2 unstable releases
Uses old Rust 2015
| 0.2.0 | Jul 18, 2016 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.0 | Jul 5, 2016 |
#4 in #black-box-testing
160KB
3K
SLoC
noir 




A rust based, DSL alike and request driven, black box testing library for HTTP APIs.
- Documentation for the latest release on crates.io.
Please Note: noir is still work in progress , there will probably be a lot of types, quite a few bugs and probably a some API changes here and there.
Screenshots
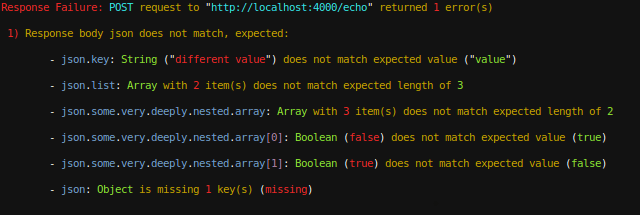
Features
-
Describe your API and the external resources it accesses
-
Setup and configure HTTP requests against your API
- Perform requests with specific headers, querystrings and bodies
- Set up expecations for response headers and bodies
-
Setup and provide external, mocked HTTP responses to your API
- These are only available for one specific request
- Any unexpected external calls made by your API will be caught
- Request order of the provided responses is also verified
- Set up expecations for headers and bodies of the requests your API perfomrs
-
Detailed and colored test output to helps you quickly figuring out what exactly went wrong
-
Great support for JSON featuring deep, detailed object and array diffing, showing you paths, types and values
-
Uses hyper for all HTTP related interfaces
Work in Progress / Unstable
- Macros for easy definition of HTTP multipart forms in tests
- API for providing custom / external mocks to be active during a test request
Testing your API with noir
Since noir provides the ability to mock out certain parts of your application in tests, you need to run your tests as library tests so the mocks can be enabled during testing.
A fully working example project that integrates with noir can be found in
the examples/api folder.
Below you'll find a high level overview of the setup steps required for testing.
Describing your API
noir comes with direct support for testing HTTP based apis, to describe your
own HTTP based API create a structure which implements the HttpApi trait.
use noir::HttpApi;
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Default)]
pub struct Api;
impl HttpApi for Api {
fn hostname(&self) -> &'static str {
"localhost"
}
fn port(&self) -> u16 {
4000
}
fn start(&self) {
application::server::run(self.host().as_str());
}
}
There are only three things you have to tell noir here:
- The hostname your application will be listening on during testing
- The port your application will be listening on during testing
- What blocking function will start your webserver
When executing your tests, noir will wait for your webserver to start up and then run each test in series.
Now, the reason for not running in parallel is that once you start using
noir provided macros like hyper_client!() (which enable you to mock
responses to outgoing HTTP requests from your application) there is no simply
way (i.e. without adding additional logic to your application) to match these
requests to the responses provided by each test and it would also be rather
unclear which exact test should fail should your application perform additional,
unexpected HTTP requests during these tests.
Describing External Resources
use noir::HttpEndpoint;
#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
pub struct ExternalResource;
impl HttpEndpoint for ExternalResource {
fn hostname(&self) -> &'static str {
"external-resouce.com"
}
fn port(&self) -> u16 {
443
}
}
Test Requests
Each noir test starts with a HTTP Method call on your defined API structure, all of these calls then return a HttpRequest instance.
A HttpRequest instance allows you to set up both the data and expecations for your test request.
You can also provide external resource responses which will be available to your application for the time the request is running.
Once a HttpRequest instance goes out of scope, its constructed request is automatically send and any of its expectations are validated.
Below is a, rather contrived, example of what is possible. For full details please refer to the Documentation.
#[macro_use]
extern crate noir;
#[test]
fn test_get_resource_with_missing_optional_data() {
// Perform a request against our API
Api::get("/")
// Set up our query string
.with_query(query! {
"page" => 2,
"sort" => "asc",
"detailed" => true
})
// Set the headers of the request
.with_headers(headers![
Accept(vec![
qitem(Mime(TopLevel::Application, SubLevel::Json, vec![]))
])
])
// Provide some mocked, external resource responses during the api request
.provide(responses![
// Provide a resource for "/data/base.json" that responds with a
// "200 OK" and a json body and expects a JSON Accept header.
ExternalResource.get("/data/base.json")
.with_status(StatusCode::Ok)
.with_body(!object {
"key" => "value"
})
.expected_header(Accept(vec![
qitem(Mime(TopLevel::Application, SubLevel::Json, vec![]))
])),
// Provide another resource with responds with "500"
ExternalResource.get("/data/optional.json")
.with_status(StatusCode::InternalServerError)
.expected_header(Accept(vec![
qitem(Mime(TopLevel::Application, SubLevel::Json, vec![]))
]))
])
// Expect a "200 OK" response from our API
.expected_status(StatusCode::Ok)
// Expect a JSON Content-Type header on our response
.expected_header(ContentType(
Mime(TopLevel::Application, SubLevel::Json, vec![])
))
// And finally expect a JSON body
.expected_body(object!{
"resource" => object! {
"key" => "value"
},
"optional" => JsonValue::Null
});
}
License
Licensed under either of
- Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
- MIT license (LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT) at your option.
Contribution
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you shall be dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.
Dependencies
~6–14MB
~178K SLoC