20 releases
| 0.2.5 | May 30, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.4 | Jul 6, 2022 |
| 0.2.3 | Mar 4, 2022 |
| 0.2.1 | Dec 29, 2021 |
| 0.1.1 | Oct 26, 2018 |
#188 in Data structures
2,330 downloads per month
Used in 4 crates
(2 directly)
110KB
2K
SLoC
IDLSet
IDLSet - Fast u64 integer set operations
IDLSet is a specialised library for fast logical set operations on u64. For example, this means union (or), intersection (and) and not operations on sets. In the best case, speed ups of 15x have been observed with the general case performing approximately 4x faster that a Vec based implementation.
These operations are heavily used in low-level implementations of databases for their indexing logic, but has applications with statistical analysis and other domains that require logical set operations.
How Does It Work?
Each set initially is "sparse". This is stored in the manner you expect historically,
using a Vec<u64> internally.
::
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, ... , 1024 ]
You can then call maybe_compress on the set, which will look at the content and determine
if it would be beneficial to compress this. When compressed, each value is transformed into
a tuple pair of range and mask. The range represents the starting value of this set of
64 values, and the mask determines if a value of that range is present. For example:
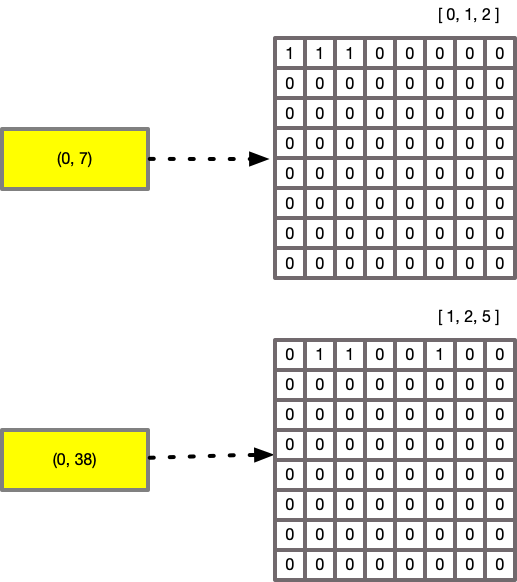
As these now contain a bit mask, we can use CPU operations for logical operations like AND, OR and
AND NOT. This example demonstrates an AND operation.
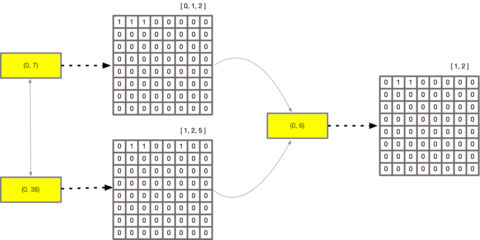
Due to this compression, on high density sets, memory is reduced, as is improvements to CPU cache behaviour due to lower pressure on the caches. It also allows faster seeking through sets to determine value presence.
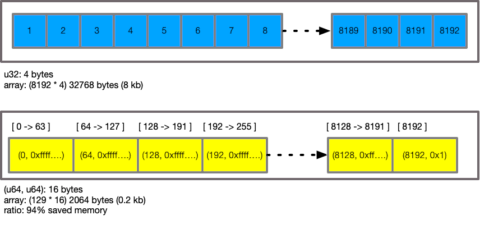
During operations between compressed and uncompressed sets, the "better" choice of compressed or uncompressed is preserved for the result set based on the inputs and operation performed. In other words, the result set may be compressed or uncompressed depending on the operation and it's interactions, to improve performance of subsequent operations. This helps to carry forward these optimisation choices to result sets meaning that chained and many operations over sets, and reduces memory consumption of intermediate set results during operations.
Contributing
Please open an issue, pr or contact me directly by email (see github)
Dependencies
~0.3–1MB
~21K SLoC