3 releases (breaking)
| 0.3.0 | Mar 1, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.0 | Feb 13, 2023 |
| 0.1.0 | Nov 8, 2022 |
#3 in #dragonball
4,196 downloads per month
1MB
24K
SLoC
dbs-upcall
dbs-upcall is a direct communication tool between VMM and guest developed upon vsock. The server side of the upcall is a driver in guest kernel (kernel patches are needed for this feature) and it'll start to serve the requests after the kernel starts. And the client side is in VMM , it'll be a thread that communicates with vsock through uds.
We have accomplished device hotplug / hot-unplug directly through upcall in order to avoid virtualization of ACPI to minimize virtual machines' overhead. And there could be many other usage through this direct communication channel.
Design
Server Design
The server side of upcall is a driver in guest kernel and the vsock port is 0xDB. After the vsock is connected, upcall related service will be registered and a kthread providing corresponding service will be created. The upcall service thread will first send a message with message type Connect to try to connect with the client side (VMM). After service successfully connects, the service thread will get into a loop for continuously receiving requests from the client side and processing the requests until the service stops.
The service we currently support:
- device manager : supports cpu hotplug / hot-unplug, virtio-mmio devices hotplug / hot-unplug
Client Design
The client side is in VMM and we abstract related logic into this crate dbs-upcall.
The upcall state machine for the client side:
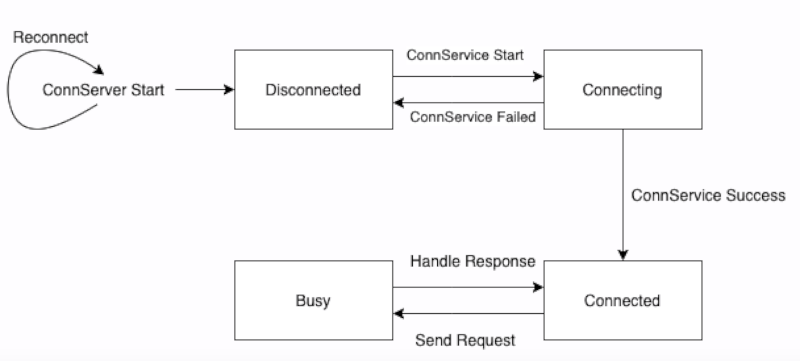
The client side's workflow:
- [Current State: WaitingServer] Check the connection with vsock server.
- [Current State: WaitingService]Check the connection with upcall server side in the guest kernel for message type Connect and magic version.
- [Current State: ServiceConnected] The request could be sent through upcall in this state.
If step 1 and 2 failed, upcall will try to reconnect. If request is sent in step 3, upcall state will change to ServiceBusy and upcall will not process other requests in this state.
Message Design
There are two parts for the upcall request message : message header and message load. And there are three parts for the upcall reply messgae: message header, result and message load.
Message Header contains following information and it remains the same for the request and the reply :
- magic_version(u32): magic version for identifying upcall and the service type
- msg_size(u32): size of the message load
- msg_type(u32): type for the message to identify its usage (e.g. ADD_CPU)
- msg_flags(u32): reserved
For the upcall request message, message load currently contains two kinds of msg_load. msg_load type 1: add_mmio_dev - for virtio-mmio hotplug / hot-unplug request:
- mmio_base
- mmio_size
- mmio_irq
msg_load type 2: cpu_dev_info - for cpu hotplug / hot-unplug request:
- count
- apic_ver
- apic_ids[256]
For the upcall reply message, reply contains result and two kinds of msg_load. If result is 0, the operation is successful. If result is not 0, result refers to the error code.
msg_load type 1: add_mmio_dev - for virtio-mmio reply: currently empty
msg_load type 2: cpu_dev_reply_info - for cpu hotplug / hot-unplug reply:
- apic_index
Kernel Patches
Kernel patches are needed for dbs-upcall. You could go to kernel patches to get the patches.
0001-dragonball-introduce-dragonball-driver.patch in /kernel is needed as a prerequisite to enable upcall.
0001-upcall-add-vsock-server-and-upcall-support.patch in /kernel/upcallis the patch for enabling upcall.
The patches have been tested on linux kernel 4.19 (stable).
License
This project is licensed under Apache License, Version 2.0.
Dependencies
~23–38MB
~701K SLoC