34 releases
Uses new Rust 2024
| new 0.3.12 | May 2, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.3.10 | Oct 1, 2024 |
| 0.3.5 | May 15, 2024 |
| 0.3.4 | Dec 24, 2023 |
| 0.1.3 | Jul 8, 2022 |
#186 in Text processing
168 downloads per month
1MB
1K
SLoC
mdbook-quiz: interactive quizzes for Markdown
This repository provides an mdBook preprocessor that allows you to add interactive quizzes to your Markdown books. A quiz looks like this:
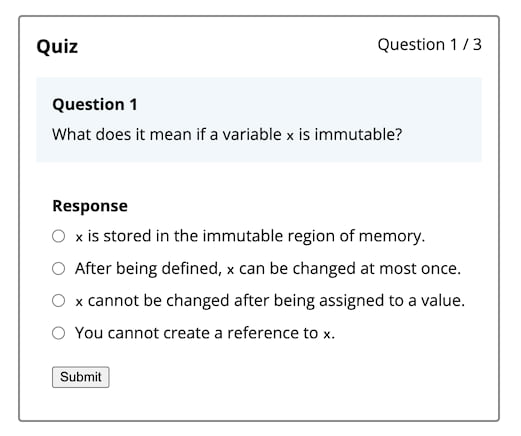
Table of contents:
Installation
These instructions assume you have an mdBook already set up. Unfamiliar with mdBook? Read the mdBook guide!
From crates.io
cargo install mdbook-quiz --locked
Note: this tool is under active development. I recommend pinning to a specific version to avoid breakage, e.g. by running
cargo install mdbook-quiz --locked --version <YOUR_VERSION>
And you can check your version by running mdbook-quiz -V. This repository uses semantic versioning for the quiz data format, so your quizzes should not break if you update to a more recent patch.
From source
You need Cargo, cargo-make, and Depot installed. Then run:
git clone https://github.com/cognitive-engineering-lab/mdbook-quiz
cd mdbook-quiz
cargo make init-bindings
cargo install --path crates/mdbook-quiz
Usage
First, create a quiz file. Quizzes are encoded as TOML files (see Quiz schema). For example:
# quizzes/rust-variables.toml
[[questions]]
type = "ShortAnswer"
prompt.prompt = "What is the keyword for declaring a variable in Rust?"
answer.answer = "let"
context = "For example, you can write: `let x = 1`"
Then in your Markdown file, add a reference to the quiz file:
<!-- src/your-chapter.md -->
And now, a _quiz_:
{{#quiz ../quizzes/rust-variables.toml}}
Configure your book.toml to activate mdbook-quiz.
# book.toml
[preprocessor.quiz]
Then mdbook build should correctly embed the quiz.
Note: due to limitations of mdBook (see mdBook#1087), the
mdbook-quizpreprocessor will copy files into your book's source directory under a subdirectory namedmdbook-quiz. I recommend adding this directory to your.gitignore.
Quiz schema
A quiz is an array of questions.
export interface Quiz {
questions: Question[];
}
A question is one of a set of predefined question types.
export type Question = ShortAnswer | Tracing | MultipleChoice;
Each question type is an instantiation of this Typescript interface:
export interface QuestionFields<Type extends string, Prompt, Answer> {
type: Type;
prompt: Prompt;
answer: Answer;
context?: Markdown;
}
It has a discriminating string name type and then a prompt and answer, along with additional context for explaining the answer.
Note that the
Markdowntype is just a string, but will be interpreted as Markdown by the quiz renderer.
Currently, mdbook-quiz supports these question types:
Short answer
A question where the answer is a one-line string.
Example
[[questions]]
type = "ShortAnswer"
prompt.prompt = "What is the keyword for declaring a variable in Rust?"
answer.answer = "let"
context = "For example, you can write: `let x = 1`"
Interface
export interface ShortAnswerPrompt {
/** The text of the prompt. */
prompt: Markdown;
}
export interface ShortAnswerAnswer {
/** The exact string that answers the question. */
answer: string;
/** Other acceptable strings answers. */
alternatives?: string[];
}
export type ShortAnswer = QuestionFields<"ShortAnswer", ShortAnswerPrompt, ShortAnswerAnswer>;
Multiple choice
A question with multiple options that the user selects from.
Example
[[questions]]
type = "MultipleChoice"
prompt.prompt = "What does it mean if a variable `x` is immutable?"
prompt.distractors = [
"`x` is stored in the immutable region of memory.",
"After being defined, `x` can be changed at most once.",
"You cannot create a reference to `x`."
]
answer.answer = "`x` cannot be changed after being assigned to a value."
context = """
Immutable means "not mutable", or not changeable.
"""
Interface
export interface MultipleChoicePrompt {
/** The text of the prompt. */
prompt: Markdown;
/** An array of incorrect answers. */
distractors: Markdown[];
/** If defined, don't randomize distractors and put answer at this index. */
answerIndex?: number;
}
export interface MultipleChoiceAnswer {
/** The text of the correct answer. */
answer: Markdown;
}
Tracing
A question where the user has to predict how a program will execute (or fail to compile).
Example
[[questions]]
type = "Tracing"
prompt.program = """
fn main() {
let x = 1;
println!("{x}");
x += 1;
println!("{x}");
}
"""
answer.doesCompile = false
context = """
This is a compiler error because line 4 tries to mutate `x` when `x` is not marked as `mut`.
"""
Interface
export interface TracingPrompt {
/** The contents of the program to trace */
program: string;
}
export interface TracingAnswer {
/** True if the program should pass the compiler */
doesCompile: boolean;
/** If doesCompile=true, then the contents of stdout after running the program */
stdout?: string;
}
export type Tracing = QuestionFields<"Tracing", TracingPrompt, TracingAnswer>;
Quiz configuration
You can configure mdbook-quiz by adding options to the [preprocessor.quiz] section of book.toml. The options are:
fullscreen(boolean): If true, then a quiz will take up the web page's full screen during use.cache-answers(boolean): If true, then the user's answers will be saved in their browser'slocalStorage. Then the quiz will show the user's answers even after they reload the page.spellcheck(boolean): If true, then run a spellchecker on all Markdown strings.more-words(path): An optional path to a.dicfile that adds valid words to the spellchecker. You can find a base dictionary for each language in wooorm/dictionaries. You can find documentation about how to write a.dicfile in this blog post.
Dependencies
~24–40MB
~659K SLoC