65 releases (stable)
| 7.6.0 | Apr 27, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 7.5.0 | Feb 1, 2025 |
| 7.4.0 | Nov 27, 2024 |
| 7.2.0 | Mar 7, 2024 |
| 0.13.0 | Aug 21, 2021 |
#18 in Rust patterns
1,263,047 downloads per month
Used in 1,543 crates
(624 directly)
315KB
6K
SLoC
miette
You run miette? You run her code like the software? Oh. Oh! Error code for coder! Error code for One Thousand Lines!
About
miette is a diagnostic library for Rust. It includes a series of
traits/protocols that allow you to hook into its error reporting facilities,
and even write your own error reports! It lets you define error types that
can print out like this (or in any format you like!):
![Hi! miette also includes a screen-reader-oriented diagnostic printer that's enabled in various situations, such as when you use NO_COLOR or CLICOLOR settings, or on CI. This behavior is also fully configurable and customizable. For example, this is what this particular diagnostic will look like when the narrated printer is enabled:
\
Error: Received some bad JSON from the source. Unable to parse.
Caused by: missing field `foo` at line 1 column 1700
\
Begin snippet for https://api.nuget.org/v3/registration5-gz-semver2/json.net/index.json starting
at line 1, column 1659
\
snippet line 1: gs":["json"],"title":"","version":"1.0.0"},"packageContent":"https://api.nuget.o
highlight starting at line 1, column 1699: last parsing location
\
diagnostic help: This is a bug. It might be in ruget, or it might be in the
source you're using, but it's definitely a bug and should be reported.
diagnostic error code: ruget::api::bad_json](https://img.gs/czjpqfbdkz/800/https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zkat/miette/main/images/serde_json.png)
NOTE: You must enable the
"fancy"crate feature to get fancy report output like in the screenshots above. You should only do this in your toplevel crate, as the fancy feature pulls in a number of dependencies that libraries and such might not want.
Table of Contents
Features
- Generic
Diagnosticprotocol, compatible (and dependent on)std::error::Error. - Unique error codes on every
Diagnostic. - Custom links to get more details on error codes.
- Super handy derive macro for defining diagnostic metadata.
- Replacements for
anyhow/eyretypesResult,Reportand themiette!macro for theanyhow!/eyre!macros. - Generic support for arbitrary
SourceCodes for snippet data, with default support forStrings included.
The miette crate also comes bundled with a default ReportHandler with
the following features:
- Fancy graphical diagnostic output, using ANSI/Unicode text
- single- and multi-line highlighting support
- Screen reader/braille support, gated on
NO_COLOR, and other heuristics. - Fully customizable graphical theming (or overriding the printers entirely).
- Cause chain printing
- Turns diagnostic codes into links in supported terminals.
Installing
$ cargo add miette
If you want to use the fancy printer in all these screenshots:
$ cargo add miette --features fancy
Example
/*
You can derive a `Diagnostic` from any `std::error::Error` type.
`thiserror` is a great way to define them, and plays nicely with `miette`!
*/
use miette::{Diagnostic, NamedSource, SourceSpan};
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Error, Debug, Diagnostic)]
#[error("oops!")]
#[diagnostic(
code(oops::my::bad),
url(docsrs),
help("try doing it better next time?")
)]
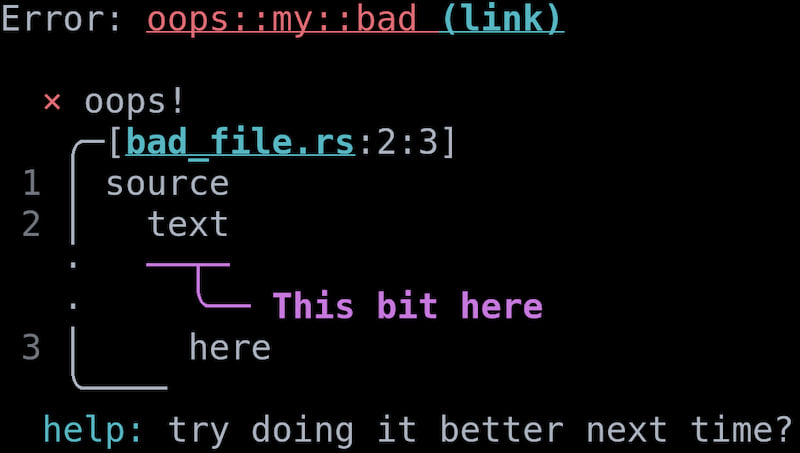
struct MyBad {
// The Source that we're gonna be printing snippets out of.
// This can be a String if you don't have or care about file names.
#[source_code]
src: NamedSource<String>,
// Snippets and highlights can be included in the diagnostic!
#[label("This bit here")]
bad_bit: SourceSpan,
}
/*
Now let's define a function!
Use this `Result` type (or its expanded version) as the return type
throughout your app (but NOT your libraries! Those should always return
concrete types!).
*/
use miette::Result;
fn this_fails() -> Result<()> {
// You can use plain strings as a `Source`, or anything that implements
// the one-method `Source` trait.
let src = "source\n text\n here".to_string();
Err(MyBad {
src: NamedSource::new("bad_file.rs", src),
bad_bit: (9, 4).into(),
})?;
Ok(())
}
/*
Now to get everything printed nicely, just return a `Result<()>`
and you're all set!
Note: You can swap out the default reporter for a custom one using
`miette::set_hook()`
*/
fn pretend_this_is_main() -> Result<()> {
// kaboom~
this_fails()?;
Ok(())
}
And this is the output you'll get if you run this program:
Using
... in libraries
miette is fully compatible with library usage. Consumers who don't know
about, or don't want, miette features can safely use its error types as
regular std::error::Error.
We highly recommend using something like thiserror
to define unique error types and error wrappers for your library.
While miette integrates smoothly with thiserror, it is not required.
If you don't want to use the Diagnostic derive macro, you can implement
the trait directly, just like with std::error::Error.
// lib/error.rs
use miette::{Diagnostic, SourceSpan};
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Error, Diagnostic, Debug)]
pub enum MyLibError {
#[error(transparent)]
#[diagnostic(code(my_lib::io_error))]
IoError(#[from] std::io::Error),
#[error("Oops it blew up")]
#[diagnostic(code(my_lib::bad_code))]
BadThingHappened,
#[error(transparent)]
// Use `#[diagnostic(transparent)]` to wrap another [`Diagnostic`]. You won't see labels otherwise
#[diagnostic(transparent)]
AnotherError(#[from] AnotherError),
}
#[derive(Error, Diagnostic, Debug)]
#[error("another error")]
pub struct AnotherError {
#[label("here")]
pub at: SourceSpan
}
Then, return this error type from all your fallible public APIs. It's a best
practice to wrap any "external" error types in your error enum instead of
using something like Report in a library.
... in application code
Application code tends to work a little differently than libraries. You don't always need or care to define dedicated error wrappers for errors coming from external libraries and tools.
For this situation, miette includes two tools: Report and
IntoDiagnostic. They work in tandem to make it easy to convert regular
std::error::Errors into Diagnostics. Additionally, there's a
Result type alias that you can use to be more terse.
When dealing with non-Diagnostic types, you'll want to
.into_diagnostic() them:
// my_app/lib/my_internal_file.rs
use miette::{IntoDiagnostic, Result};
use semver::Version;
pub fn some_tool() -> Result<Version> {
"1.2.x".parse().into_diagnostic()
}
miette also includes an anyhow/eyre-style Context/WrapErr traits
that you can import to add ad-hoc context messages to your Diagnostics, as
well, though you'll still need to use .into_diagnostic() to make use of
it:
// my_app/lib/my_internal_file.rs
use miette::{IntoDiagnostic, Result, WrapErr};
use semver::Version;
pub fn some_tool() -> Result<Version> {
"1.2.x"
.parse()
.into_diagnostic()
.wrap_err("Parsing this tool's semver version failed.")
}
To construct your own simple adhoc error use the miette! macro:
// my_app/lib/my_internal_file.rs
use miette::{miette, Result};
use semver::Version;
pub fn some_tool() -> Result<Version> {
let version = "1.2.x";
version
.parse()
.map_err(|_| miette!("Invalid version {}", version))
}
There are also similar [bail!] and [ensure!] macros.
... in main()
main() is just like any other part of your application-internal code. Use
Result as your return value, and it will pretty-print your diagnostics
automatically.
NOTE: You must enable the
"fancy"crate feature to get fancy report output like in the screenshots here.** You should only do this in your toplevel crate, as the fancy feature pulls in a number of dependencies that libraries and such might not want.
use miette::{IntoDiagnostic, Result};
use semver::Version;
fn pretend_this_is_main() -> Result<()> {
let version: Version = "1.2.x".parse().into_diagnostic()?;
println!("{}", version);
Ok(())
}
Please note: in order to get fancy diagnostic rendering with all the pretty
colors and arrows, you should install miette with the fancy feature
enabled:
miette = { version = "X.Y.Z", features = ["fancy"] }
Another way to display a diagnostic is by printing them using the debug formatter. This is, in fact, what returning diagnostics from main ends up doing. To do it yourself, you can write the following:
use miette::{IntoDiagnostic, Result};
use semver::Version;
fn just_a_random_function() {
let version_result: Result<Version> = "1.2.x".parse().into_diagnostic();
match version_result {
Err(e) => println!("{:?}", e),
Ok(version) => println!("{}", version),
}
}
... diagnostic code URLs
miette supports providing a URL for individual diagnostics. This URL will
be displayed as an actual link in supported terminals, like so:
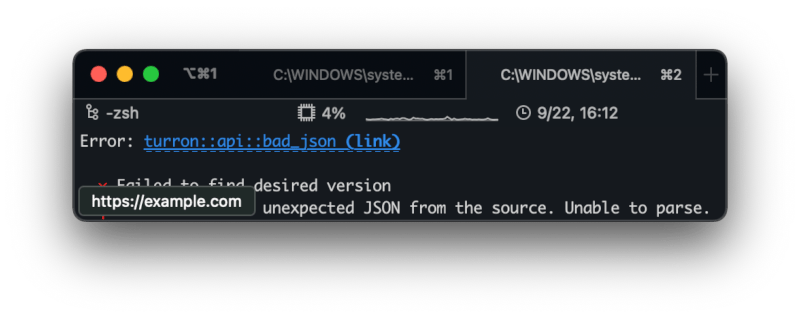
To use this, you can add a url() sub-param to your #[diagnostic]
attribute:
use miette::Diagnostic;
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Error, Diagnostic, Debug)]
#[error("kaboom")]
#[diagnostic(
code(my_app::my_error),
// You can do formatting!
url("https://my_website.com/error_codes#{}", self.code().unwrap())
)]
struct MyErr;
Additionally, if you're developing a library and your error type is exported
from your crate's top level, you can use a special url(docsrs) option
instead of manually constructing the URL. This will automatically create a
link to this diagnostic on docs.rs, so folks can just go straight to your
(very high quality and detailed!) documentation on this diagnostic:
use miette::Diagnostic;
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Error, Diagnostic, Debug)]
#[diagnostic(
code(my_app::my_error),
// Will link users to https://docs.rs/my_crate/0.0.0/my_crate/struct.MyErr.html
url(docsrs)
)]
#[error("kaboom")]
struct MyErr;
... snippets
Along with its general error handling and reporting features, miette also
includes facilities for adding error spans/annotations/labels to your
output. This can be very useful when an error is syntax-related, but you can
even use it to print out sections of your own source code!
To achieve this, miette defines its own lightweight SourceSpan type.
This is a basic byte-offset and length into an associated SourceCode
and, along with the latter, gives miette all the information it needs to
pretty-print some snippets! You can also use your own Into<SourceSpan>
types as label spans.
The easiest way to define errors like this is to use the
derive(Diagnostic) macro:
use miette::{Diagnostic, SourceSpan};
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Diagnostic, Debug, Error)]
#[error("oops")]
#[diagnostic(code(my_lib::random_error))]
pub struct MyErrorType {
// The `Source` that miette will use.
#[source_code]
src: String,
// This will underline/mark the specific code inside the larger
// snippet context.
#[label = "This is the highlight"]
err_span: SourceSpan,
// You can add as many labels as you want.
// They'll be rendered sequentially.
#[label("This is bad")]
snip2: (usize, usize), // `(usize, usize)` is `Into<SourceSpan>`!
// Snippets can be optional, by using Option:
#[label("some text")]
snip3: Option<SourceSpan>,
// with or without label text
#[label]
snip4: Option<SourceSpan>,
}
... help text
miette provides two facilities for supplying help text for your errors:
The first is the #[help()] format attribute that applies to structs or
enum variants:
use miette::Diagnostic;
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("welp")]
#[diagnostic(help("try doing this instead"))]
struct Foo;
The other is by programmatically supplying the help text as a field to your diagnostic:
use miette::Diagnostic;
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("welp")]
#[diagnostic()]
struct Foo {
#[help]
advice: Option<String>, // Can also just be `String`
}
let err = Foo {
advice: Some("try doing this instead".to_string()),
};
... severity level
miette provides a way to set the severity level of a diagnostic.
use miette::Diagnostic;
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("welp")]
#[diagnostic(severity(Warning))]
struct Foo;
... multiple related errors
miette supports collecting multiple errors into a single diagnostic, and
printing them all together nicely.
To do so, use the #[related] tag on any IntoIter field in your
Diagnostic type:
use miette::Diagnostic;
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Debug, Error, Diagnostic)]
#[error("oops")]
struct MyError {
#[related]
others: Vec<MyError>,
}
... delayed source code
Sometimes it makes sense to add source code to the error message later.
One option is to use with_source_code()
method for that:
use miette::{Diagnostic, SourceSpan};
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Diagnostic, Debug, Error)]
#[error("oops")]
#[diagnostic()]
pub struct MyErrorType {
// Note: label but no source code
#[label]
err_span: SourceSpan,
}
fn do_something() -> miette::Result<()> {
// This function emits actual error with label
return Err(MyErrorType {
err_span: (7..11).into(),
})?;
}
fn main() -> miette::Result<()> {
do_something().map_err(|error| {
// And this code provides the source code for inner error
error.with_source_code(String::from("source code"))
})
}
Also source code can be provided by a wrapper type. This is especially
useful in combination with related, when multiple errors should be
emitted at the same time:
use miette::{Diagnostic, Report, SourceSpan};
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Diagnostic, Debug, Error)]
#[error("oops")]
#[diagnostic()]
pub struct InnerError {
// Note: label but no source code
#[label]
err_span: SourceSpan,
}
#[derive(Diagnostic, Debug, Error)]
#[error("oops: multiple errors")]
#[diagnostic()]
pub struct MultiError {
// Note source code by no labels
#[source_code]
source_code: String,
// The source code above is used for these errors
#[related]
related: Vec<InnerError>,
}
fn do_something() -> Result<(), Vec<InnerError>> {
Err(vec![
InnerError {
err_span: (0..6).into(),
},
InnerError {
err_span: (7..11).into(),
},
])
}
fn main() -> miette::Result<()> {
do_something().map_err(|err_list| MultiError {
source_code: "source code".into(),
related: err_list,
})?;
Ok(())
}
... Diagnostic-based error sources.
When one uses the #[source] attribute on a field, that usually comes
from thiserror, and implements a method for
std::error::Error::source. This works in many cases, but it's lossy:
if the source of the diagnostic is a diagnostic itself, the source will
simply be treated as an std::error::Error.
While this has no effect on the existing reporters, since they don't use that information right now, APIs who might want this information will have no access to it.
If it's important for you for this information to be available to users,
you can use #[diagnostic_source] alongside #[source]. Not that you
will likely want to use both:
use miette::Diagnostic;
use thiserror::Error;
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("MyError")]
struct MyError {
#[source]
#[diagnostic_source]
the_cause: OtherError,
}
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("OtherError")]
struct OtherError;
... handler options
MietteHandler is the default handler, and is very customizable. In
most cases, you can simply use MietteHandlerOpts to tweak its behavior
instead of falling back to your own custom handler.
Usage is like so:
miette::set_hook(Box::new(|_| {
Box::new(
miette::MietteHandlerOpts::new()
.terminal_links(true)
.unicode(false)
.context_lines(3)
.tab_width(4)
.break_words(true)
.build(),
)
}))
See the docs for MietteHandlerOpts for more details on what you can
customize!
... dynamic diagnostics
If you...
- ...don't know all the possible errors upfront
- ...need to serialize/deserialize errors
then you may want to use
miette!,diagnostic!macros orMietteDiagnosticdirectly to create diagnostic on the fly.
let source = "2 + 2 * 2 = 8".to_string();
let report = miette!(
labels = vec![
LabeledSpan::at(12..13, "this should be 6"),
],
help = "'*' has greater precedence than '+'",
"Wrong answer"
).with_source_code(source);
println!("{:?}", report)
... syntax highlighting
miette can be configured to highlight syntax in source code snippets.
To use the built-in highlighting functionality, you must enable the
syntect-highlighter crate feature. When this feature is enabled, miette will
automatically use the syntect crate to highlight the #[source_code]
field of your Diagnostic.
Syntax detection with syntect is handled by checking 2 methods on the SpanContents trait, in order:
language()- Provides the name of the language as a string. For example"Rust"will indicate Rust syntax highlighting. You can set the language of theSpanContentsproduced by aNamedSourcevia thewith_languagemethod.name()- In the absence of an explicitly set language, the name is assumed to contain a file name or file path. The highlighter will check for a file extension at the end of the name and try to guess the syntax from that.
If you want to use a custom highlighter, you can provide a custom
implementation of the Highlighter
trait to MietteHandlerOpts by calling the
with_syntax_highlighting
method. See the highlighters module docs for more details.
... primary label
You can use the primary parameter to label to indicate that the label
is the primary label.
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("oops!")]
struct MyError {
#[label(primary, "main issue")]
primary_span: SourceSpan,
#[label("other label")]
other_span: SourceSpan,
}
The primary parameter can be used at most once:
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("oops!")]
struct MyError {
#[label(primary, "main issue")]
primary_span: SourceSpan,
#[label(primary, "other label")] // Error: Cannot have more than one primary label.
other_span: SourceSpan,
}
... collection of labels
When the number of labels is unknown, you can use a collection of SourceSpan
(or any type convertible into SourceSpan). For this, add the collection
parameter to label and use any type than can be iterated over for the field.
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("oops!")]
struct MyError {
#[label("main issue")]
primary_span: SourceSpan,
#[label(collection, "related to this")]
other_spans: Vec<Range<usize>>,
}
let report: miette::Report = MyError {
primary_span: (6, 9).into(),
other_spans: vec![19..26, 30..41],
}.into();
println!("{:?}", report.with_source_code("About something or another or yet another ...".to_string()));
A collection can also be of LabeledSpan if you want to have different text
for different labels. Labels with no text will use the one from the label
attribute
#[derive(Debug, Diagnostic, Error)]
#[error("oops!")]
struct MyError {
#[label("main issue")]
primary_span: SourceSpan,
#[label(collection, "related to this")]
other_spans: Vec<LabeledSpan>, // LabeledSpan
}
let report: miette::Report = MyError {
primary_span: (6, 9).into(),
other_spans: vec![
LabeledSpan::new(None, 19, 7), // Use default text `related to this`
LabeledSpan::new(Some("and also this".to_string()), 30, 11), // Use specific text
],
}.into();
println!("{:?}", report.with_source_code("About something or another or yet another ...".to_string()));
MSRV
This crate requires rustc 1.70.0 or later.
Acknowledgements
miette was not developed in a void. It owes enormous credit to various
other projects and their authors:
anyhowandcolor-eyre: these two enormously influential error handling libraries have pushed forward the experience of application-level error handling and error reporting.miette'sReporttype is an attempt at a very very rough version of theirReporttypes.thiserrorfor setting the standard for library-level error definitions, and for being the inspiration behindmiette's derive macro.rustcand @estebank for their state-of-the-art work in compiler diagnostics.ariadnefor pushing forward how pretty these diagnostics can really look!
License
miette is released to the Rust community under the Apache license
2.0.
It also includes code taken from eyre,
and some from thiserror, also
under the Apache License. Some code is taken from
ariadne, which is MIT licensed.
Dependencies
~1–11MB
~127K SLoC