6 releases
| new 0.2.2 | May 19, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.1 | May 15, 2025 |
| 0.2.0 | Apr 30, 2025 |
| 0.1.2 | Apr 27, 2025 |
#130 in Machine learning
526 downloads per month
120KB
2K
SLoC
FlyLLM
FlyLLM is a Rust library that provides a load-balanced, multi-provider client for Large Language Models. It enables developers to seamlessly work with multiple LLM providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Mistral...) through a unified API with request routing, load balancing, and failure handling.

Features
- Multiple Provider Support 🌐: Unified interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Ollama and Mistral APIs
- Task-Based Routing 🧭: Route requests to the most appropriate provider based on predefined tasks
- Load Balancing ⚖️: Automatically distribute load across multiple provider instances
- Failure Handling 🛡️: Retry mechanisms and automatic failover between providers
- Parallel Processing ⚡: Process multiple requests concurrently for improved throughput
- Custom Parameters 🔧: Set provider-specific parameters per task or request
- Usage Tracking 📊: Monitor token consumption for cost management
- Builder Pattern Configuration ✨: Fluent and readable setup for tasks and providers.
Installation
Add FlyLLM to your Cargo.toml:
[dependencies]
flyllm = "0.2.0"
tokio = { version = "1", features = ["full"] } # For async runtime
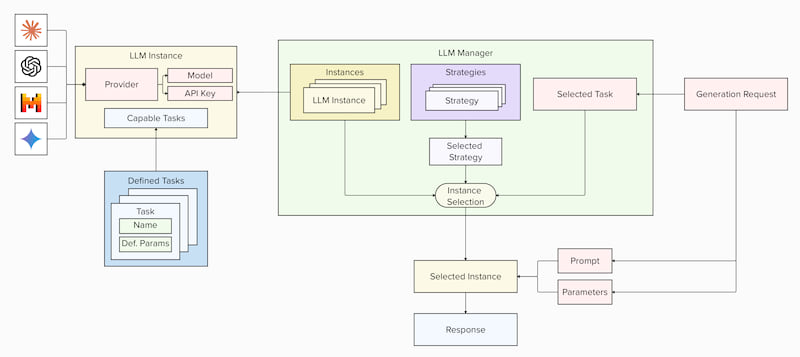
Architecture
The LLM Manager (LLMManager) serves as the core component for orchestrating language model interactions in your application. It manages multiple LLM instances (LLMInstance), each defined by a model, API key, and supported tasks (TaskDefinition).
When your application sends a generation request (GenerationRequest), the manager automatically selects an appropriate instance based on configurable strategies (Last Recently Used, Quickest Response Time, etc.) and returns the generated response by the LLM (LLMResponse). This design prevents rate limiting by distributing requests across multiple instances (even of the same model) with different API keys.
The manager handles failures gracefully by re-routing requests to alternative instances. It also supports parallel execution for significant performance improvements when processing multiple requests simultaneously!
You can define default parameters (temperature, max_tokens) for each task while retaining the ability to override these settings in specific requests. The system also tracks token usage across all instances:
--- Token Usage Statistics ---
ID Provider Model Prompt Tokens Completion Tokens Total Tokens
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 mistral mistral-small-latest 109 897 1006
1 anthropic claude-3-sonnet-20240229 133 1914 2047
2 anthropic claude-3-opus-20240229 51 529 580
3 google gemini-2.0-flash 0 0 0
4 openai gpt-3.5-turbo 312 1003 1315
Usage Examples
The following sections describe the usage of flyllm. You can also check out the example given in examples/task_routing.rs! To activate FlyLLM's debug messages by setting the environment variable RUST_LOG to the value "debug".
Quick Start
use flyllm::{
ProviderType, LlmManager, GenerationRequest, TaskDefinition, LlmResult,
use_logging, // Helper to setup basic logging
};
use std::env; // To read API keys from environment variables
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> LlmResult<()> { // Use LlmResult for error handling
// Initialize logging (optional, requires log and env_logger crates)
use_logging();
// Retrieve API key from environment
let openai_api_key = env::var("OPENAI_API_KEY").expect("OPENAI_API_KEY not set");
// Configure the LLM manager using the builder pattern
let manager = LlmManager::builder()
// Define a task with specific default parameters
.define_task(
TaskDefinition::new("summary")
.with_max_tokens(500) // Set max tokens for this task
.with_temperature(0.3) // Set temperature for this task
)
// Add a provider instance and specify the tasks it supports
.add_provider(
ProviderType::OpenAI,
"gpt-3.5-turbo",
&openai_api_key, // Pass the API key
)
.supports("summary") // Link the provider to the "summary" task
// Finalize the manager configuration
.build()?; // Use '?' for error propagation
// Create a generation request using the builder pattern
let request = GenerationRequest::builder(
"Summarize the following text: Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures..."
)
.task("summary") // Specify the task for routing
.build();
// Generate response sequentially (for a single request)
// The Manager will automatically choose the configured OpenAI provider for the "summary" task.
let responses = manager.generate_sequentially(vec![request]).await;
// Handle the response
if let Some(response) = responses.first() {
if response.success {
println!("Response: {}", response.content);
} else {
println!("Error: {}", response.error.as_ref().unwrap_or(&"Unknown error".to_string()));
}
}
// Print token usage statistics
manager.print_token_usage();
Ok(())
}
Adding Multiple Providers
Configure the LlmManager with various providers, each supporting different tasks.
use flyllm::{ProviderType, LlmManager, TaskDefinition, LlmResult};
use std::env;
async fn configure_manager() -> LlmResult<LlmManager> {
// --- API Keys ---
let openai_api_key = env::var("OPENAI_API_KEY").expect("OPENAI_API_KEY not set");
let anthropic_api_key = env::var("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY").expect("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY not set");
let mistral_api_key = env::var("MISTRAL_API_KEY").expect("MISTRAL_API_KEY not set");
let google_api_key = env::var("GOOGLE_API_KEY").expect("GOOGLE_API_KEY not set");
// Ollama typically doesn't require an API key for local instances
let manager = LlmManager::builder()
// Define all tasks first
.define_task(TaskDefinition::new("summary").with_max_tokens(500).with_temperature(0.3))
.define_task(TaskDefinition::new("qa").with_max_tokens(1000))
.define_task(TaskDefinition::new("creative_writing").with_max_tokens(1500).with_temperature(0.9))
.define_task(TaskDefinition::new("code_generation").with_temperature(0.1))
.define_task(TaskDefinition::new("translation")) // Task with default provider parameters
// Add OpenAI provider supporting summary and QA
.add_provider(ProviderType::OpenAI, "gpt-4-turbo", &openai_api_key)
.supports_many(&["summary", "qa"]) // Assign multiple tasks
// Add Anthropic provider supporting creative writing and code generation
.add_provider(ProviderType::Anthropic, "claude-3-sonnet-20240229", &anthropic_api_key)
.supports("creative_writing")
.supports("code_generation")
// Add Mistral provider supporting summary and translation
.add_provider(ProviderType::Mistral, "mistral-large-latest", &mistral_api_key)
.supports("summary")
.supports("translation")
// Add Google (Gemini) provider supporting QA and creative writing
.add_provider(ProviderType::Google, "gemini-1.5-pro", &google_api_key)
.supports("qa")
.supports("creative_writing")
// Add a local Ollama provider supporting summary and code generation
.add_provider(ProviderType::Ollama, "llama3:8b", "") // API key often empty for local Ollama
.supports("summary")
.supports("code_generation")
.custom_endpoint("http://localhost:11434/api/chat") // Optional: Specify if not default
// Finalize configuration
.build()?;
println!("LlmManager configured with multiple providers.");
Ok(manager)
}
Task-Based Routing
Define tasks with specific default parameters and create requests targeting those tasks. FlyLLM routes the request to a provider configured to support that task.
use flyllm::{LlmManager, GenerationRequest, TaskDefinition, LlmResult};
use std::env;
// Assume manager is configured as shown in "Adding Multiple Providers"
async fn route_by_task(manager: LlmManager) -> LlmResult<()> {
// Define tasks centrally in the builder (shown conceptually here)
// LlmManager::builder()
// .define_task(
// TaskDefinition::new("summary")
// .with_max_tokens(500)
// .with_temperature(0.3)
// )
// .define_task(
// TaskDefinition::new("creative_writing")
// .with_max_tokens(1500)
// .with_temperature(0.9)
// )
// // ... add providers supporting these tasks ...
// .build()?;
// Create requests with different tasks using the request builder
let summary_request = GenerationRequest::builder(
"Summarize the following article about renewable energy: ..."
)
.task("summary") // This request will be routed to providers supporting "summary"
.build();
let story_request = GenerationRequest::builder(
"Write a short story about a futuristic city powered by algae."
)
.task("creative_writing") // This request uses the "creative_writing" task defaults
.build();
// Example: Override task defaults for a specific request
let short_story_request = GenerationRequest::builder(
"Write a VERY short story about a time traveler meeting a dinosaur."
)
.task("creative_writing") // Based on "creative_writing" task...
.max_tokens(200) // ...but override max_tokens for this specific request
.param("temperature", 0.95) // Can override any parameter
.build();
// Process requests (e.g., sequentially)
let requests = vec![summary_request, story_request, short_story_request];
let results = manager.generate_sequentially(requests).await;
// Handle results...
for (i, result) in results.iter().enumerate() {
println!("Request {}: Success = {}, Content/Error = {}",
i + 1,
result.success,
if result.success { &result.content[..std::cmp::min(result.content.len(), 50)] } else { result.error.as_deref().unwrap_or("Unknown") }
);
}
Ok(())
}
Parallel Processing
// Process in parallel
let parallel_results = manager.batch_generate(requests).await;
// Process each result
for result in parallel_results {
if result.success {
println!("Success: {}", result.content);
} else {
println!("Error: {}", result.error.as_ref().unwrap_or(&"Unknown error".to_string()));
}
}
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Contributing
Contributions are always welcome! If you're interested in contributing to FlyLLM, please fork the repository and create a new branch for your changes. When you're done with your changes, submit a pull request to merge your changes into the main branch.
Supporting FlyLLM
If you want to support FlyLLM, you can:
- Star ⭐ the project in Github!
- Donate 🪙 to my Ko-fi page!
- Share ❤️ the project with your friends!
Dependencies
~10–23MB
~314K SLoC