11 releases
| 0.4.0 | Apr 1, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.3.3 | Feb 18, 2025 |
| 0.3.2 | Mar 5, 2024 |
| 0.3.1 | Oct 11, 2023 |
| 0.1.0 | Nov 16, 2020 |
#355 in Embedded development
3,023 downloads per month
Used in 9 crates
410KB
1.5K
SLoC
defmt-test
defmt-test is a test harness for embedded devices that lets you write and run unit tests on your device as if you were using the built-in #[test] attribute.
It is compatible with rust-analyzer's ▶ Run Test button, which means you can flash and run your tests straight from VS Code:
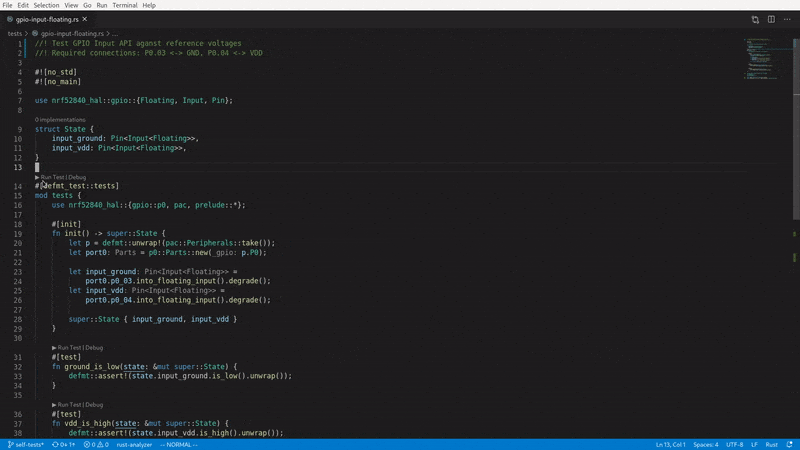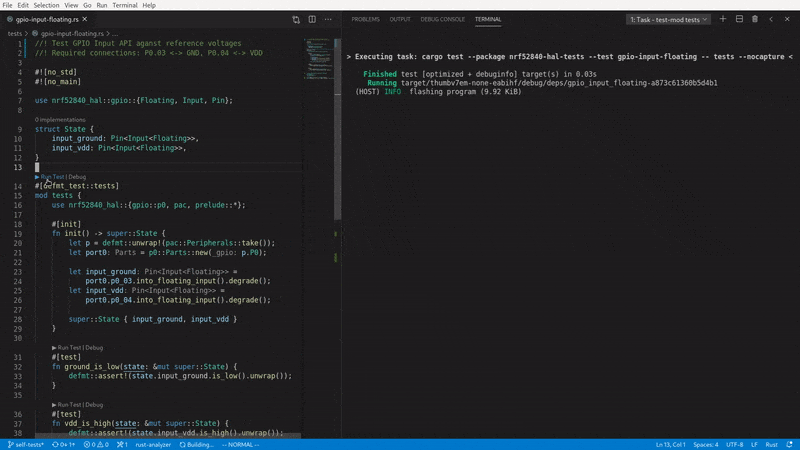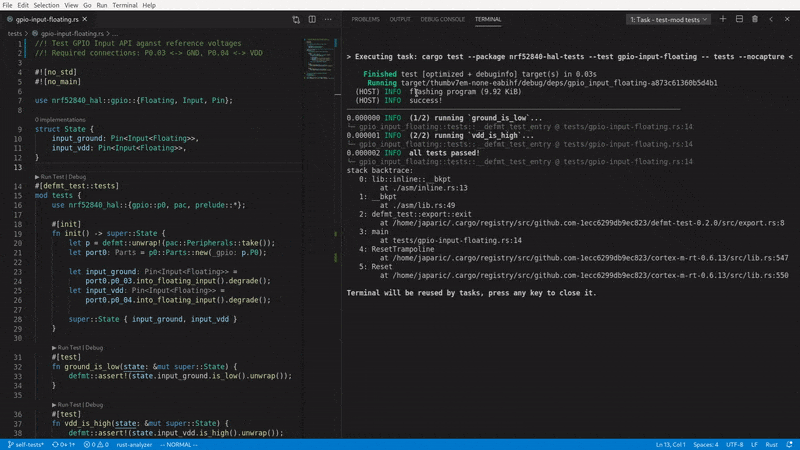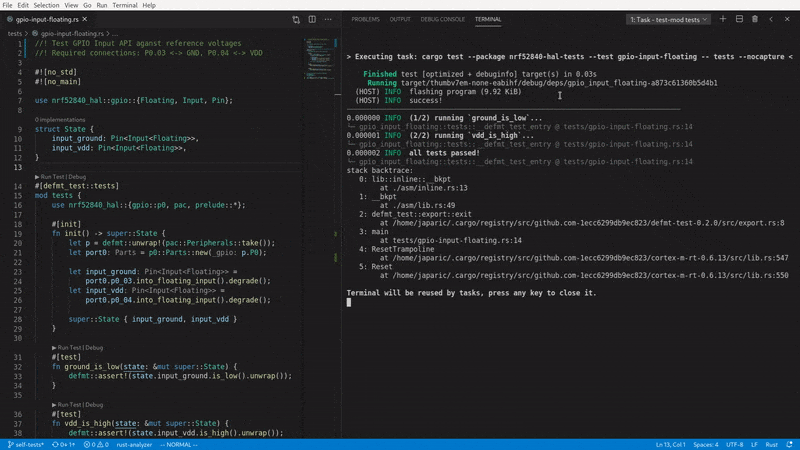
For a full list of defmt-test's capabilities, please refer to the documentation below.
Using defmt-test in a new project
We suggest you start from the app-template.
From there you can execute cargo test --lib to run library unit tests, i.e. #[test] functions in the library crate (src/lib.rs).
$ cargo test --lib
(..)
(1/1) running `it_works`...
└─ app::unit_tests::__defmt_test_entry @ src/lib.rs:33
all tests passed!
└─ app::unit_tests::__defmt_test_entry @ src/lib.rs:28
(..)
(HOST) INFO device halted without error
And execute cargo test --test integration to run integration tests, i.e. the tests/integration.rs file.
$ cargo test --test integration
(..)
0.000000 INFO (1/2) running `assert_true`...
└─ test::tests::__defmt_test_entry @ tests/test.rs:7
0.000001 INFO (2/2) running `assert_false`...
└─ test::tests::__defmt_test_entry @ tests/test.rs:7
0.000002 ERROR panicked at 'TODO: write actual tests', testsuite/tests/test.rs:16:9
└─ panic_probe::print_defmt::print @ (..omitted..)
stack backtrace:
0: HardFaultTrampoline
<exception entry>
1: __udf
2: cortex_m::asm::udf
at (..omitted..)
3: rust_begin_unwind
at (..omitted..)
4: core::panicking::panic_fmt
at (..omitted..)
5: core::panicking::panic
at (..omitted..)
6: test::tests::assert_false
at tests/test.rs:16
7: main
at tests/test.rs:7
8: ResetTrampoline
at (..omitted..)
9: Reset
at (..omitted..)
NOTE all #[test] functions within a file are guaranteed to run sequentially
Adding defmt-test to an existing project
If you want to add defmt-test to an existing Cargo project / package, for each crate that you want to test you need to do these changes in Cargo.toml:
- add
defmt-testas adev-dependency - for each crate that you want to test, set
harnesstofalseto disable the default test harness, thetestcrate which depends onstd. examples below
# Cargo.toml
# for the library crate (src/lib.rs)
[lib]
harness = false
# for each crate in the `tests` directory
[[test]]
name = "test-name" # tests/test-name.rs
harness = false
[[test]]
name = "second" # tests/second.rs
harness = false
The other thing to be aware is that cargo test will compile all crates in the package, or workspace.
This may include crates that you don't want to test, like src/main.rs or each crate in src/bin or examples.
To identify which crates are being compiled by cargo test, run cargo test -j1 -v and look for the --crate-name flag passed to each rustc invocation.
To test only a subset of the crates in the package / workspace you have two options:
- you can specify each crate when you invoke
cargo test. for example,cargo test --lib --test integrationtests two crates: the library crate (src/lib.rs) andtests/integration.rs - you can disable tests for the crates that you don't want to test -- example below -- and then you can use
cargo testto test all crates that were not disabled.
if you have this project structure
$ tree .
.
├── Cargo.toml
├── src
│ ├── lib.rs
│ └── main.rs
└── tests
└── integration.rs
and have src/lib.rs set up for tests but don't want to test src/main.rs you'll need to disable tests for src/main.rs
# Cargo.toml
[package]
# ..
name = "app"
[[bin]] # <- add this section
name = "app" # src/main.rs
test = false
Adding state
An #[init] function can be written within the #[tests] module.
This function will be executed before all unit tests and its return value, the test suite state, can be passed to unit tests as an argument.
// state shared across unit tests
struct MyState {
flag: bool,
}
#[defmt_test::tests]
mod tests {
#[init]
fn init() -> super::MyState {
// state initial value
super::MyState {
flag: true,
}
}
// This function is called before each test case.
// It accesses the state created in `init`,
// though like with `test`, state access is optional.
#[before_each]
fn before_each(state: &mut super::MyState) {
defmt::println!("State flag before is {}", state.flag);
}
// This function is called after each test
#[after_each]
fn after_each(state: &mut super::MyState) {
defmt::println!("State flag after is {}", state.flag);
}
// this unit test doesn't access the state
#[test]
fn assert_true() {
assert!(true);
}
// but this test does
#[test]
fn assert_flag(state: &mut super::MyState) {
assert!(state.flag)
state.flag = false;
}
}
$ cargo test -p testsuite
0.000000 (1/2) running `assert_true`...
└─ integration::tests::__defmt_test_entry @ tests/integration.rs:37
0.000001 State flag before is true
└─ integration::tests::before_each @ tests/integration.rs:26
0.000002 State flag after is true
└─ integration::tests::after_each @ tests/integration.rs:32
0.000003 (2/2) running `assert_flag`...
└─ integration::tests::__defmt_test_entry @ tests/integration.rs:43
0.000004 State flag before is true
└─ integration::tests::before_each @ tests/integration.rs:26
0.000005 State flag after is false
└─ integration::tests::after_each @ tests/integration.rs:32
0.000006 all tests passed!
└─ integration::tests::__defmt_test_entry @ tests/integration.rs:11
Teardown
A #[teardown] function can be written within the #[tests] module.
This function will be executed after all unit tests passed.
The test suite state may be passed to the teardown function as an argument.
// state shared across unit tests
struct MyState {
flag: bool,
}
#[defmt_test::tests]
mod tests {
#[init]
fn init() -> super::MyState {
// state initial value
super::MyState {
flag: true,
}
}
// This function is called after all test cases passed.
// It accesses the state created in `init`,
// though like with `test`, state access is optional.
#[teardown]
fn teardown(state: &mut super::MyState) {
defmt::println!("State flag in teardown is {}", state.flag);
}
// this test accesses the state created in `init`
#[test]
fn assert_flag(state: &mut super::MyState) {
assert!(state.flag)
state.flag = false;
}
}
Test Outcome
Test functions may either return () and panic on failure, or return any other type that implements the TestOutcome trait, such as Result.
This allows tests to indicate failure via Result, which allows using the ? operator to propagate errors.
Similar to Rust's built-in #[should_panic] attribute, defmt-test supports a #[should_error] attribute, which inverts the meaning of the returned TestOutcome.
Err makes the test pass, while Ok/() make it fail.
Support
defmt-test is part of the Knurling project, Ferrous Systems' effort at
improving tooling used to develop for embedded systems.
If you think that our work is useful, consider sponsoring it via GitHub Sponsors.
License
Licensed under either of
-
Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
-
MIT license (LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
Contribution
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you, as defined in the Apache-2.0 license, shall be licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.
Dependencies
~1–1.5MB
~26K SLoC