10 releases
| 0.7.9 | Mar 25, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.7.8 | Mar 14, 2025 |
| 0.7.6 | Feb 3, 2025 |
| 0.7.5 | Jan 3, 2025 |
| 0.6.8 | Jul 16, 2024 |
#26 in Debugging
152,962 downloads per month
Used in 36 crates
(25 directly)
185KB
3.5K
SLoC
fastrace
fastrace is a tracing library 10~100x faster than others:
Features:
- Extremely fast
- Rich features for logging
- Compatible with Jaeger, Datadog, and OpenTelemetry
Resources
Getting Started
In Libraries
Libraries should include fastrace as a dependency without enabling any extra features.
[dependencies]
fastrace = "0.7"
Add a trace attribute to the function you want to trace. In this example, a SpanRecord will be collected every time the function is called, if a tracing context is set up by the caller.
#[fastrace::trace]
pub fn send_request(req: HttpRequest) -> Result<(), Error> {
// ...
}
Libraries are able to set up an individual tracing context, regardless of whether the caller has set up a tracing context or not. This can be achieved by using Span::root() to start a new trace and Span::set_local_parent() to set up a local context for the current thread.
The func_path!() macro can detect the function's full name, which is used as the name of the root span.
use fastrace::prelude::*;
pub fn send_request(req: HttpRequest) -> Result<(), Error> {
let root = Span::root(func_path!(), SpanContext::random());
let _guard = root.set_local_parent();
// ...
}
In Applications
Applications should include fastrace as a dependency with the enable feature set. To disable fastrace statically, simply remove the enable feature.
[dependencies]
fastrace = { version = "0.7", features = ["enable"] }
Applications should initialize a Reporter implementation early in the program's runtime. Span records generated before the reporter is initialized will be ignored. Before terminating, flush() should be called to ensure all collected span records are reported.
When the root span is dropped, all of its children spans and itself will be reported at once. Since that, it's recommended to create root spans for short tasks, such as handling a request, just like the example below. Otherwise, an endingless trace will never be reported.
use fastrace::collector::Config;
use fastrace::collector::ConsoleReporter;
use fastrace::prelude::*;
fn main() {
fastrace::set_reporter(ConsoleReporter, Config::default());
loop {
let root = Span::root("worker-loop", SpanContext::random());
let _guard = root.set_local_parent();
handle_request();
}
fastrace::flush();
}
Benchmarks
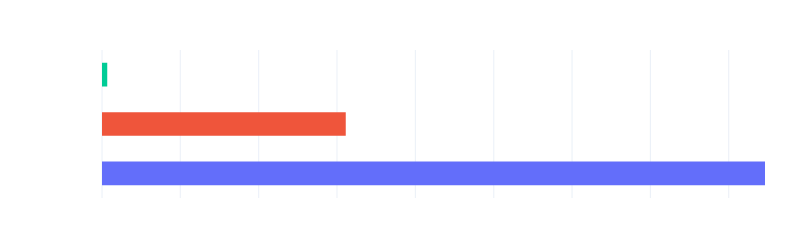
By different architectures:
| x86-64 (Intel Broadwell) | x86-64 (Intel Skylake) | x86-64 (AMD Zen) | ARM (AWS Graviton2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tokio-tracing | 124x slower | 33x slower | 36x slower | 29x slower |
| rustracing | 45x slower | 10x slower | 11x slower | 9x slower |
| fastrace (baseline) | 1x (3.4us) | 1x (3.2us) | 1x (3.8us) | 1x (4.2us) |
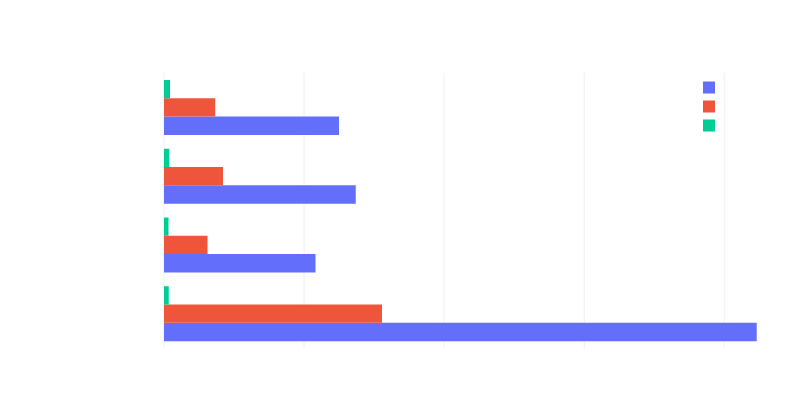
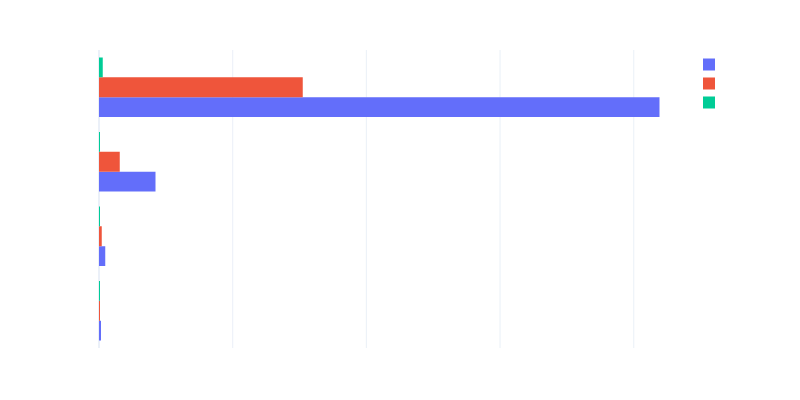
By creating different number of spans:
| 1 span | 10 spans | 100 spans | 1000 spans | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tokio-tracing | 19x slower | 61x slower | 124x slower | 151x slower |
| rustracing | 13x slower | 26x slower | 45x slower | 55x slower |
| fastrace (baseline) | 1x (0.4us) | 1x (0.8us) | 1x (3.4us) | 1x (27.8us) |
Detailed results are available in etc/benchmark-result.
Supported Rust Versions (MSRV 1.80.0)
Fastrace is built against the latest stable release. The minimum supported version is 1.80.0. The current Fastrace version is not guaranteed to build on Rust versions earlier than the minimum supported version.
Projects using fastrace
Feel free to open a PR and add your projects here:
- Conductor: Open-source GraphQL Gateway
- Apache OpenDAL: A data access layer for various storage
- Databend: Cost-Effective alternative to Snowflake
- foyer: Hybrid in-memory and disk cache in Rust
- Sail: Unifying stream, batch, and AI workloads with Apache Spark compatibility
FAQ
Why is fastrace so fast?
There are some articles posted by the maintainer of fastrace:
- The Design of A High-performance Tracing Library in Rust (Chinese)
- How We Trace a KV Database with Less than 5% Performance Impact
What is library-level tracing?
Library-level tracing refers to the capability of incorporating tracing capabilities directly within libraries, as opposed to restricting them to application-level or system-level tracing.
Tracing can introduce overhead to a program's execution. While this is generally acceptable at the application level, where the added overhead is often insignificant compared to the overall execution time, it can be more problematic at the library level. Here, functions may be invoked frequently or performance may be critical, and the overhead from tracing can become substantial. As a result, tracing libraries not designed with speed and efficiency in mind may not be suitable for library-level tracing.
In the realm of the fastrace library, library-level tracing is engineered to be fast and lightweight, resulting in zero overhead when it's not activated. This makes fastrace an excellent choice for use in performance-sensitive applications, and it can be seamlessly integrated into libraries in a similar fashion to the log crate, something other tracing libraries may not offer.
How does fastrace differ from other tracing libraries?
While many tracing libraries aim for extensive features, fastrace prioritizes performance and simplicity.
For example, fastrace doesn't introduce new logging macros, e.g. info!() or error!(), but seamlessly integrates with the log crate. This allows you to use existing logging macros and dependencies, with logs automatically attached to the current tracing span.
Will fastrace incorporate 'level' for spans?
The concept of 'level' may not be an optimal feature for tracing systems. While tokio-tracing incorporates this feature, the underlying motivation for having levels in a span primarily revolves around performance. More specifically, it relates to the performance implications of tracing elements that are not of interest. However, tracing differs from logging in two key aspects:
- Disregarding a low-level span might inadvertently discard a high-level child span.
- The process of filtering, or 'level' as it's often called, in a tracing system should be applied to a trace as a whole rather than individual spans within a trace.
In this context, fastrace offers a more efficient solution by filtering out entire traces that are not of interest through its unique tail-sampling design. Therefore, the concept of 'level', borrowed directly from logging systems, may not be suitable for fastrace.
Migrating from tokio-tracing
If you're using the tokio-tracing ecosystem and want to switch to fastrace for better performance, you can use fastrace-tracing to make the transition easier.
The fastrace-tracing crate provides a compatibility layer that lets you capture spans from libraries instrumented with tokio-tracing in two lines of code:
let subscriber = tracing_subscriber::Registry::default().with(fastrace_tracing::FastraceCompatLayer::new());
tracing::subscriber::set_global_default(subscriber).unwrap();
For more details, refer to the fastrace-tracing documentation.
License
This project is licensed under the Apache-2.0 license.
Originally, this project is a fork of minitrace. See this thread for more information:
Dependencies
~1.3–6.5MB
~42K SLoC