14 releases (8 breaking)
| 0.8.2 | Dec 11, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.7.0 | Dec 6, 2024 |
| 0.6.0 | Nov 29, 2024 |
| 0.4.0 | Jan 4, 2024 |
| 0.0.5 | Feb 28, 2023 |
#44 in Command line utilities
22 downloads per month
25KB
379 lines
Raffi - Fuzzel Launcher Using YAML Configuration
[!NOTE] This uses my Fuzzel configuration, see below for more details
Description
Raffi is a launcher for the Fuzzel utility that uses a YAML configuration file to define the commands to be executed.
Features
- Launch applications with custom configurations.
- Support for icons.
- Script execution with a configurable interpreter.
Installation
Binaries
Visit the release page and download the archive or package for your platform.
Ensure you have Fuzzel installed.
Homebrew
brew tap chmouel/raffi https://github.com/chmouel/raffi
brew install raffi
Crates.io
cargo install raffi
Arch
Using your preferred AUR helper, for example, yay:
yay -S raffi-bin
NixOS / Nix (unstable)
nix-shell -p raffi
To install Raffi from source, clone the repository and build it using Cargo:
git clone https://github.com/chmouel/raffi.git
cd raffi
cargo build --release
Usage
You can launch Raffi directly, and it will run the binary and arguments as defined in the configuration.
Use the -p/--print-only option to only print the command to be executed.
Specify a custom configuration file with the -c/--configfile option.
Icon paths are automatically searched on your system and cached. To refresh the
cache, use the -r/--refresh-cache option. If you want to have fuzzel running
faster you can use the option -I/--disable-icons to disable them.
Command-line Options
raffi [OPTIONS]
Options:
--help: Print help message.--version: Print version.--configfile <FILE>: Specify the config file location.--print-only: Print the command to stdout, do not run it.--refresh-cache: Refresh the icon cache.--no-icons: Do not show icons.--default-script-shell <SHELL>: Default shell when using scripts (default:bash).
Sway
Here is an example of how to use Raffi with Sway:
// Set a variable that can be easily used later in the config file
// These variables are optional
set $menu raffi -p
// Mod4 is the Super key for me, but use whatever you want.
set $super Mod4
// Bind the Super+Space key to launch the launcher
bindsym $super+Space exec $menu | xargs swaymsg exec --
Configuration
Fuzzel
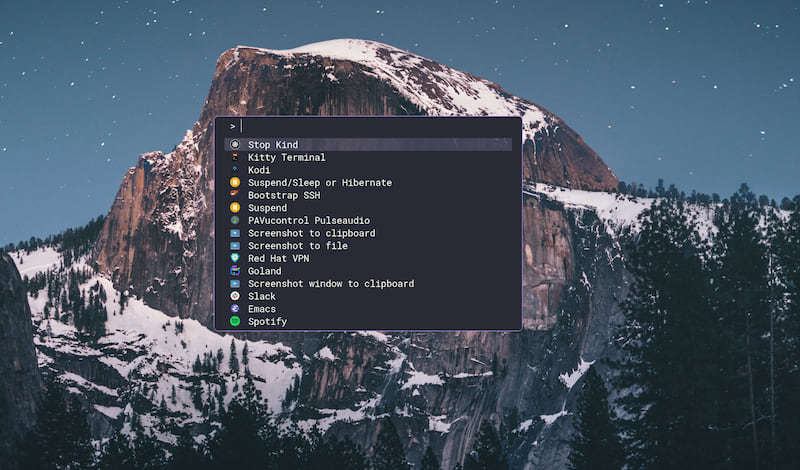
First, configure your Fuzzel appearance and behavior by editing the file ~/.config/fuzzel/fuzzel.ini. See the manpages here. Below is my configuration, which matches the screenshot above:
dpi-aware=yes
font=RobotoMonoNerdFont-Thin:size=16
terminal=kitty
width=50
layer=overlay
exit-on-keyboard-focus-loss=no
inner-pad=15
fields=filename,name
[colors]
background=282a36ff
text=f8f8f2ff
match=8be9fdff
selection-match=8be9fdff
selection=44475add
selection-text=f8f8f2ff
border=bd93f9ff
Raffi
The Raffi configuration file is located at $HOME/.config/raffi/raffi.yaml and has the following structure:
firefox:
binary: firefox
args: [--marionette]
icon: firefox
description: Firefox browser with marionette enabled
- binary: The binary to be executed (if it does not exist in the PATH, it will be skipped).
- description: The description to be displayed in the launcher.
- args: The arguments to be passed to the binary as an array, e.g.,
[foo, bar](optional). - icon: The icon to be displayed in the launcher. If not specified, it will
try to use the binary name (optional). Icons are searched in
/usr/share/icons,/usr/share/pixmaps,$HOME/.local/share/icons, or$XDG_DATA_HOMEif set and matched to the icon name. The icons paths are cached for optimization, use the-roption to refresh it. You can also specify a full path to the icon. - script: See below for more information.
- disabled: If set to
true, the entry will be disabled.
Script Feature
You can define a script to be executed instead of a binary. The script will be executed using the default script shell bash unless you specify another one in --default-script-shell.
Here is an example configuration with a script:
hello_script:
script: |
echo "hello world and show me your env"
env
description: "Hello Script"
icon: "script"
If you want a script running, for example, with python3, you can specify it like this:
hello_script:
binary: python3
script: |
import os
print("hello world and show me your env")
print(os.environ)
description: "Hello Python script"
icon: "script"
If you want to add some specific arguments to the interpreter, you can do it like this:
hello_script:
binary: sh
args: ["-xv"]
script: |
echo "hello world and show me your env"
env
description: "Hello debug"
icon: "script"
Conditions
There is limited support for conditions, allowing you to run a command only if a specific condition is met. These conditions are optional and cannot be combined.
- ifexist: Display the entry if a binary exists in the PATH or if the full path is specified.
- ifenvset: Display the entry if the environment variable is set.
- ifenvnotset: Display the entry if the environment variable is not set.
- ifenveq: Display the entry if the environment variable equals a specified value.
Example
Here is an example of how to use conditions. This will only display the entry
if the DESKTOP_SESSION environment variable is set to GNOME and the
WAYLAND_DISPLAY environment variable is set and the firefox binary exists
in the PATH:
ifenveq: [DESKTOP_SESSION, GNOME]
ifenvset: WAYLAND_DISPLAY
ifexist: firefox
See the file located in examples/raffi.yaml for a more comprehensive example.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Binary not found: Ensure that the binary specified in the configuration file exists in the PATH.
- Invalid configuration: Verify that the YAML configuration file is correctly formatted and all required fields are provided.
- Icons not displayed: Ensure that the icon paths are correct and refresh the icon cache using the
--refresh-cacheoption if necessary.
Debugging
Use the --print-only option to print the command that will be executed. This can help identify issues with the configuration or command execution.
Development
All contributions are welcome! If you have any suggestions, bug reports, or feature requests, please open an issue or a pull request.
Pre-commit Hooks
To ensure code quality, you can set up pre-commit hooks to run cargo clippy automatically before pushing commits. First, install pre-commit:
pip install pre-commit
Then, install the pre-commit hooks:
pre-commit install
This will automatically run cargo clippy before each commit to catch any potential issues.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
Authors
- Chmouel Boudjnah https://github.com/chmouel
- Fediverse - <@chmouel@fosstodon.org>
- Twitter - <@chmouel>
- Blog - <https://blog.chmouel.com>
Dependencies
~4–14MB
~201K SLoC