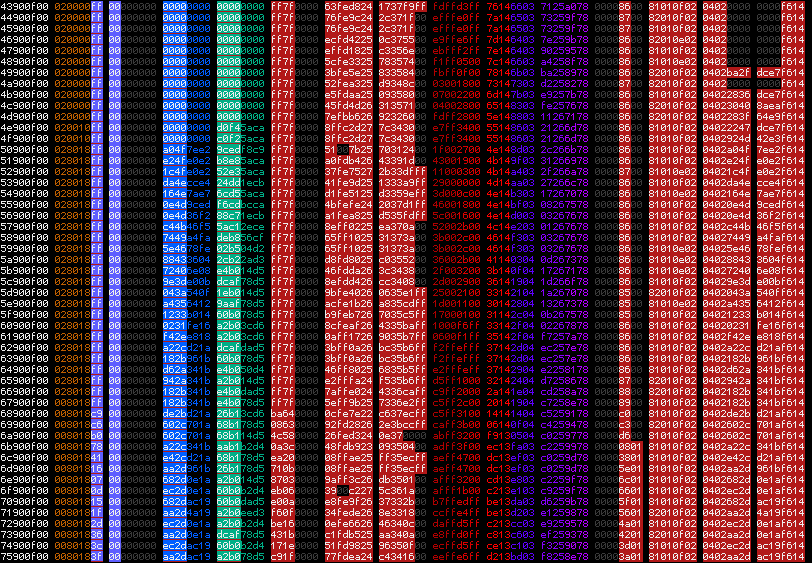
Dependencies
~235KB