8 releases
| 0.2.1 | Mar 4, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.0 | Mar 3, 2025 |
| 0.1.5 | Mar 1, 2025 |
| 0.1.3 | Feb 28, 2025 |
#317 in Math
833 downloads per month
150KB
828 lines
Balanced Directions
Balanced Directions is a Rust crate for modeling directions and movements in a 3x3 grid using a balanced ternary-inspired logic. It can be viewed as a 2D ternary digit.
It provides tools to manipulate positions, paths, and directions on a grid-based structure, making it useful in scenarios requiring discrete grid movement, coordinated navigation, or 2D spatial logic.
Features
- Enum Representation (
Balance):
Represents positions in a 3x3 grid with easy access to their 2D vector representation. - Grid Navigation:
Convenient methods for grid-based movement operations (up,down,left,right) as well as rotations, flips, and vector transformations. - Path Manipulation:
APathstructure for modeling sequences of movements, offering utilities to normalize, reverse, and transform paths. - Ternary Integration (Optional, active by default):
Balanced-ternary-based coordinates when integrating with thebalanced-ternarycrate.
Adds double balanced-ternary logic operations. #![no_std]Compatibility:
A lightweight design for use in embedded or low-level systems.
Examples
Position Representation and Movement
The core Balance enum represents positions in a 3x3 grid. For example, you can easily identify positions such as
TopLeft or Center. Use movement methods to perform grid operations.
use balanced_directions::Balance;
fn example_usage() {
let position = Balance::TopLeft;
assert_eq!(position.to_vector(), (-1, -1));
let moved = position.right();
assert_eq!(moved, Balance::Top);
let rotated = moved.rotate_left();
assert_eq!(rotated, Balance::Left);
assert_eq!(rotated.to_angle(), Balance::WEST);
}
Path Representation and Manipulation
The Path structure enables you to work with sequences of grid movements.
use balanced_directions::{Balance, Path};
fn path_example() {
let movements = vec![Balance::Top, Balance::Right, Balance::Bottom];
let path = Path::new(movements);
assert_eq!(path.len(), 3);
assert_eq!(path.to_vector(), (1, 0)); // Cumulative movement: right by 1
let movements = vec![Balance::Top, Balance::Top, Balance::Top, Balance::Bottom];
let path = Path::new(movements);
assert_eq!(path.to_vector(), (0, -2)); // Cumulative movement: top by 2
let normalized_path = path.normalized();
assert_eq!(normalized_path.to_vector(), (0, -2));
assert_eq!(normalized_path.len(), 2);
}
Integration with Balanced Ternary
With the feature "ternary", you can convert grid positions to and from balanced ternary representations.
use balanced_directions::Balance;
use balanced_ternary::Digit;
fn ternary_example() {
let position = Balance::Top;
let ternary_pair = position.to_ternary_pair();
assert_eq!(ternary_pair, (Digit::Zero, Digit::Neg)); // Top is represented as (0, -1)
let recreated_position = Balance::from_ternary_pair(Digit::Zero, Digit::Neg);
assert_eq!(recreated_position, Balance::Top);
let possibly = recreated_position.possibly();
assert_eq!(possibly, Balance::TopRight);
}
API Overview
Balance
The Balance enumrepresents nine positions of a 3x3 grid |
As a 2D ternary digit its cases can be viewed as False/Unknown/Trueon 2 dimensions |
|---|---|
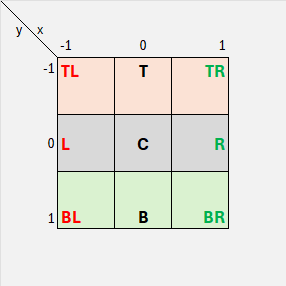 |
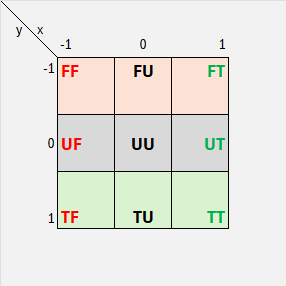 |
Balance enum cases:
TopLeft,Top,TopRightLeft,Center,RightBottomLeft,Bottom,BottomRight
Operations:
A lot of operation can be performed with one (unary operations) or two (binary operations) Balance(s).
Below, the operation table of all Balance operations.
Unary directions
Moves with bounds (up, right, down, left) or wraps around (up_wrap, right_wrap, down_wrap, left_wrap).
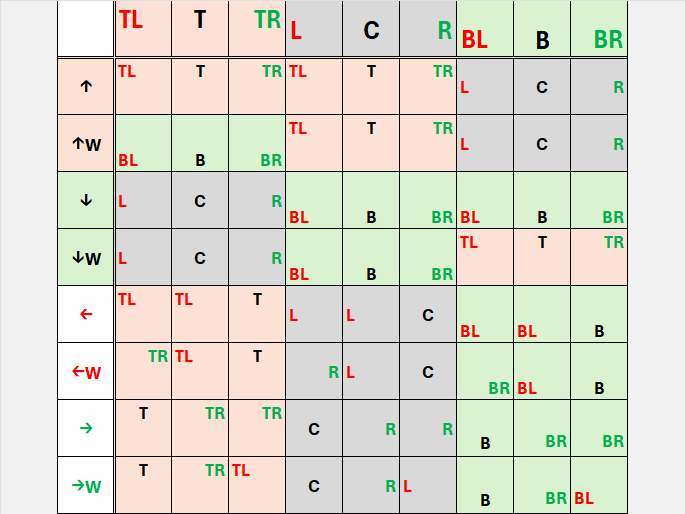
Unary operations
Performs some useful transformations on a Balance (flip_h, neg, flip_v, not (transpose), rotate_left,
rotate_right,center_h, center_v).
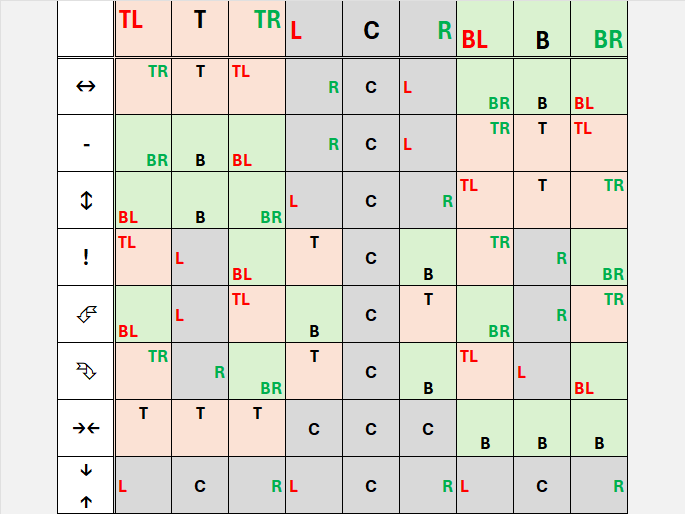
Double balanced-ternary logic
Shorthands for Digit operations :
possibly,necessary,contingently,absolute_positive,positive,not_negative,not_positive,negative,absolute_negative,ht_not,post,pre.
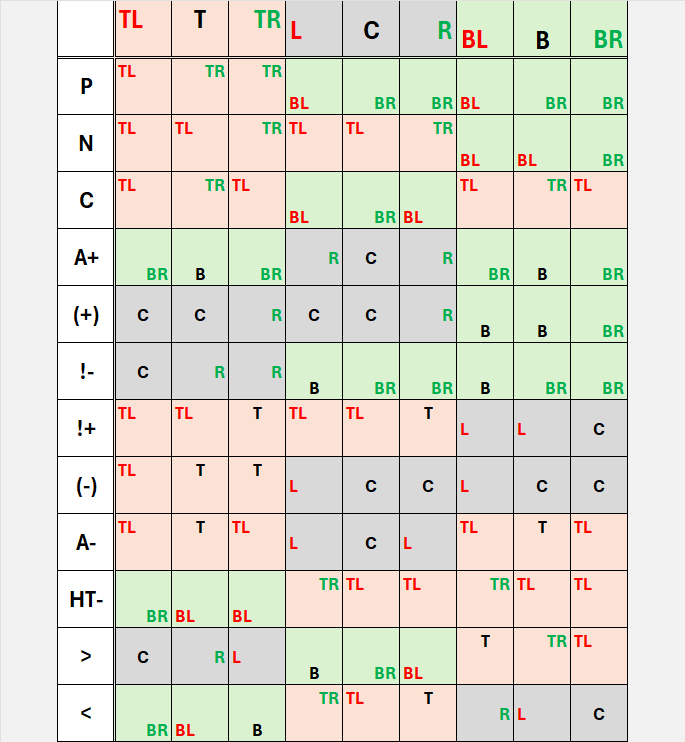
Binary operations
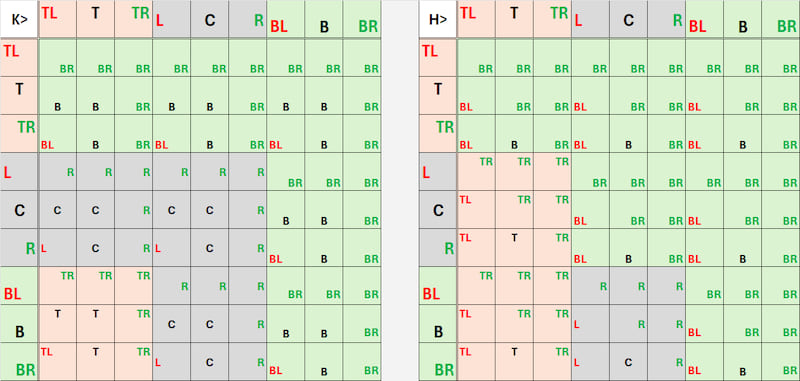
Combines two Balances into one (add, mul, sub, and with the ternary feature : bitand, bitor, bitxor, k3_imply, ht_imply).
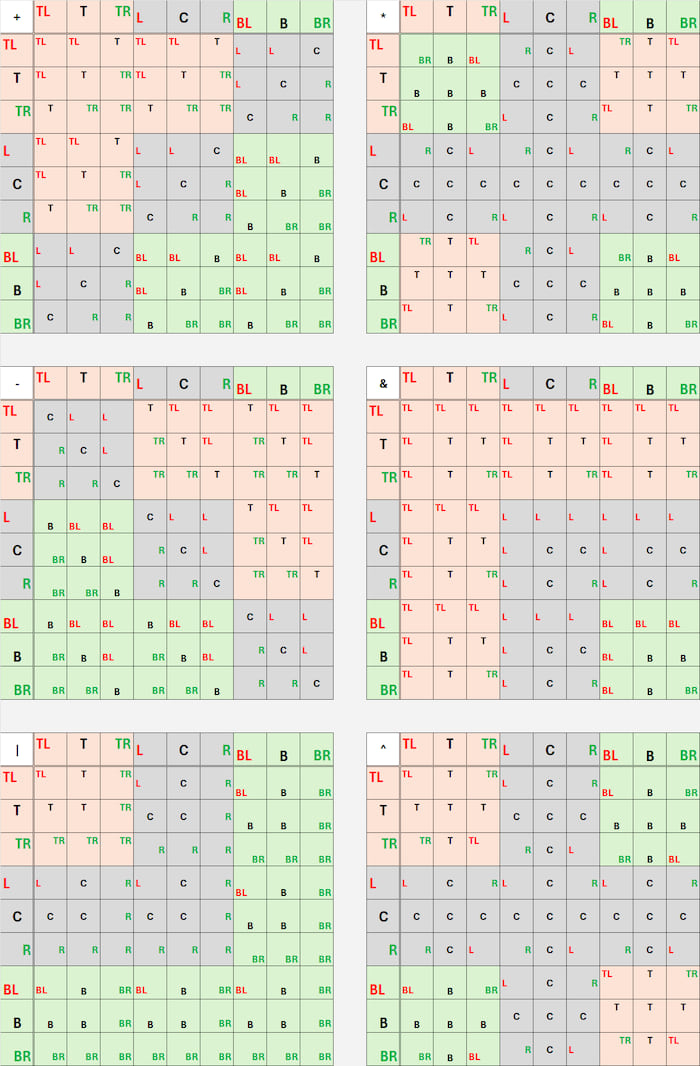
Path
A collection of Balance movements stored as steps in a sequence. Paths can be created, traversed, and normalized for
efficient representation of cumulative movement.
Key Methods:
- Construction:
new(),from_vector() - Traversal:
iter(),iter_mut() - Transformation:
normalized(),reversed(),each(),each_zip()
Cases
- Grid-based Movement in Games Simulate and manipulate movements within 3x3 environments for character navigation, AI paths, or puzzle logic.
- Embedded Robotics Applications Represent grid movements for sensor or actuator navigation without relying on the standard library.
- Spatial Modeling or Math-based Algorithms Perform 2D spatial computations with a high-level abstraction for vector-based movements.
Documentation
The complete API documentation is available on docs.rs. It contains details on each type, method, and their use cases.
Related Libraries
balanced-ternary: Provides balanced ternary number manipulations used for optional integration.
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sébastien GELDREICH
Balanced Direction is licensed under the MIT License.