229 releases (120 stable)
Uses new Rust 2024
| 1.73.0 | Apr 17, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 1.72.0 | Mar 11, 2025 |
| 1.71.30 | Dec 22, 2024 |
| 1.71.29 | Nov 5, 2024 |
| 0.6.10 | Jul 31, 2019 |
#40 in Command line utilities
318 downloads per month
350KB
7K
SLoC
IRust
Cross Platform Rust Repl
You can try out IRust with no installation or setup (via Gitpod.io) by visiting https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/sigmaSd/IRust
Keywords / Tips & Tricks
:help => print help, use :help full for the full version
:reset => reset repl
:show => show repl current code (optionally depends on rustfmt to format output)
:add <dep_list> => add dependencies also it accepts most cargo add arguments, for example you can import local dependencies with :add --path path_to_crate
:type <expression> => shows the expression type, example :type vec!(5)
:time <expression> => return the amount of time the expression took to execute. example: :time 5+4 :time my_fun(arg1,arg2)
:time_release <expression> => same as time command but with release mode
:load => load a rust file into the repl
:reload => reload the last specified file
:pop => remove last repl code line
:del <line_num> => remove a specific line from repl code (line count starts at 1 from the first expression statement)
:edit [editor] => edit internal buffer using an external editor, example: :edit micro. If no editor is specified then the one from the EDITOR environment variable is used (if set). Note some gui terminal requires using :sync command after the edit (vscode)
:sync sync the changes written after using :edit with a gui editor (vscode) to the repl
:cd => change current working directory
:color <key> <value> => change token highlight color at runtime, for the token list and value representation check the Theme section, exp: :color function red :color macro #ff12ab :color reset
:toolchain <value> => switch between toolchains, supported value are: stable, beta, nightly, default
:theme <value> => if used without arguments list currently installed themes, otherwise set irust to the given theme, see Themes section for more info
:check_statements true/false => If its set to true, irust will check each statemnt (input that ends with ;) with cargo_check before inserting it to the repl
:bench => run cargo bench
:asm <function> => shows assembly of the specified function, note that the function needs to be public, and there has to be no free standing statements/expressions (requires cargo-show-asm)
:executor <executor> => set the executor to be used by IRust, available options are: sync tokio async_std, by using an async executor, await becomes usable with no other modifications for async executors)
:evaluator <evaluator>> => set the evaluator statement, exmaple: :evaluator println!("{}",{$$}) the $$
will be replaced by IRust by the input code (the default evaluator uses debug formatting). To reset the evaluator to default you can use :evaluator reset
:scripts: => if invoked with no arguments it prints a list of detected scripts, if invoked with on argument it print that script info if it exits, if invoked with 2 arguments, it tries to activate/deactivate a script, example: :scripts Vim deactivate
:compile_time <on/off> => if set to on, IRust will print compiling time on each input, compile time includes rustc compiling + some IRust code (should be marginal)
:compile_mode <debug/release> => Sets how cargo will compile the code in release or debug mode
:main_result <value> => Change main result type, available options are Unit and Result (which is Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>>), Using Result as type allows to use ? in the repl without any boilerplate
:dbg <expression> => Spawn rust-lldb/rust-gdb with (an optional expression), example: :dbg or :dbg fact(12), The debugger can be specified in the config file
:expand [function] => Shows the result of macro expansion, requires https://github.com/dtolnay/cargo-expand, function is optional, example fn b() { println!("42"); } then :expand b
:exit | :quit => Exit IRust immediately
$$ => Shell commands can be interpolated with rust code with '$$', for example: let a = $$ls -l$$;, this feature can be en/disabled via the config file
:: => run a shell command, example ::ls
You can use arrow keys to cycle through commands history.
You can disable all colors by setting NO_COLOR env variable.
To enable completion with tab via rust-analyzer, set enable_rust_analyzer to true in the config.
Keybindings
ctrl-l clear screen
ctrl-c clear line
ctrl-d exit if buffer is empty
ctrl-z [unix only] send IRust to the background
ctrl-r search history, hitting ctrl-r again continues searching the history backward, hitting ctrl-s searches the history forward
ctrl-left/right jump through words
HOME/END go to line start / line end
Tab/ShiftTab cycle through completion suggestions
Alt-Enter | ctrl-s add line break
ctrl-e force evaluation
ctrl-o->[+-]key Start recording a macro and saved on the specified key, if ctrl-o is clicked again the recording is stopped
ctrl-p->key Play a macro saved on the specified key
ctrl-u Undo
ctrl-y Redo
ctrl-x Delete current line

Cli commands
--help prints help message
--reset-config reset IRust configuration to default
If input is piped to IRust then it will evaluate it and exit, example: echo '"hello".chars()' | irust
Configuration
IRust config file is located in:
Linux: /home/$USER/.config/irust/config.toml
Win: C:\Users\$USER\AppData\Roaming/irust/config.toml
Mac: /Users/$USER/Library/Application Support/irust/config.toml
default config:
# history
add_irust_cmd_to_history = true
add_shell_cmd_to_history = false
# colors
ok_color = "Blue"
eval_color = "White"
irust_color = "DarkBlue"
irust_warn_color = "Cyan"
out_color = "Red"
shell_color = "DarkYellow"
err_color = "DarkRed"
input_color = "Green"
insert_color = "White"
welcome_msg = ""
welcome_color = "DarkBlue"
# Rust analyzer
ra_inline_suggestion_color = "Cyan"
ra_suggestions_table_color = "Green"
ra_selected_suggestion_color = "DarkRed"
ra_max_suggestions = 5
enable_rust_analyzer = false
# other
first_irust_run = false
toolchain = "stable"
check_statements = true
auto_insert_semicolon = true
#use last output by replacing the specified marker
replace_marker = "$out"
replace_output_with_marker = false
# modify input prmopt
input_prompt = "In: "
output_prompt = "Out: "
# activate scripting feature
activate_scripting = false
# select executor (Sync, Tokio, Asyncstd)
executor = "Sync"
evaluator = ["println!(\"{:?}\", {\n", "\n});"]
compile_time = false
main_result = "Unit"
show_warnings = false
edition = "E2021"
debugger = "LLDB"
shell_interpolate = true
local_server = false
local_server_adress = "127.0.0.1:9000"
theme = "default"
Theme
Since release 1.66.0 IRust can now parse any theme file located under $config_dir/irust/themes and use it for the highlighting colors.
To select a theme, set its name in the irust config. for example to set themes/mytheme.toml set theme = "mytheme"
Colors can be specified as names ("red") or as hex representation ("#ff12ab").
Default theme file (default.toml):
keyword = "magenta"
keyword2 = "dark_red"
function = "blue"
type = "cyan"
symbol = "red"
macro = "dark_yellow"
literal = "yellow"
lifetime = "dark_magenta"
comment = "dark_grey"
const = "dark_green"
ident = "white"
Prelude
IRust automatically creates irust_prelude crate at xdg_data_dir/irust/irust_prelude, this crate is imported at startup, any changes to it (that are marked with pub) will be immediately reflected on the repl after saving.
Scripts
IRust supports scripting, all over the code base there are hooks that scripts can react to and usually answer back to IRust with a command.
Check out SCRIPTS.md for more info.
Vim Plugin
For nvim you can use https://github.com/hkupty/iron.nvim (needs irust 1.67.4)
Old method:
Since version 1.60.0 IRust supports spawning a local server, by changing local_server to true in the configuration file.
This allows it to be controlled programmatically, which in turns allows writing vim plugins that uses this, see https://github.com/sigmaSd/irust-vim-plugin
Jupyter Notebook
A Jupyter Kernel is available, see https://github.com/sigmaSd/IRust/blob/master/crates/irust_repl/README.md#jupyter-kernel for instructions
Book
The IRust Book is intended to document a couple of tips and tricks https://sigmasd.github.io/irust_book
Releases
Automatic releases by github actions are uploaded here https://github.com/sigmaSd/irust/releases
Install
cargo install irustcargo binstall irust(using cargo-binstall)
Building
cargo b --release
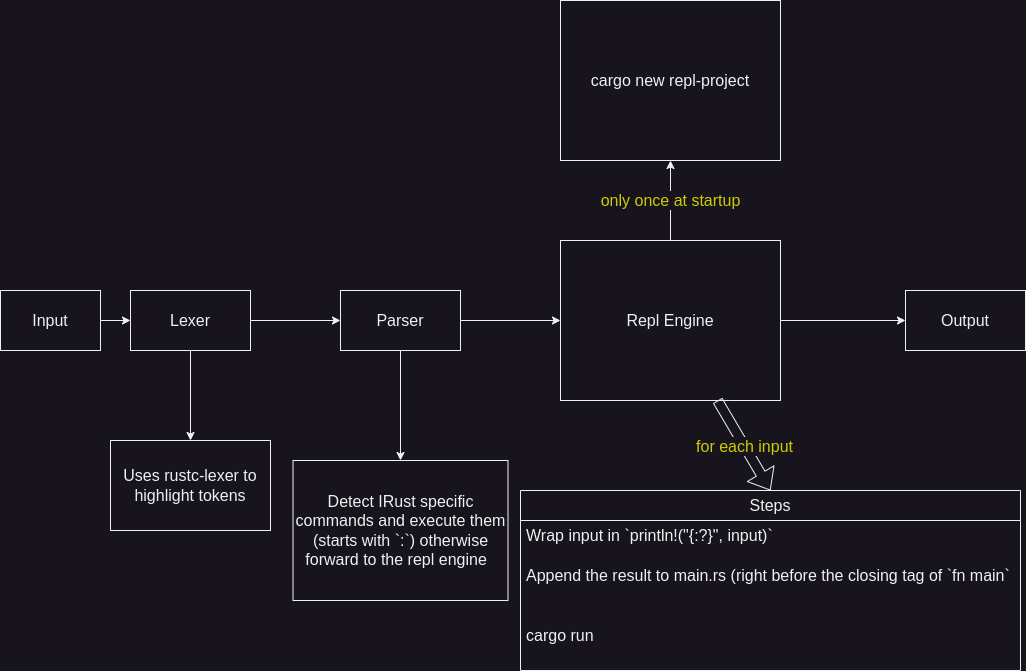
How It Works (random drawing ahead)
FAQ
1- I want to hack on irust but dbg! overlaps with the output!!
Personaly I do this:
- Run 2 terminals side by side
- run
ttyin the first which should output something like/dev/pts/4 - run
cargo r 2>/dev/pts4in the second
Now the dbg! statements are printed on the second terminal and the output in the first terminal is not messed up.
Changelog
Dependencies
~4–12MB
~137K SLoC