43 releases (15 breaking)
| 0.16.0 | Dec 26, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 0.14.0 | Dec 4, 2023 |
| 0.13.0 | Oct 24, 2023 |
| 0.8.13 | Jul 15, 2023 |
| 0.3.3 | Mar 31, 2023 |
#26 in Value formatting
541,012 downloads per month
Used in 7 crates
(6 directly)
525KB
9K
SLoC
Readable
Human readable strings.
This library:
- Transforms various data types into human-readable strings
- Parses raw string data into human-readable versions
- Provides various string types and utilities
Most of the strings are implemented as fixed sized stack allocated arrays that are Copy-able.
In general, readable types are often used where you need to quickly format some data into a more human-friendly string, display it, then throw it away (although most readable types are perfectly fine to permanently store).
Creation of readable types is relatively performant.
Examples
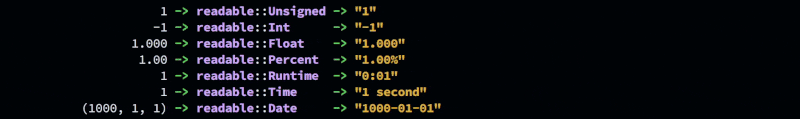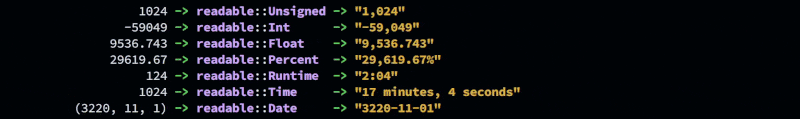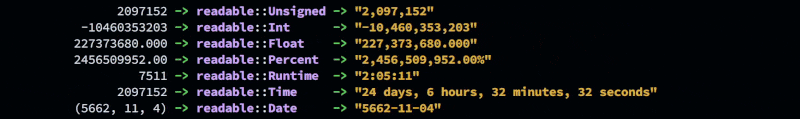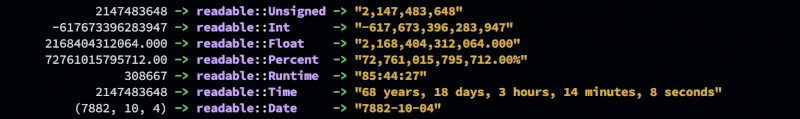
Unsigned
use readable::num::*;
assert_eq!(Unsigned::from(1000_u64), "1,000");
Int
use readable::num::*;
assert_eq!(Int::from(-1000), "-1,000");
Float
use readable::num::*;
assert_eq!(Float::from(1000.123), "1,000.123");
Percent
use readable::num::*;
assert_eq!(Percent::from(1000.123), "1,000.12%");
Runtime
use readable::run::*;
assert_eq!(Runtime::from(311.123), "5:11");
assert_eq!(RuntimePad::from(311.123), "00:05:11");
assert_eq!(RuntimeMilli::from(311.123), "00:05:11.123");
Uptime
use readable::up::*;
assert_eq!(Uptime::from(172799_u32), "1d, 23h, 59m, 59s");
assert_eq!(UptimeFull::from(172799_u32), "1 day, 23 hours, 59 minutes, 59 seconds");
assert_eq!(Htop::from(172799_u32), "1 day, 23:59:59");
Date
use readable::date::*;
assert_eq!(Date::from_ymd(2014, 12, 31).unwrap(), "2014-12-31");
assert_eq!(Nichi::new(2014, 12, 31).unwrap(), "Wed, Dec 31, 2014");
assert_eq!(NichiFull::new(2014, 12, 31).unwrap(), "Wednesday, December 31st, 2014");
Time
use readable::time::*;
assert_eq!(Time::new(86399), "11:59:59 PM");
assert_eq!(Military::new(86399), "23:59:59");
Byte
use readable::byte::*;
assert_eq!(Byte::from(1234), "1.234 KB");
Comparison
All number types implement PartialEq against str and their internal numbers.
This is comparing b's inner String:
use readable::up::*;
let a = std::time::Duration::from_secs(86399);
let b = UptimeFull::from(a);
assert_eq!(b, "23 hours, 59 minutes, 59 seconds");
This is comparing a's inner i64:
use readable::num::*;
let a = Int::from(-1000);
assert_eq!(a, -1000);
This compares both the u64 AND String inside a and b:
use readable::num::*;
let a = Unsigned::from(1000_u64);
let b = Unsigned::from(1000_u64);
assert_eq!(a, b);
Arithmetic
All number types implement the common arithmetic operators +, -, /, *, %, outputting a new Self.
+ Addition
use readable::num::*;
let f1 = Float::from(1.0);
let f2 = Float::from(2.0);
assert_eq!(f1 + f2, 3.0);
- Subtraction
use readable::num::*;
let p50 = Percent::from(50.0);
let p25 = Percent::from(25.0);
assert_eq!(p50 - p25, "25.00%");
/ Division
use readable::num::*;
let u100 = Unsigned::from(100_u64);
let u10 = Unsigned::from(10_u64);
assert_eq!(u100 / u10, 10);
* Multiplication
use readable::num::*;
let u10 = Unsigned::from(10_u64);
assert_eq!(u10 * u10, Unsigned::from(100_u64));
% Modulo
use readable::num::*;
let u10 = Unsigned::from(10_u64);
assert_eq!(u10 % u10, 0);
Feature Flags
These features are for (de)serialization.
| Feature Flag | Purpose |
|---|---|
serde |
Enables serde's Serialize & Deserialize |
bincode |
Enables bincode 2.0.0-rc.3's Encode & Decode |
borsh |
Enables borsh's BorshSerialize & BorshDeserialize |
MSRV
The Minimum Supported Rust Version is 1.71.0.
Dependencies
~0–1.6MB
~29K SLoC