46 stable releases
| 3.3.10 | Apr 5, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 3.3.9 | Mar 23, 2025 |
| 3.3.8 | Jan 11, 2025 |
| 3.3.7 | Nov 10, 2024 |
| 2.18.0 | Jul 21, 2022 |
#49 in Command line utilities
279 downloads per month
2MB
4K
SLoC
Riff, the Refining Diff
Riff is a wrapper around diff that highlights which parts of lines have changed.
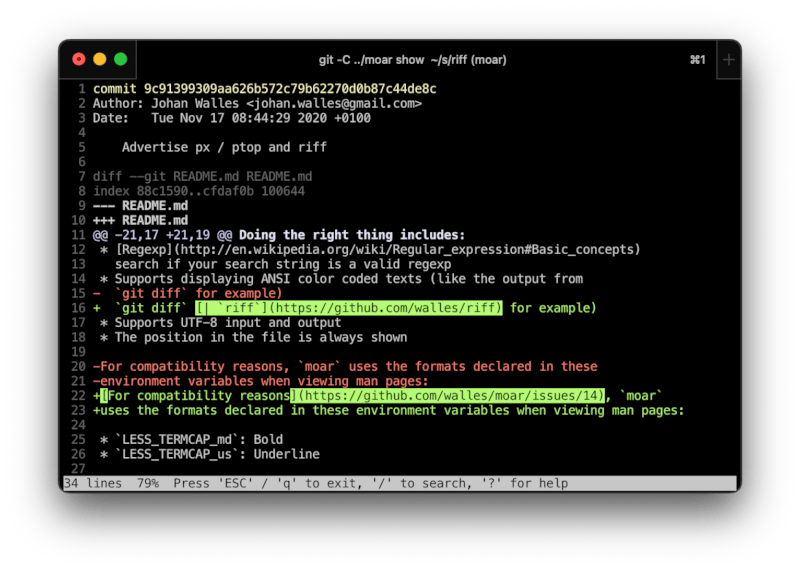
Unchanged parts of changed lines are shown in yellow.
riff also helpfully highlights conflicts and merge commits.
Much like git, Riff sends its output to a pager, trying these in order:
- Whatever is specified in the
$PAGERenvironment variable - moar because it is nice
lessbecause it is ubiquitous
Usage
git diff | riff
Or if you do...
git config --global pager.diff riff
git config --global pager.show riff
git config --global pager.log riff
git config --global interactive.diffFilter "riff --color=on"
... then all future git diff, git show and git log --patch output will be
refined.
Or you can use riff as an alias for diff:
riff file1.txt file2.txt
Configuration
You can configure riff by setting the RIFF environment variable to one or
more (space separated) command line options.
For example, set RIFF=--no-adds-only-special to disable adds-only special
highlighting.
Installation
With Homebrew
brew install riff
With Archlinux User Repository (AUR)
paru -S riffdiff
From the Rust Crate
cargo install riffdiff
Manual Install
-
Go here and download the correct binary for your platform
- If no binary exists for your platform, please report it
-
chmod a+x riff-* -
mv riff-* /usr/local/bin/riff -
Optionally followed by this to have riff highlight
gitoutput by default:
git config --global pager.diff riff
git config --global pager.show riff
git config --global pager.log riff
git config --global interactive.diffFilter "riff --color=on"
See Also
This VSCode extension for improved Git commit message editing is nice. Yes, I wrote it and I'm tooting my own horn here.
Good choice if you (like me!) are using VSCode for Git commit message editing.
More Features
riff can highlight conflict markers created by git:
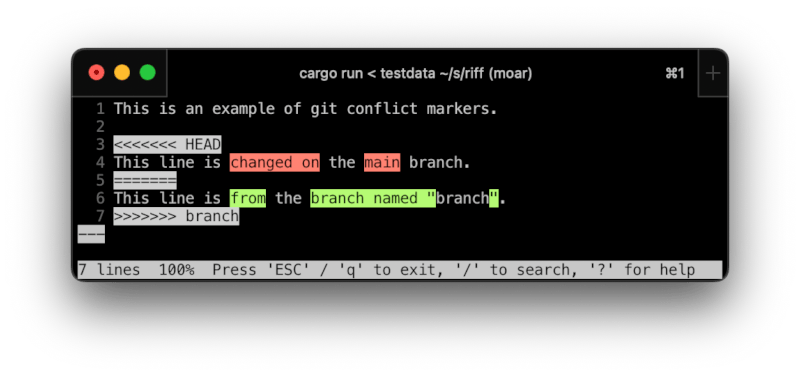
riff highlighting a git merge commits highlighting
Development
If you put example input and output in the testdata directory, then cargo test will verify that they match.
On mismatches, you can run testdata-examples.sh to compare current output to
the expected output for all examples, and optionally update expectations.
Invoke ci.sh to run the same thing as CI.
Invoke benchmark.py to get numbers for how fast your current source code is
versus earlier releases.
Invoke git log -p | cargo run -- to demo highlighting.
Making a new release
Just invoke ./release.sh and follow instructions.
If you want to test the release script without actually releasing anything, do:
./release.sh --dry
TODO
Misc
--help: Only print installing-into-$PATHhelp if we aren't already being executed from inside of the$PATH- Add test for never changing the number of lines in the input, that
messes up
git add -pbehavior. - Make sure we highlight the output of
git show --statproperly - Given three files on the command line, we should pass them and any
options on to
diff3and highlight the result
TODO future
- Detect moved blocks and use a number as a prefix for both the add and the remove part of the move. Highlight any changes just like for other changes.
DONE
- Make a main program that can read input from stdin and print it to stdout.
- Make the main program identify different kinds of lines by prefix
and color them accordingly. Use the same color scheme as
git. - Make the main program identify blocks of lines that have been replaced by another block of lines.
- Make the Refiner not highlight anything if either old or new is empty
- Use https://crates.io/crates/diffus to refine hunks
- Build refined hunks and print them
- Highlight
^diff,^index,^+++and^---lines in bold white - Prefix all added / removed lines with the correct ANSI color code
- Don't highlight the initial
+/-on added / removed lines - Make sure we get the linefeeds right in diffs, try
git show 28e074bd0fc246d1caa3738432806a94f6773185with and withoutriff. - Visualize added line endings
- Visualize removed line endings
- Visualize removed linefeed at end of file properly
- Visualize adding a missing linefeed at end of file properly
- Visualize missing linefeed at end of file as part of the context properly
- Refine
ax->bx\ncproperly - Strip all color from the input before handling it to enable users to set Git's pager.diff and pager.show variables to 'riff' without also needing to set color.diff=false.
- If stdout is a terminal, pipe the output to a pager using the
algorithm described under
core.pageringit help config. - You can do
git diff | riffand get reasonable output. - Do not highlight anything if there are "too many" differences between the sections. The point here is that we want to highlight changes, but if it's a replacement rather than a change then we don't want to highlight it.
- Refine by word rather than by character
- Test case
git show 2ac5b06: Should highlight all of bothsomeandone or.
- Test case
- Do some effort to prevent fork loops if people set
$PAGERtoriff - Add support for
--help - Add support for
--version - Print help and bail if stdin is a terminal
- On exceptions, print the current version just like
--version - On exceptions, print a link to the issue tracker
- Add test case verifying that the
Inspired bypart ofgit show 77c8f77 -- bin/riffis highlighted as an upside down L. - Find out how the LCS algorithm scales and improve the heuristic for when not to call it.
- Tune the upper bound on how large regions we should attempt to refine
- Make a CI script
- Set up CI calling the CI script
- Document
ci.sh's existence - Figure out cross compiling to Linux and macOS ARM (look into
crosswhich uses Docker for cross compiling) - Make a release script
- Document
release.sh's existence - Verify that the Linux binary works
- Document install instructions
- Make a public release
- Remedy
release.shFIXMEs - Add a trailing whitespace analysis pass to the Refiner
- Let the Refiner highlight whitespace errors among the added lines in reverse red.
- Highlight whitespace in added parts only
- Add highlighting of non-leading tabs to the whitespace analysis
- Profile and see if we can go faster
- In
ci.sh, add a test case verifying that our exception handler prints backtraces in release builds (should fail when stripping the release binary) - In
ci.sh, add a test case verifying that our exception handler prints line numbers for theriffframes in the backtraces, in release builds. This should fail when stripping the release binary. - Require line numbers in backtraces in release builds
- Make the Linux binary smaller
- Put argv contents in crash report
- Handle plain non-git diff files
- Given two files on the command line, we should pass them on to
diffand highlight the result. - Support
riff -b path1 path2to diff files ignoring whitespace - Bound how-much-to-highlight restriction by number of characters highlighted rather than by number of tokens highlighted
- Get ourselves some kind of benchmark suite / example(s)
- Do
git show 5e0a1b2b13528f40299e78e3bfa590d9f96637afand scroll to the end. How should we visualize the reformatting of the No-newline-at-eof code? - Do
git show 0f5dd84and think about how to visualize one line changing to itself with a comma at the end plus a bunch of entirely new lines. Think of a constant array getting one or more extra members. - Do
git show -b 77c8f77and think about what rule we should use to highlight the leading spaces of the+ refinedand+ pagelines at the end of the file. - Do
git show 57f27daand think about what rule we should use to get the REVERSE vs reversed() lines highlighted. - Think about how to visualize an added line break together with some indentation on the following line.
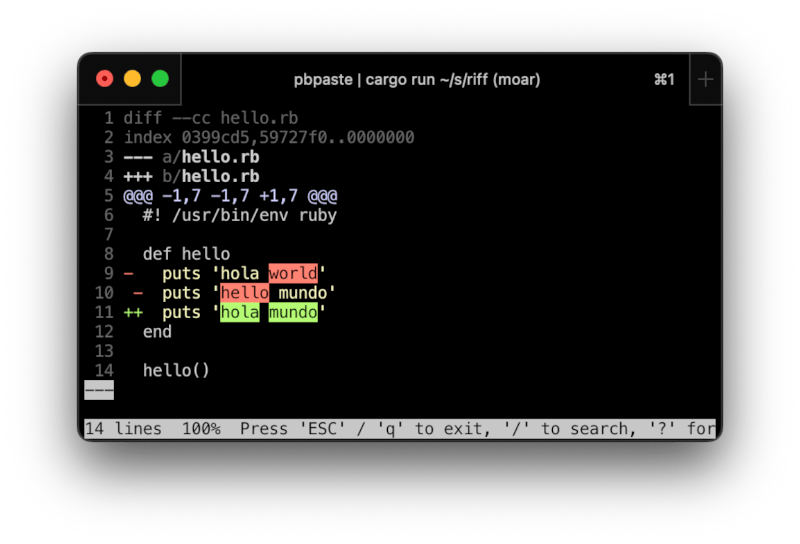
- Make sure we can handle a
gitconflict resolution diff. File format is described at http://git-scm.com/docs/git-diff#_combined_diff_format. - Render ESC characters in the diff as Unicode ␛
Dependencies
~6–13MB
~168K SLoC