11 unstable releases (3 breaking)
| 0.4.3 | Mar 13, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.4.2 | Mar 10, 2025 |
| 0.4.1 | Feb 13, 2025 |
| 0.3.3 | Feb 5, 2025 |
| 0.1.1 | Oct 27, 2024 |
#144 in Filesystem
55 downloads per month
2MB
1.5K
SLoC
Cargo Workspace Analyzer
A CLI tool which provides insights about how packages within a Cargo workspace are related to each other. Currently, the following is supported.
See cargo-workspace-analyzer --help for all options.
Workspace Visualization
It visualizes the workspace with a Mermaid diagram. That way the user can see how packages depend on each other may identify layers of the application. As an example, here is the resulting diagram a randomly selected workspace, Tauri.
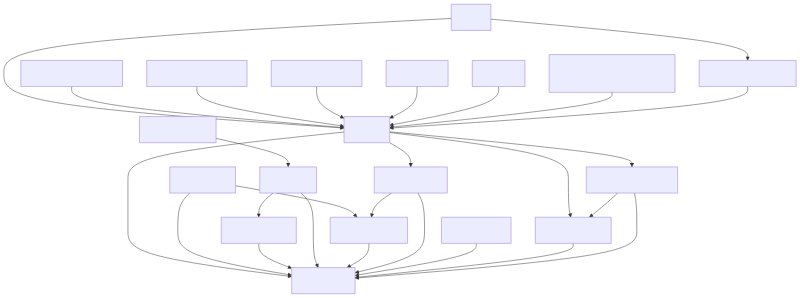
To have such diagram gives you the following advantages:
- a high level overview of the software
- an idea about the degree of coupling between your packages
By default, the tool creates an SVG file called cargo-workspace-analyzer.svg. You can change the output format to a
.mmd file with the option -o mdd.
Circular Dependency Detection
This analyzer finds circular dependencies. It highlights those packages, which form a circle. By running the analyzer regularly, one can detect circular dependencies before they get hard if not impossible to resolve later on. See this example.
Metric calculations
The created graph is used to calculate common metrics in regard to the coupling of packages. The following metric are supported:
- Fan In
- Fan Out
- Instability Metric
Package and Dependency Count
It will also display the amount of packages and the amount of dependencies. Once for all the founds packages and dependencies in the codebase, and once only for the packages actually within the workspace and interdependencies.
Installation
Install it globally:
cargo install cargo-workspace-analyzer
To render the Mermaid diagram and store it so disk (which is the default behaviour), you would need to have the Mermaid CLI installed as well, which run on Node.js.
npm install -g @mermaid-js/mermaid-cli
Usage
For all details, use cargo-workspace-analyzer --help. However here is how you can use it generally:
Navigate to a Cargo workspace and run the tool:
cd path/to/your/workspace
cargo-workspace-analyzer
Or use an argument to specify the location of the workspace and run it from where ever you want.
cargo-workspace-analyzer --working-dir /path/to/your/workspace
By default, it will create an SVG files in the directory where it run. You can also create a mmd file, in which then only the diagram is placed in Mermaid syntax. You can use it then for further processing. Here's an example of the content:
graph TD
service-1 --> db-connector
API --> service-2
API --> service-1
service-2 --> db-connector
Dependencies
~4–11MB
~104K SLoC