48 releases (26 stable)
| 1.22.0 | Dec 9, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 1.21.1 | Nov 9, 2024 |
| 1.21.0 | Oct 30, 2024 |
| 1.19.0 | Jun 18, 2024 |
| 0.7.0 | Mar 14, 2022 |
#73 in Development tools
135 downloads per month
Used in runme
325KB
9K
SLoC
Argc
Argc is a powerful Bash framework that simplifies building full-featured CLIs. It lets you define your CLI through comments, focusing on your core logic without dealing with argument parsing, usage text, error messages, and other boilerplate code.
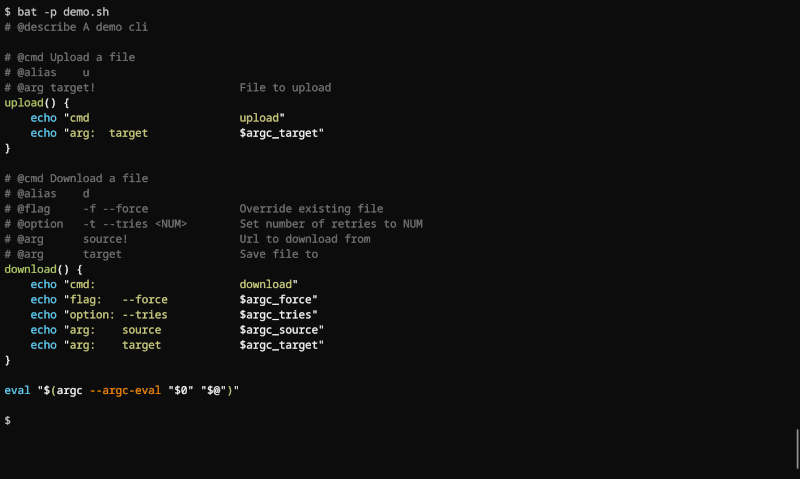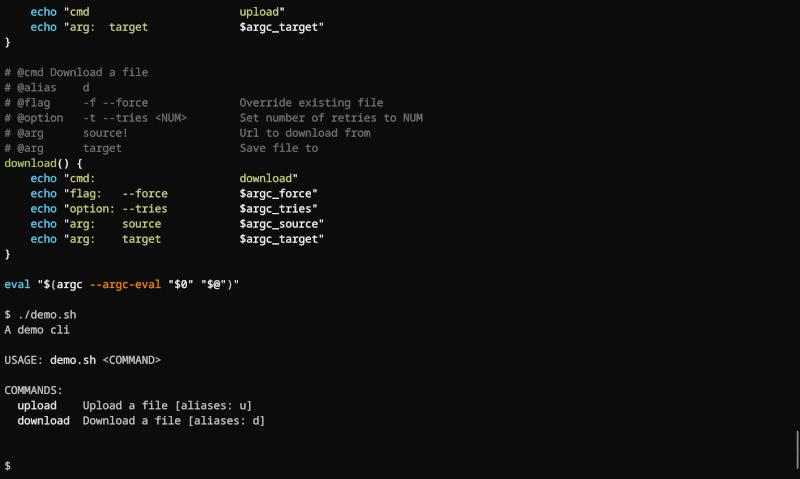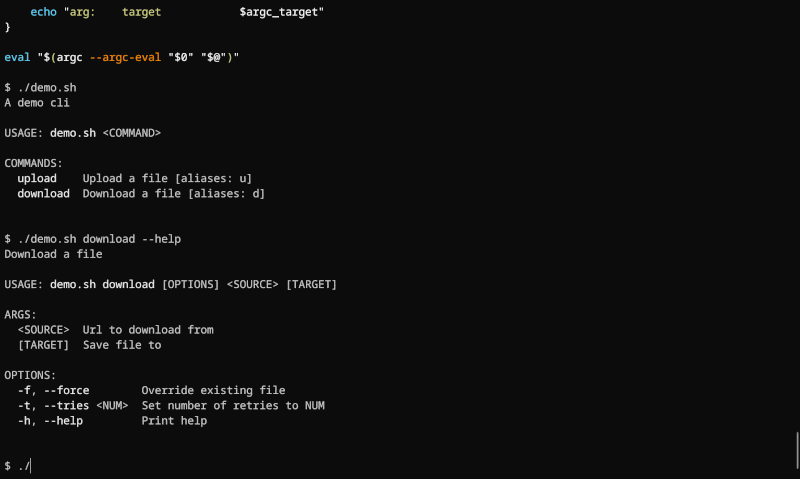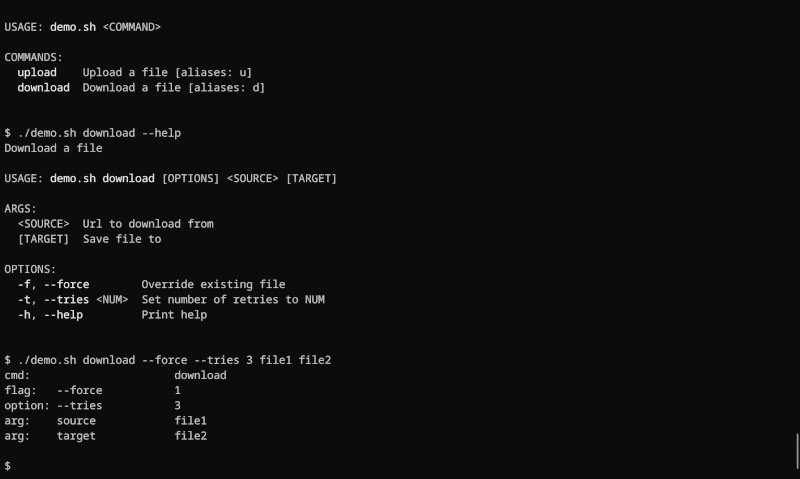
Features
- Effortless Argument Parsing:
- Handles flags, options, positional arguments, and subcommands.
- Validates user input for robust error handling.
- Generates information-rich usage text.
- Maps arguments to corresponding variables.
- Standalone Bash Script Creation:
- Build a bash script that incorporates all functionalities without depending on Argc itself.
- Cross-shell Autocompletion:
- Generate autocompletion scripts for various shells (bash, zsh, fish, powershell, etc.).
- Man Page Generation:
- Automatically create comprehensive man page documentation for your script.
- Environment Variable Integration:
- Define, validate, and bind environment variables to options and positional arguments.
- Task Automation:
- An Bash-based command runner that automates tasks via Argcfile.sh.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Seamlessly run your Argc-based scripts on macOS, Linux, Windows, and BSD systems.
Install
Package Managers
- Rust Developers:
cargo install argc - Homebrew/Linuxbrew Users:
brew install argc - Pacman Users:
yay -S argc
Pre-built Binaries
Alternatively, download pre-built binaries for macOS, Linux, and Windows from GitHub Releases, extract it, and add the argc binary to your $PATH.
You can use the following command on Linux, MacOS, or Windows to download the latest release.
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sigoden/argc/main/install.sh | sh -s -- --to /usr/local/bin
GitHub Actions
install-binary can be used to install argc in a GitHub Actions workflow.
- uses: sigoden/install-binary@v1
with:
repo: sigoden/argc
Get Started
Building a command-line program using Argc is a breeze. Just follow these two steps:
1. Design Your CLI Interface:
Describe options, flags, positional parameters, and subcommands using comment tags (explained later).
2. Activate Argument Handling:
Add this line to your script: eval "$(argc --argc-eval "$0" "$@")". This integrates Argc's parsing magic into your program.
Let's illustrate with an example:
# @flag -F --foo Flag param
# @option --bar Option param
# @option --baz* Option param (multi-occurs)
# @arg val* Positional param
eval "$(argc --argc-eval "$0" "$@")"
echo foo: $argc_foo
echo bar: $argc_bar
echo baz: ${argc_baz[@]}
echo val: ${argc_val[@]}
Run the script with some sample arguments:
./example.sh -F --bar=xyz --baz a --baz b v1 v2
Argc parses these arguments and creates variables prefixed with argc_:
foo: 1
bar: xyz
baz: a b
val: v1 v2
Just run ./example.sh --help to see the automatically generated help information for your CLI:
USAGE: example [OPTIONS] [VAL]...
ARGS:
[VAL]... Positional param
OPTIONS:
-F, --foo Flag param
--bar <BAR> Option param
--baz [BAZ]... Option param (multi-occurs)
-h, --help Print help
-V, --version Print version
With these simple steps, you're ready to leverage Argc and create robust command-line programs!
Comment Tags
Comment tags are standard Bash comments prefixed with @ and a specific tag. They provide instructions to Argc for configuring your script's functionalities.
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
@describe |
Sets the description for the command. |
@cmd |
Defines a subcommand. |
@alias |
Sets aliases for the subcommand. |
@arg |
Defines a positional argument. |
@option |
Defines an option argument. |
@flag |
Defines a flag argument. |
@env |
Defines an environment variable. |
@meta |
Adds metadata. |
See specification for the grammar and usage of all the comment tags.
Argc-build
Generate an independent bash script that incorporates all functionalities typically available when the argc command is present.
The generated script removes the argc dependency, enhances compatibility, and enables deployment in a wider range of environments.
argc --argc-build <SCRIPT> [OUTPATH]
argc --argc-build ./example.sh build/
./build/example.sh -h # The script's functionality does not require the `argc` dependency
Argcscript
Argc is a also command runner built for those who love the efficiency and flexibility of Bash scripting.
Similar to how Makefile define commands for the make tool, Argcscript uses an Argcfile.sh to store your commands, referred to as "recipes".
Why Choose Argc for Your Projects?
- Leverage Bash Skills: No need to learn a new language, perfect for Bash aficionados.
- GNU Toolset Integration: Utilize familiar tools like awk, sed, grep, find, and others.
- Environment variables Management: Load dotenv, document, and validate environment variables effortlessly.
- Powerful Shell Autocompletion: Enjoy autocomplete suggestions for enhanced productivity.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility:: Works seamlessly across Linux, macOS, Windows, and BSD systems.
See command runner for more details.
Completions
Argc automatically provides shell completions for all argc-based scripts.
argc --argc-completions <SHELL> [CMDS]...
In the following, we use cmd1 and cmd2 as examples to show how to add a completion script for various shells.
# bash (~/.bashrc)
source <(argc --argc-completions bash cmd1 cmd2)
# elvish (~/.config/elvish/rc.elv)
eval (argc --argc-completions elvish cmd1 cmd2 | slurp)
# fish (~/.config/fish/config.fish)
argc --argc-completions fish cmd1 cmd2 | source
# nushell (~/.config/nushell/config.nu)
argc --argc-completions nushell cmd1 cmd2 # update config.nu manually according to output
# powershell ($PROFILE)
Set-PSReadlineKeyHandler -Key Tab -Function MenuComplete
argc --argc-completions powershell cmd1 cmd2 | Out-String | Invoke-Expression
# xonsh (~/.config/xonsh/rc.xsh)
exec($(argc --argc-completions xonsh cmd1 cmd2))
# zsh (~/.zshrc)
source <(argc --argc-completions zsh cmd1 cmd2)
# tcsh (~/.tcshrc)
eval `argc --argc-completions tcsh cmd1 cmd2`
The core of all completion scripts is to call argc --argc-compgen to obtain completion candidates.
$ argc --argc-compgen bash ./example.sh example --
--foo (Flag param)
--bar (Option param)
--baz (Option param (multi-occurs))
--help (Print help)
--version (Print version)
So argc is a also completion engine, see argc-completions.
Manpage
Generate man pages for your argc-based CLI.
argc --argc-mangen <SCRIPT> [OUTDIR]
argc --argc-mangen ./example.sh man/
man man/example.1
MacOS
The built-in Bash in macOS is version 3.2 (released in 2007), and the known tools (ls, cp, grep, sed, awk, etc.) are based on BSD.
For better functionality and compatibility, it is recommended to install Bash version 5 and GNU tools.
Use brew to install Bash and GNU tools:
brew install bash coreutils gawk gnu-sed grep
And update the PATH environment variable:
export PATH="/opt/homebrew/opt/coreutils/libexec/gnubin:/opt/homebrew/opt/gawk/libexec/gnubin:/opt/homebrew/opt/gnu-sed/libexec/gnubin:/opt/homebrew/opt/grep/libexec/gnubin:$PATH"
Windows
The only dependency for argc is Bash. Since most developers working on Windows have Git installed, which includes Git Bash, you can safely use argc and GNU tools (like grep, sed, awk, etc.) in the Windows environment.
argc is Bash. Since most developers working on Windows have Git installed, which includes Git Bash, you can safely use argc and GNU tools (like grep, sed, awk, etc.) in the Windows environment.Make .sh file executable
To execute a .sh script file directly like a .cmd or .exe file, execute the following code in PowerShell.
# Add .sh to PATHEXT
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATHEXT", [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATHEXT", "Machine") + ";.SH", "Machine")
# Associate the .sh file extension with Git Bash
New-Item -LiteralPath Registry::HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.sh
New-ItemProperty -LiteralPath Registry::HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.sh -Name "(Default)" -Value "sh_auto_file" -PropertyType String -Force
New-ItemProperty -LiteralPath Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\sh_auto_file\shell\open\command `
-Name '(default)' -Value '"C:\Program Files\Git\bin\bash.exe" "%1" %*' -PropertyType String -Force
License
Copyright (c) 2023-2024 argc developers.
argc is made available under the terms of either the MIT License or the Apache License 2.0, at your option.
See the LICENSE-APACHE and LICENSE-MIT files for license details.
Dependencies
~2–17MB
~177K SLoC